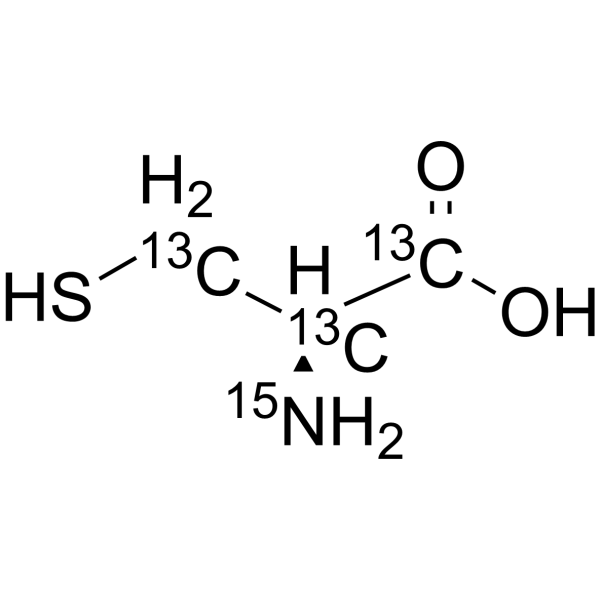Search Result
Results for "
Taurine
" in MedChemExpress (MCE) Product Catalog:
1
Biochemical Assay Reagents
15
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Areas |
Chemical Structure |
-
- HY-B0351
-
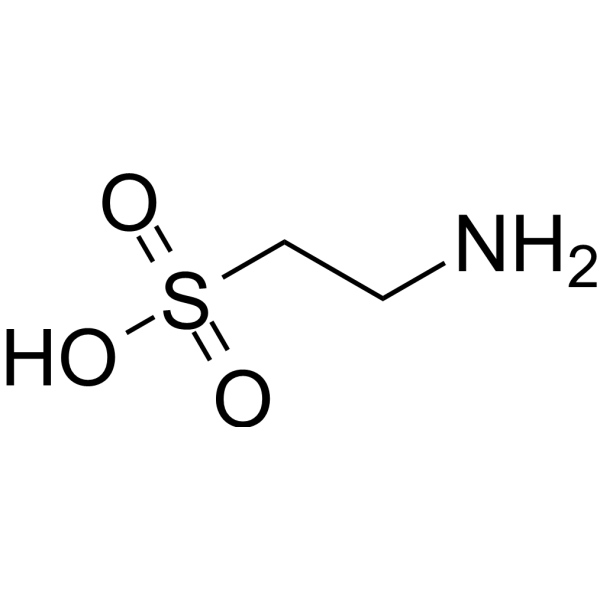
Taurine
5 Publications Verification
2-Aminoethanesulfonic acid
|
Autophagy
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
Cancer
|
|
Taurine, a sulphur-containing amino acid and an organic osmolyte involved in cell volume regulation, provides a substrate for the formation of bile salts, and plays a role in the modulation of intracellular free calcium concentration. Taurine has the ability to activate autophagy in adipocytes .
|
-
-
- HY-B0351S
-
|
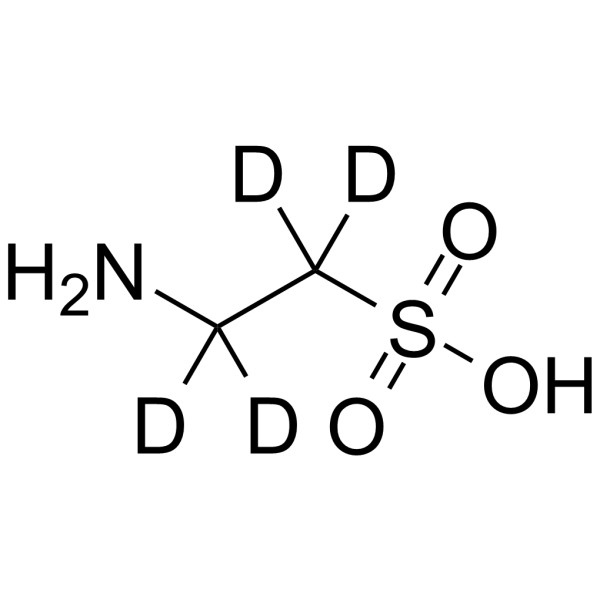
2-Aminoethanesulfonic acid-d4
|
Autophagy
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
Taurine-d4 is the deuterium labeled Taurine. Taurine, a sulphur-containing amino acid and an organic osmolyte involved in cell volume regulation, provides a substrate for the formation of bile salts, and plays a role in the modulation of intracellular free calcium concentration. Taurine has the ability to activate autophagy in adipocytes[1][2][3].
|
-
-
- HY-B0351S2
-
|
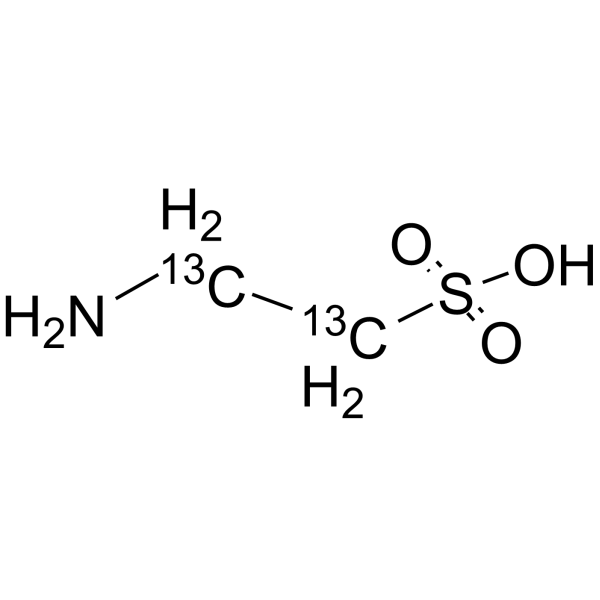
2-Aminoethanesulfonic acid-13C2,15N
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Autophagy
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
Taurine- 13C2, 15N is the 13C- and 15N- labeled Taurine. Taurine, a sulphur-containing amino acid and an organic osmolyte involved in cell volume regulation, provides a substrate for the formation of bile salts, and plays a role in the modulation of intracellular free calcium concentration. Taurine has the ability to activate autophagy in adipocytes[1][2][3].
|
-
-
- HY-B0351S1
-
|
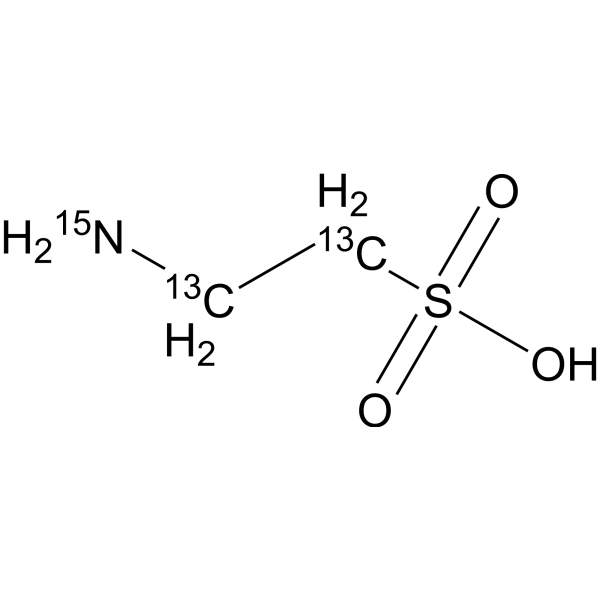
2-Aminoethanesulfonic acid-13C2
|
Autophagy
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
Taurine- 13C2 is the 13C-labeled Taurine. Taurine, a sulphur-containing amino acid and an organic osmolyte involved in cell volume regulation, provides a substrate for the formation of bile salts, and plays a role in the modulation of intracellular free calcium concentration. Taurine has the ability to activate autophagy in adipocytes[1][2][3].
|
-
-
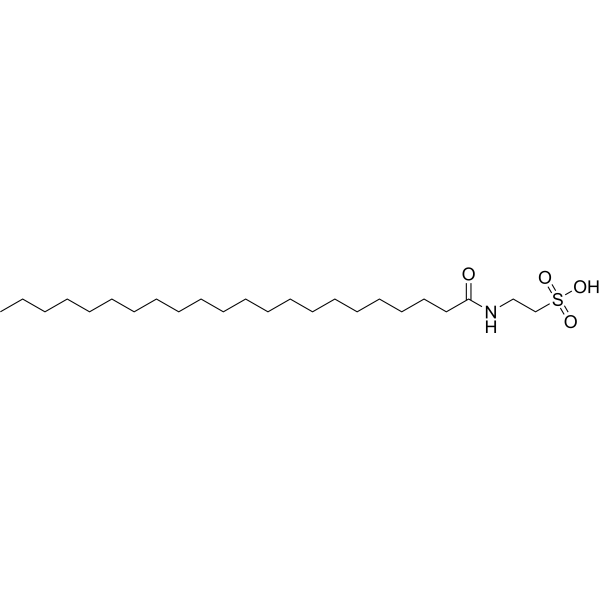
- HY-124001
-
|
|
TRP Channel
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
N-Docosanoyl taurine is a lipoamino acid. N-Docosanoyl taurine is a discriminatory metabolity that drive the classification of brain regions .
|
-
-
- HY-120962S
-
-
-
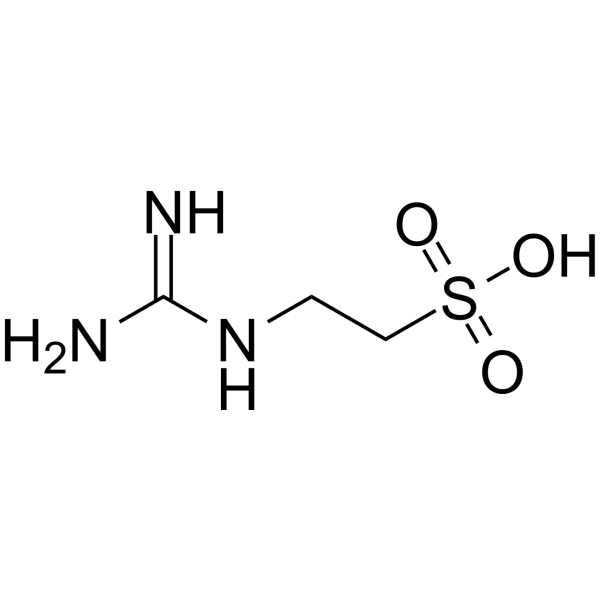
- HY-113329
-
|
Taurocyamine
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
Guanidinoethyl sulfonate (Taurocyamine), a transport antagonist of taurine, induces much urinary taurine excretion with a resulting decrease in the tissue taurine content and readily produces taurine-deficient fetal rats in pregnant rats . Guanidinoethyl sulfonate, a structural analogue of taurine, acts as a competitive inhibitor of taurine transport .
|
-
-
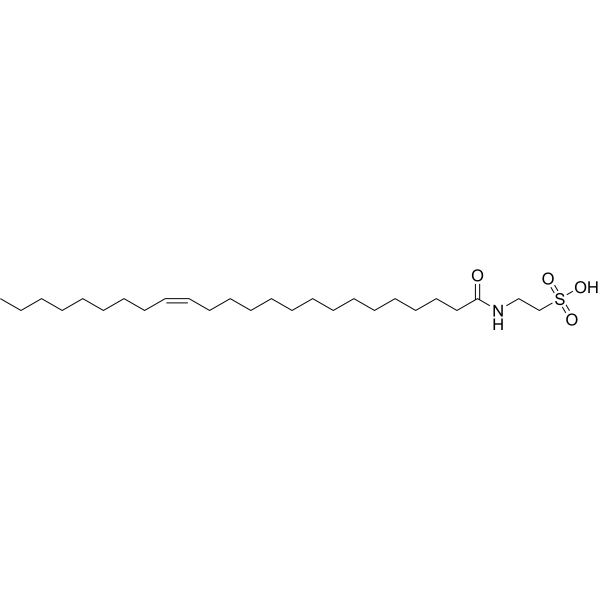
- HY-W751418
-
|
(Z)-2-tetracos-15-enamidoethanesulfonic acid
|
FAAH
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
N-Nervonoyl taurine ((Z)-2-tetracos-15-enamidoethanesulfonic acid) is a fatty acid-taurine conjugate derived from nervonic acid. N-Nervonoyl taurine is a substrate of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) discovered during metabolite profiling .
|
-
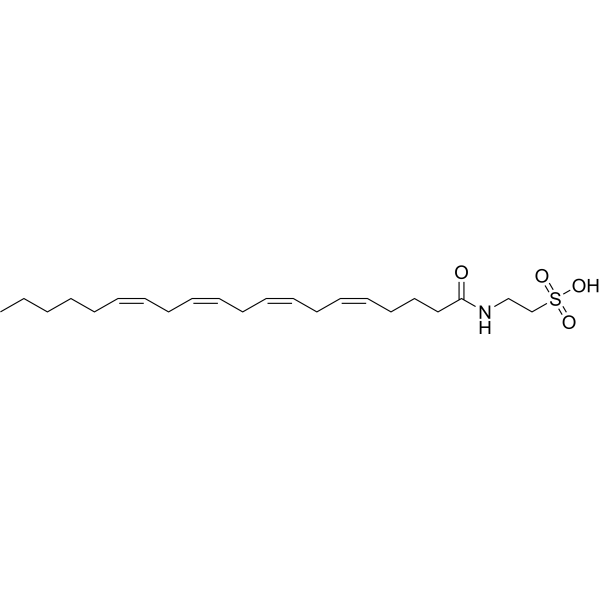
-
- HY-120962
-
|
|
TRP Channel
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
N-Arachidonoyl Taurine is an activator of the transient receptor potential vanilloid TRPV1 and TRPV4, with EC50s value of 28 μM and 21 μM, respectively .
|
-
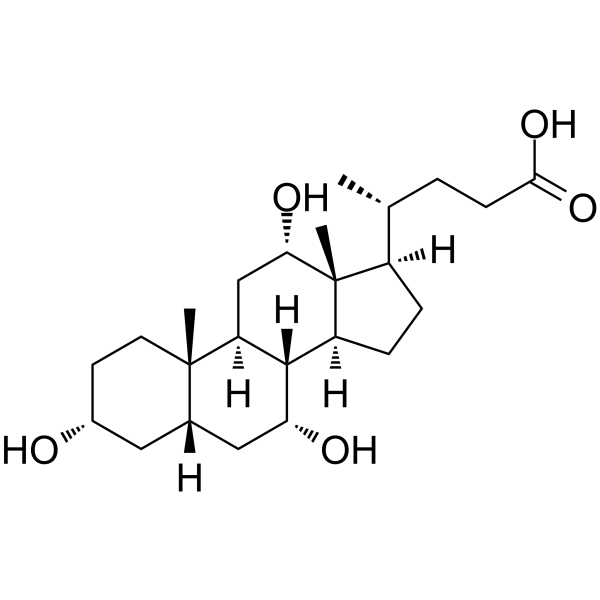
-
- HY-N0324
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
Cholic acid is a major primary bile acid produced in the liver and usually conjugated with glycine or taurine. It facilitates fat absorption and cholesterol excretion. Cholic acid is orally active .
|
-
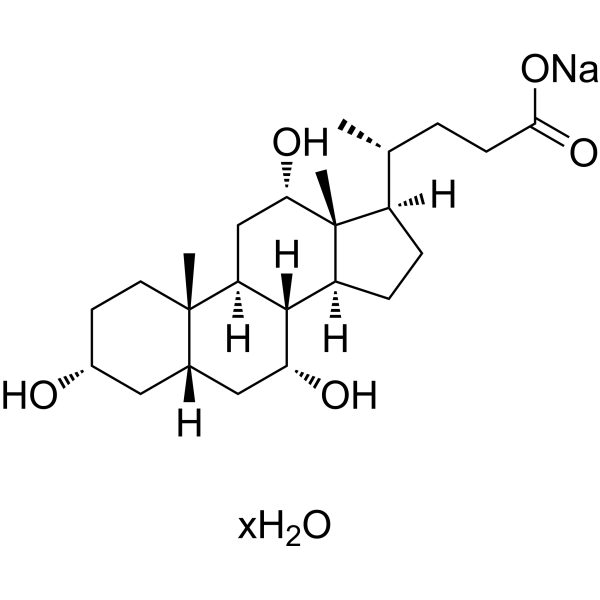
-
- HY-N0324B
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
Cholic acid sodium hydrate is a major primary bile acid produced in the liver and usually conjugated with glycine or taurine. Cholic acid sodium hydrate facilitates fat absorption and cholesterol excretion. Cholic acid sodium hydrate is orally active .
|
-
-
- HY-106608
-
|
Litoralon
|
Thyroid Hormone Receptor
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
Glutaurine containing glutamine and taurine residues is an orally active hormone of the parathyroid. Glutaurine, as a hormone, is isolated from parathyroid gland oxyphil cells. Glutaurine can be used for the research of antiepileptic and anti-amnesia .
|
-
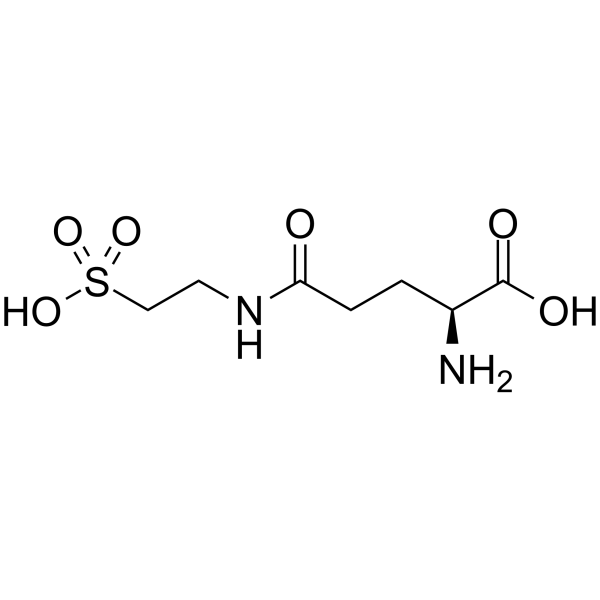
-
- HY-106608A
-
|
Litoralon TFA
|
Thyroid Hormone Receptor
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
Glutaurine (Litoralon) TFA containing glutamine and taurine residues is an orally active hormone of the parathyroid. Glutaurine (Litoralon) TFA, as a hormone, is isolated from parathyroid gland oxyphil cells. Glutaurine (Litoralon) TFA can be used for the research of antiepileptic and anti-amnesia .
|
-
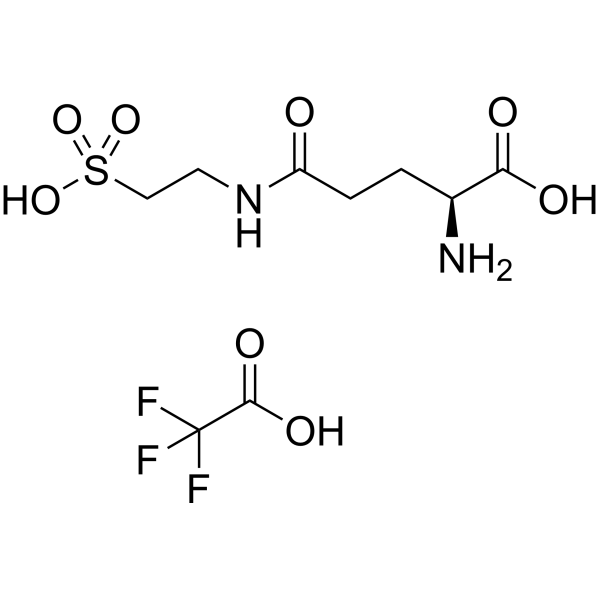
-
- HY-101960A
-
|
AG-183
|
EGFR
|
Others
|
|
Tyrphostin A51 is a potent protein tyrosine kinase (PTK) inhibitor. Tyrphostin A51 inhibits the volume-dependent release of [ 3H]taurine in a dose-dependent manner. Tyrphostin A51 markedly reduces cellular tyrosyl phosphorylation level. Tyrphostin A51 inhibits both basal and EGF-induced human bone cell proliferation .
|
-
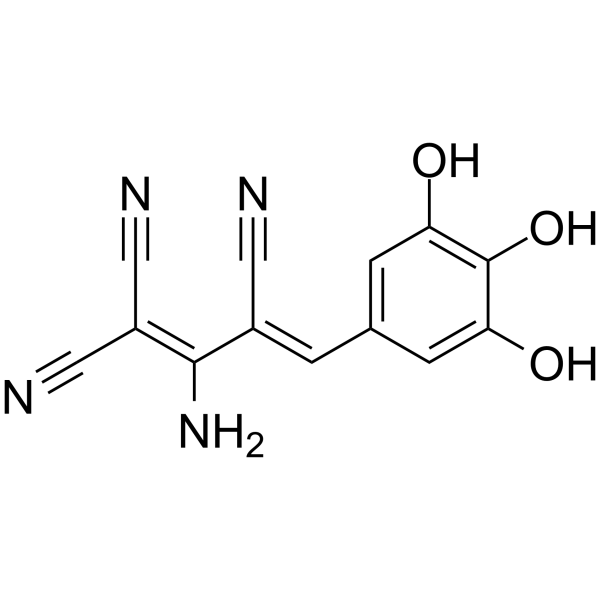
-
- HY-101960
-
|
(Z)-AG-183
|
EGFR
|
Others
|
|
(Z)-Tyrphostin A51 is the Z configuration of Lanoconazole A51. Tyrphostin A51 is a potent protein tyrosine kinase (PTK) inhibitor. Tyrphostin A51 inhibits the volume-dependent release of [ 3H]taurine in a dose-dependent manner. Tyrphostin A51 markedly reduces cellular tyrosyl phosphorylation level. Tyrphostin A51 inhibits both basal and EGF-induced human bone cell proliferation .
|
-
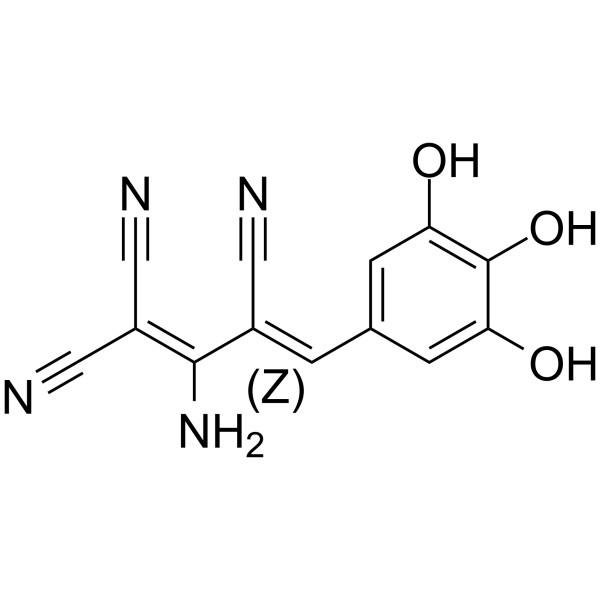
-
- HY-100189
-
|
|
Others
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
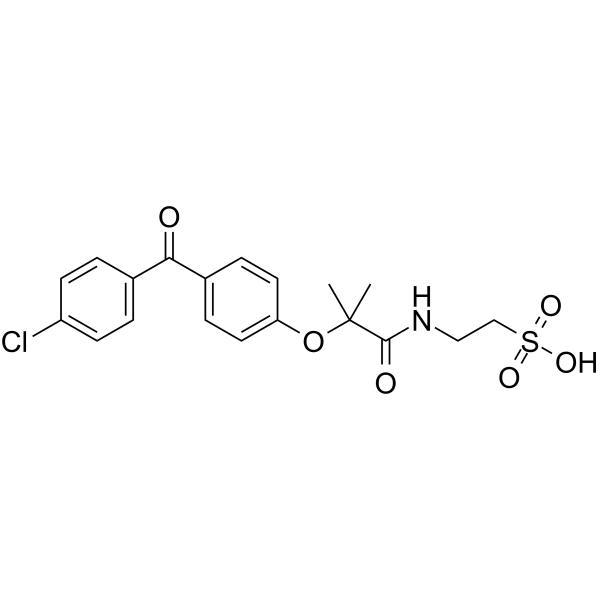
LS2265 is a taurine derivative of fenofibrate and can induce proliferation of peroxisomes in liver cells of rats.
|
-
-
- HY-100803
-
|
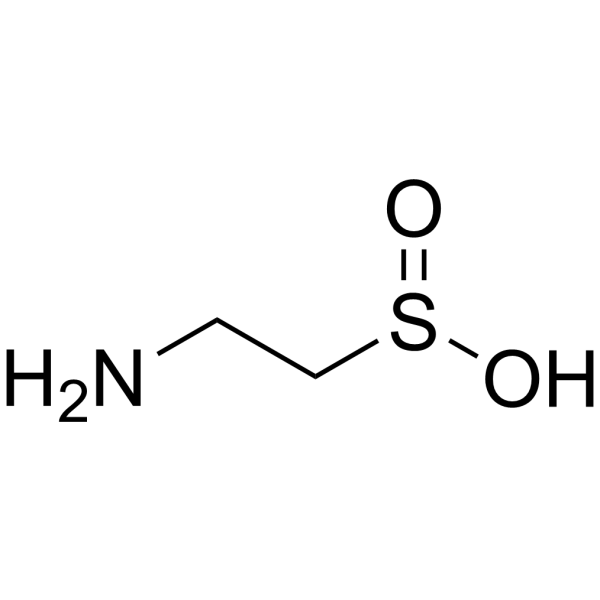
2-Aminoethanesulfinic acid
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
Hypotaurine (2-aminoethanesulfinic acid), an intermediate in taurine biosynthesis from cysteine in astrocytes, is an endogenous inhibitory amino acid of the glycine receptor. Antioxidant .
|
-
-
- HY-N0324A
-
|
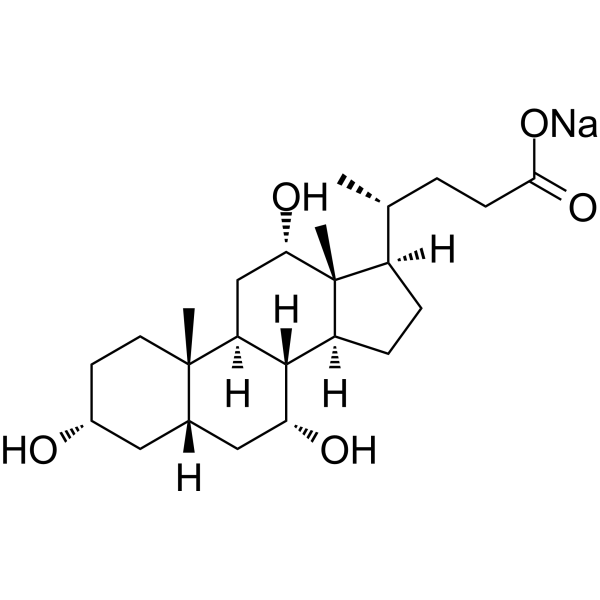
Sodium cholate
|
|
|
|
Cholic acid sodium is a major primary bile acid produced in the liver and usually conjugated with glycine or taurine. It facilitates fat absorption and cholesterol excretion. Cholic acid sodium is orally active .
|
-
-
- HY-N0324S
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
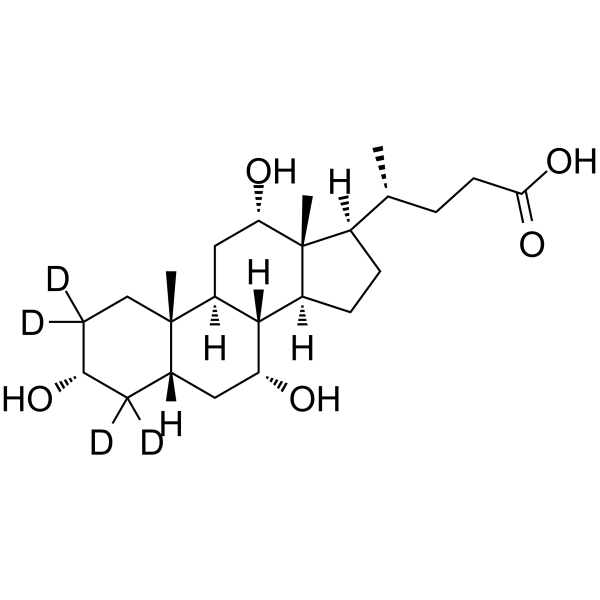
Cholic acid-d4 is the deuterium labeled Cholic acid. Cholic acid is a major primary bile acid produced in the liver and usually conjugated with glycine or taurine. It facilitates fat absorption and cholesterol excretion.
|
-
-
- HY-N0324S1
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
Cholic acid-d5 is the deuterium labeled Cholic acid. Cholic acid is a major primary bile acid produced in the liver and usually conjugated with glycine or taurine. It facilitates fat absorption and cholesterol excretion.
|
-
-
- HY-N0324S2
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
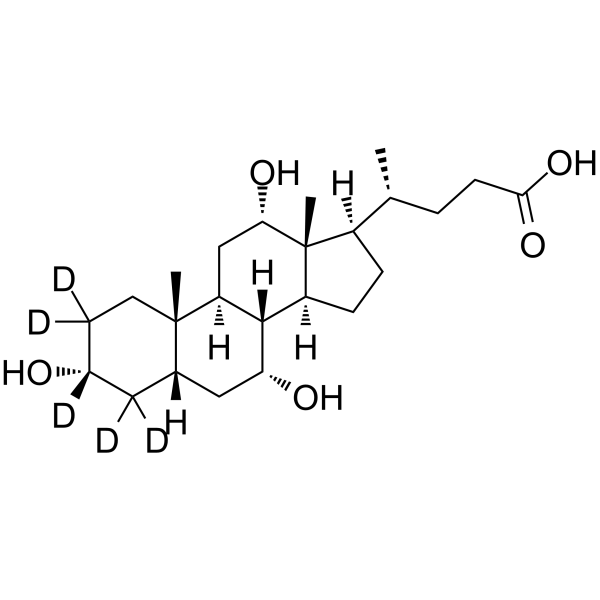
Cholic acid- 13C is the 13C-labeled Cholic acid. Cholic acid is a major primary bile acid produced in the liver and usually conjugated with glycine or taurine. It facilitates fat absorption and cholesterol excretion.
|
-
-
- HY-Y0337
-
|
Cysteine
|
|
|
|
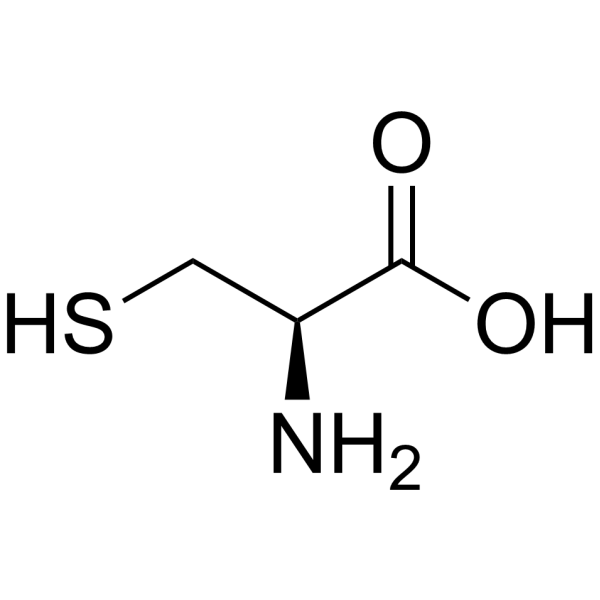
L-Cysteine is a conditionally essential amino acid, which acts as a precursor for biologically active molecules such as hydrogen sulphide (H2S), glutathione and taurine. L-Cysteine suppresses ghrelin and reduces appetite in rodents and humans .
|
-
-
- HY-Y0337A
-
|
|
|
|
|
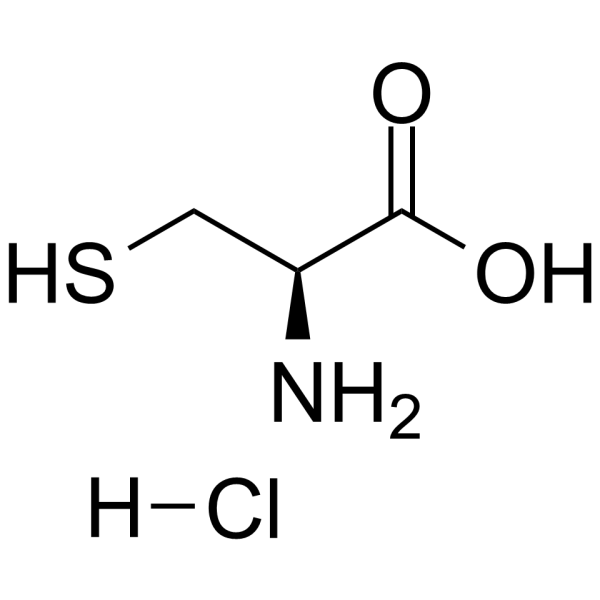
L-Cysteine hydrochloride is a conditionally essential amino acid, which acts as a precursor for biologically active molecules such as hydrogen sulphide (H2S), glutathione and taurine. L-Cysteine hydrochloride suppresses ghrelin and reduces appetite in rodents and humans .
|
-
-
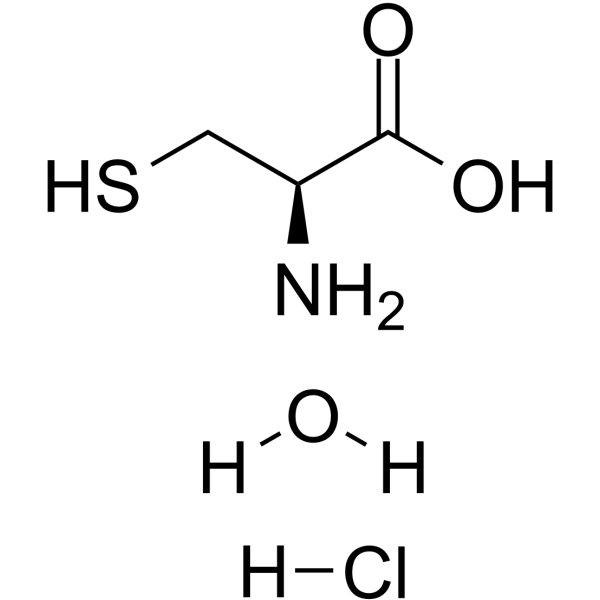
- HY-W016715
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
L-Cysteine hydrochloride hydrate is a conditionally essential amino acid, which acts as a precursor for biologically active molecules such as hydrogen sulphide (H2S), glutathione and taurine. L-Cysteine hydrochloride hydrate suppresses ghrelin and reduces appetite in rodents and humans .
|
-
-
- HY-114360A
-
|
|
Interleukin Related
TNF Receptor
|
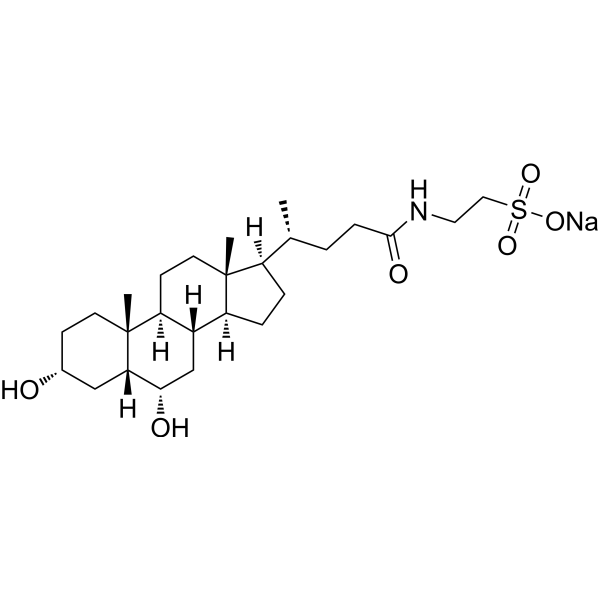
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
Taurohyodeoxycholic acid (THDCA) sodium is the taurine-conjugated form of the secondary bile acid hyodeoxycholic acid. Taurohyodeoxycholic acid can also reduce the activity and expression of myeloperoxidase TNF-α and IL-6, as well as colonic damage in TNBS-induced ulcerative colitis mouse model.
|
-
-
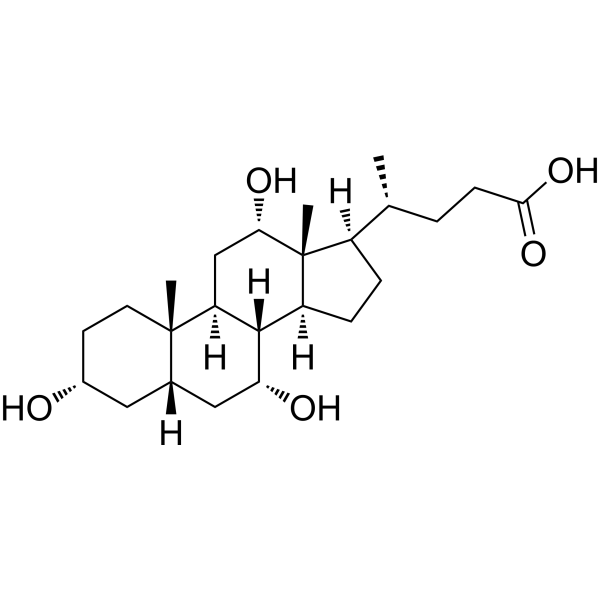
- HY-N0324R
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
Cholic acid (Standard) is the analytical standard of Cholic acid. This product is intended for research and analytical applications. Cholic acid is a major primary bile acid produced in the liver and usually conjugated with glycine or taurine. It facilitates fat absorption and cholesterol excretion. Cholic acid is orally active .
|
-
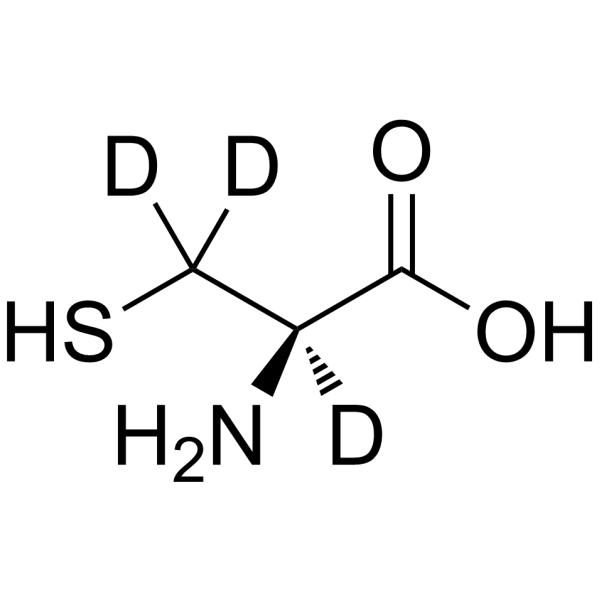
-
- HY-Y0337S5
-
|
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
L-Cysteine-d3 is the deuterium labeled L-Cysteine. L-Cysteine is a conditionally essential amino acid, which acts as a precursor for biologically active molecules such as hydrogen sulphide (H2S), glutathione and taurine. L-Cysteine suppresses ghrelin and reduces appetite in rodents and humans[1].
|
-
-
- HY-Y0337S6
-
|
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
L-Cysteine-d2 is the deuterium labeled L-Cysteine. L-Cysteine is a conditionally essential amino acid, which acts as a precursor for biologically active molecules such as hydrogen sulphide (H2S), glutathione and taurine. L-Cysteine suppresses ghrelin and reduces appetite in rodents and humans[1].
|
-
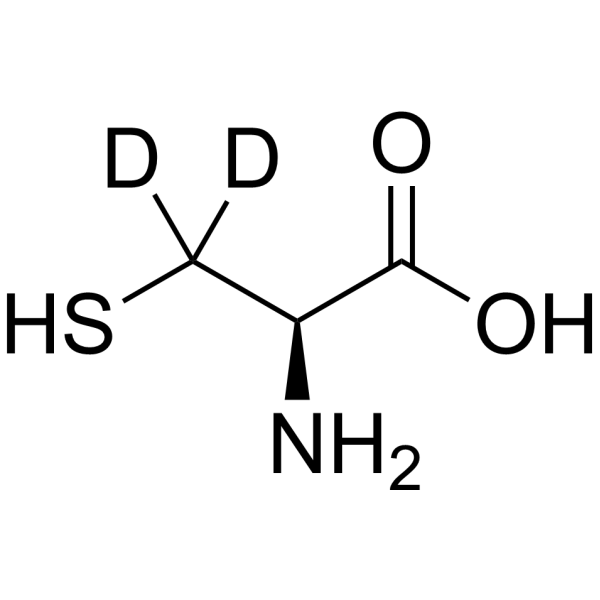
-
- HY-Y0337S1
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
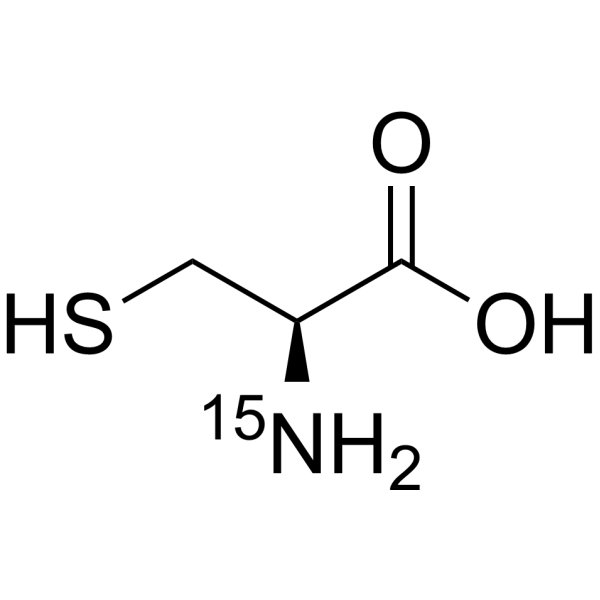
L-Cysteine- 15N is the 15N-labeled L-Cysteine. L-Cysteine is a conditionally essential amino acid, which acts as a precursor for biologically active molecules such as hydrogen sulphide (H2S), glutathione and taurine. L-Cysteine suppresses ghrelin and reduces appetite in rodents and humans[1].
|
-
-
- HY-Y0337S4
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
L-Cysteine- 13C3 is the 13C-labeled L-Cysteine. L-Cysteine is a conditionally essential amino acid, which acts as a precursor for biologically active molecules such as hydrogen sulphide (H2S), glutathione and taurine. L-Cysteine suppresses ghrelin and reduces appetite in rodents and humans[1].
|
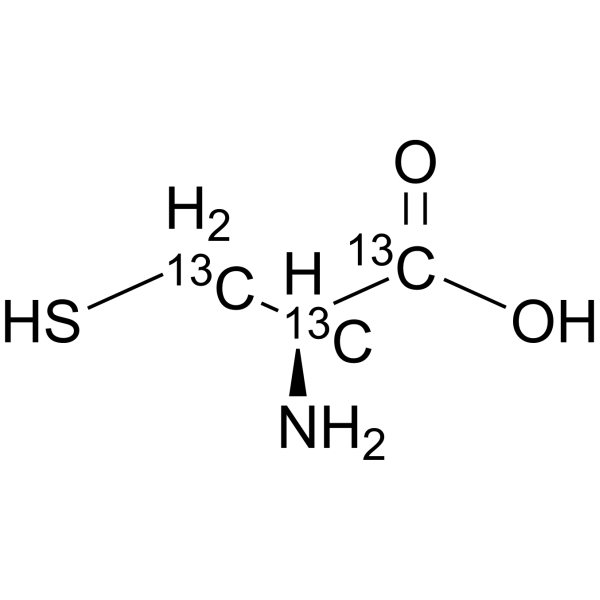
-
-
- HY-Y0337S2
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
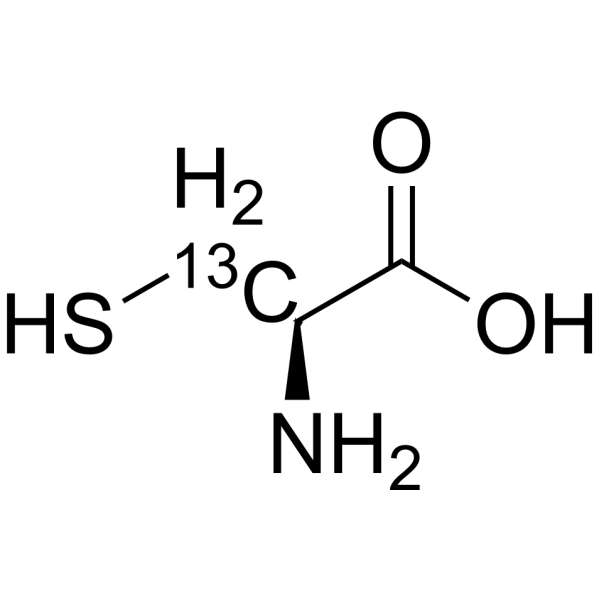
L-Cysteine-3- 13C is the 13C-labeled L-Cysteine. L-Cysteine is a conditionally essential amino acid, which acts as a precursor for biologically active molecules such as hydrogen sulphide (H2S), glutathione and taurine. L-Cysteine suppresses ghrelin and reduces appetite in rodents and humans[1].
|
-
-
- HY-Y0337S3
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
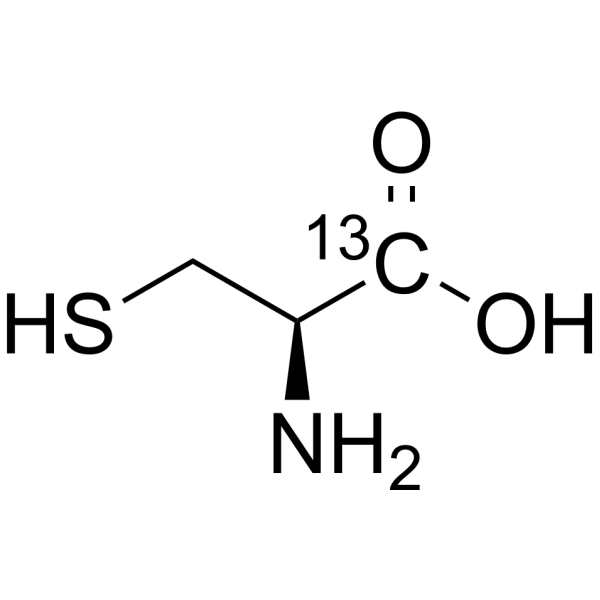
L-Cysteine-1- 13C is the 13C-labeled L-Cysteine. L-Cysteine is a conditionally essential amino acid, which acts as a precursor for biologically active molecules such as hydrogen sulphide (H2S), glutathione and taurine. L-Cysteine suppresses ghrelin and reduces appetite in rodents and humans[1].
|
-
-
- HY-Y0337S
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
L-Cysteine- 13C3, 15N is the 13C- and 15N-labeled L-Cysteine. L-Cysteine is a conditionally essential amino acid, which acts as a precursor for biologically active molecules such as hydrogen sulphide (H2S), glutathione and taurine. L-Cysteine suppresses ghrelin and reduces appetite in rodents and humans[1].
|
-
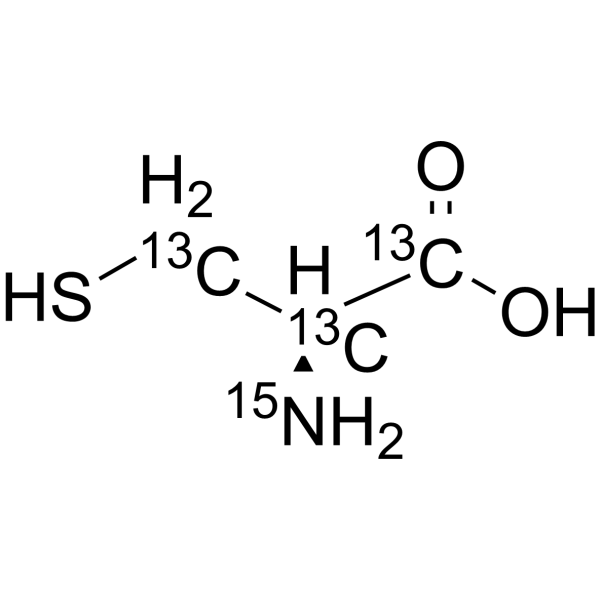
-
- HY-Y0337S7
-
|
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
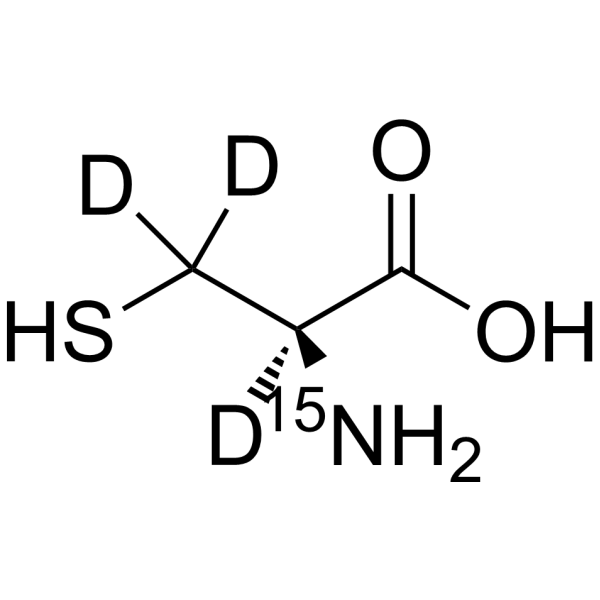
L-Cysteine-d3, 15N is the deuterium and 15N-labeled L-Cysteine. L-Cysteine is a conditionally essential amino acid, which acts as a precursor for biologically active molecules such as hydrogen sulphide (H2S), glutathione and taurine. L-Cysteine suppresses ghrelin and reduces appetite in rodents and humans[1].
|
-
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Type |
-
- HY-114360A
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Taurohyodeoxycholic acid (THDCA) sodium is the taurine-conjugated form of the secondary bile acid hyodeoxycholic acid. Taurohyodeoxycholic acid can also reduce the activity and expression of myeloperoxidase TNF-α and IL-6, as well as colonic damage in TNBS-induced ulcerative colitis mouse model.
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Area |
-
- HY-P3214
-
|
MLCK(11-19) amide
|
Peptides
|
Cancer
|
|
Myosin light chain kinase fragment 11-19 amide (MLCK(11-19) amide) is a substrate-specific peptide inhibitor of MLCK. Myosin light chain kinase fragment 11-19 amide inhibits hypotonicity-induced Ca 2+ entry. Myosin light chain kinase fragment 11-19 amide can be used in the research of human cervical cancer .
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Category |
Target |
Chemical Structure |
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Chemical Structure |
-
- HY-B0351S
-
|
|
|
Taurine-d4 is the deuterium labeled Taurine. Taurine, a sulphur-containing amino acid and an organic osmolyte involved in cell volume regulation, provides a substrate for the formation of bile salts, and plays a role in the modulation of intracellular free calcium concentration. Taurine has the ability to activate autophagy in adipocytes[1][2][3].
|
-

-
- HY-B0351S2
-
|
|
|
Taurine- 13C2, 15N is the 13C- and 15N- labeled Taurine. Taurine, a sulphur-containing amino acid and an organic osmolyte involved in cell volume regulation, provides a substrate for the formation of bile salts, and plays a role in the modulation of intracellular free calcium concentration. Taurine has the ability to activate autophagy in adipocytes[1][2][3].
|
-

-
- HY-N0324S
-
|
|
|
Cholic acid-d4 is the deuterium labeled Cholic acid. Cholic acid is a major primary bile acid produced in the liver and usually conjugated with glycine or taurine. It facilitates fat absorption and cholesterol excretion.
|
-

-
- HY-B0351S1
-
|
|
|
Taurine- 13C2 is the 13C-labeled Taurine. Taurine, a sulphur-containing amino acid and an organic osmolyte involved in cell volume regulation, provides a substrate for the formation of bile salts, and plays a role in the modulation of intracellular free calcium concentration. Taurine has the ability to activate autophagy in adipocytes[1][2][3].
|
-

-
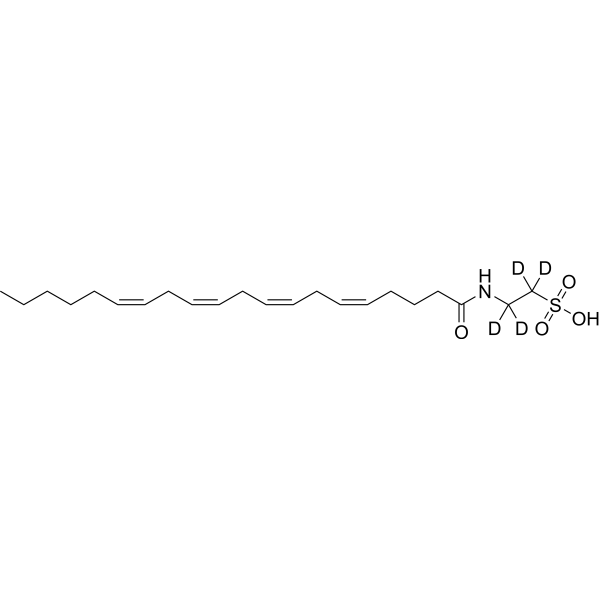
- HY-120962S
-
|
|
|
N-Arachidonoyl Taurine-d4 is the deuterium labeled N-Arachidonoyl Taurine[1].
|
-

-
- HY-N0324S1
-
|
|
|
Cholic acid-d5 is the deuterium labeled Cholic acid. Cholic acid is a major primary bile acid produced in the liver and usually conjugated with glycine or taurine. It facilitates fat absorption and cholesterol excretion.
|
-

-
- HY-N0324S2
-
|
|
|
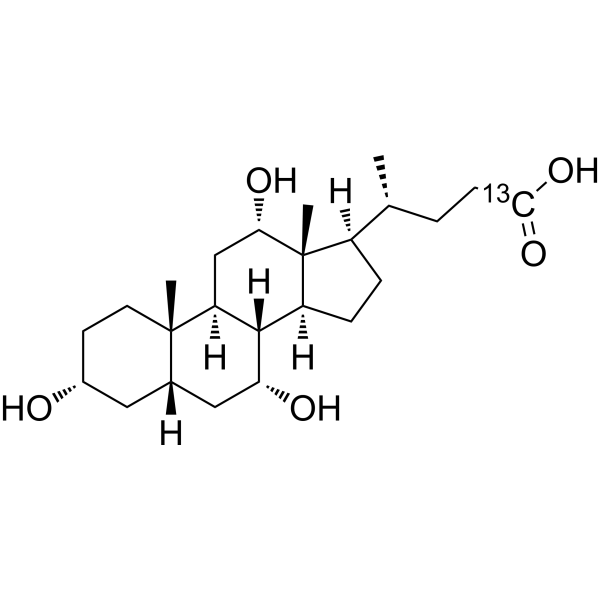
Cholic acid- 13C is the 13C-labeled Cholic acid. Cholic acid is a major primary bile acid produced in the liver and usually conjugated with glycine or taurine. It facilitates fat absorption and cholesterol excretion.
|
-

-
- HY-Y0337S5
-
|
|
|
L-Cysteine-d3 is the deuterium labeled L-Cysteine. L-Cysteine is a conditionally essential amino acid, which acts as a precursor for biologically active molecules such as hydrogen sulphide (H2S), glutathione and taurine. L-Cysteine suppresses ghrelin and reduces appetite in rodents and humans[1].
|
-

-
- HY-Y0337S6
-
|
|
|
L-Cysteine-d2 is the deuterium labeled L-Cysteine. L-Cysteine is a conditionally essential amino acid, which acts as a precursor for biologically active molecules such as hydrogen sulphide (H2S), glutathione and taurine. L-Cysteine suppresses ghrelin and reduces appetite in rodents and humans[1].
|
-

-
- HY-Y0337S1
-
|
|
|
L-Cysteine- 15N is the 15N-labeled L-Cysteine. L-Cysteine is a conditionally essential amino acid, which acts as a precursor for biologically active molecules such as hydrogen sulphide (H2S), glutathione and taurine. L-Cysteine suppresses ghrelin and reduces appetite in rodents and humans[1].
|
-

-
- HY-Y0337S4
-
|
|
|
L-Cysteine- 13C3 is the 13C-labeled L-Cysteine. L-Cysteine is a conditionally essential amino acid, which acts as a precursor for biologically active molecules such as hydrogen sulphide (H2S), glutathione and taurine. L-Cysteine suppresses ghrelin and reduces appetite in rodents and humans[1].
|
-

-
- HY-Y0337S2
-
|
|
|
L-Cysteine-3- 13C is the 13C-labeled L-Cysteine. L-Cysteine is a conditionally essential amino acid, which acts as a precursor for biologically active molecules such as hydrogen sulphide (H2S), glutathione and taurine. L-Cysteine suppresses ghrelin and reduces appetite in rodents and humans[1].
|
-

-
- HY-Y0337S3
-
|
|
|
L-Cysteine-1- 13C is the 13C-labeled L-Cysteine. L-Cysteine is a conditionally essential amino acid, which acts as a precursor for biologically active molecules such as hydrogen sulphide (H2S), glutathione and taurine. L-Cysteine suppresses ghrelin and reduces appetite in rodents and humans[1].
|
-

-
- HY-Y0337S
-
|
|
|
L-Cysteine- 13C3, 15N is the 13C- and 15N-labeled L-Cysteine. L-Cysteine is a conditionally essential amino acid, which acts as a precursor for biologically active molecules such as hydrogen sulphide (H2S), glutathione and taurine. L-Cysteine suppresses ghrelin and reduces appetite in rodents and humans[1].
|
-
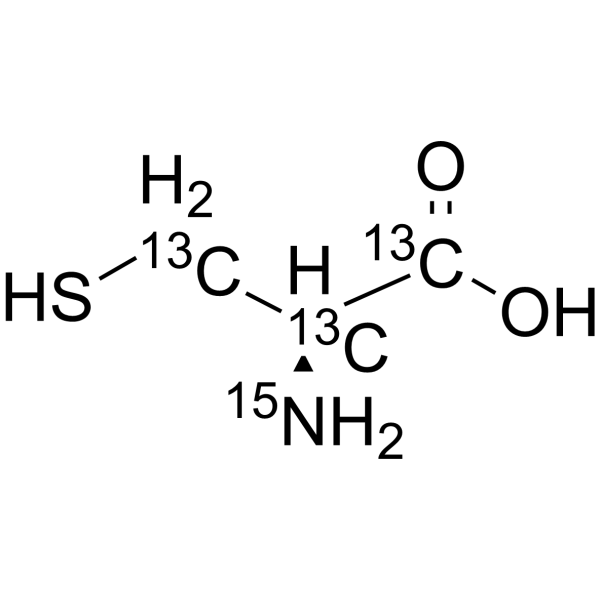
-
- HY-Y0337S7
-
|
|
|
L-Cysteine-d3, 15N is the deuterium and 15N-labeled L-Cysteine. L-Cysteine is a conditionally essential amino acid, which acts as a precursor for biologically active molecules such as hydrogen sulphide (H2S), glutathione and taurine. L-Cysteine suppresses ghrelin and reduces appetite in rodents and humans[1].
|
-

Your information is safe with us. * Required Fields.
Inquiry Information
- Product Name:
- Cat. No.:
- Quantity:
- MCE Japan Authorized Agent: