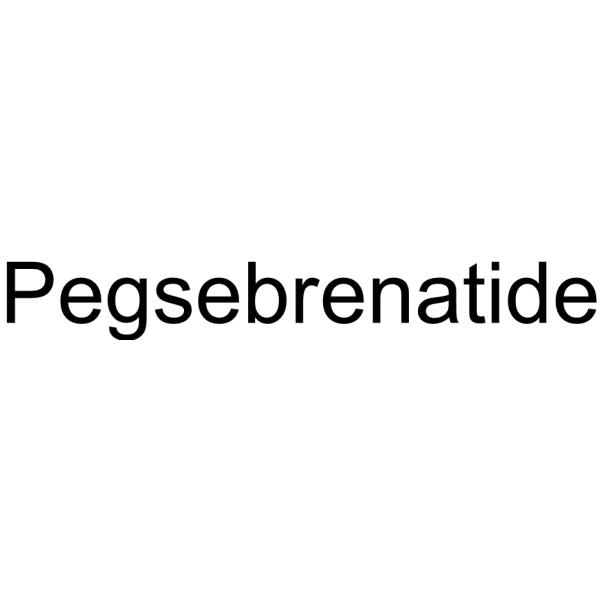Search Result
Results for "
dopaminergic
" in MedChemExpress (MCE) Product Catalog:
17
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Areas |
Chemical Structure |
-
- HY-W008719
-
|
|
Mitochondrial Metabolism
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
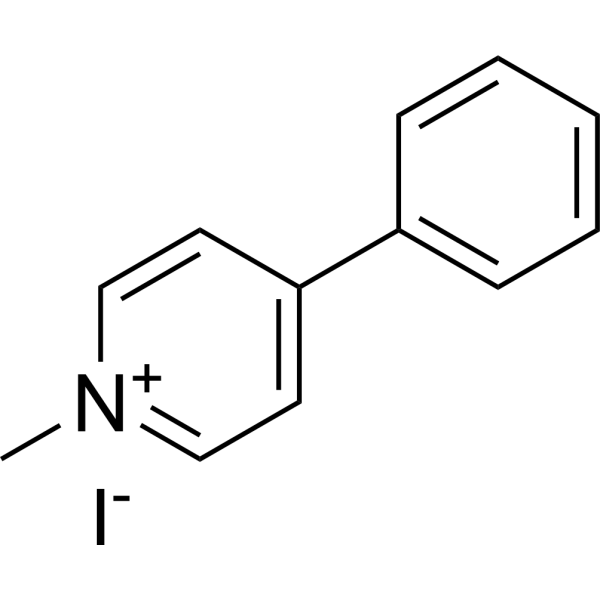
MPP+ iodide, a toxic metabolite of the neurotoxin MPTP, causes symptom of Parkinson's disease in animal models by selectively destroying dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra. MPP+ iodide is taken up by the dopamine transporter into dopaminergic neurons where it exerts its neurotoxic action on mitochondria by affecting complex I of the respiratory chain. MPP+ iodide is also a high affinity substrate for the serotonin transporter (SERT) .
|
-
-
- HY-110080
-
|
|
Dopamine Receptor
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
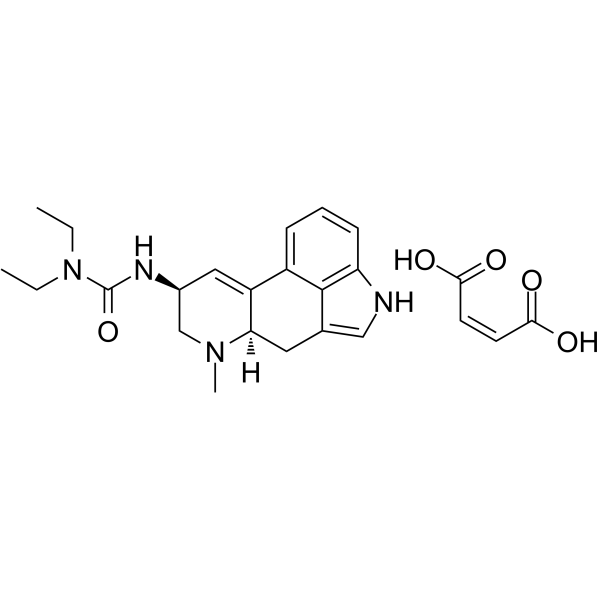
Lisuride (maleate) is a potent agonist of dopamine with a probably direct action on dopaminergic receptors. Lisuride (maleate) is an ergot derivative. Lisuride (maleate) releases the premenstrual mastalgia without significant side effects .
|
-
-
- HY-136390
-
|
|
Dopamine Receptor
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
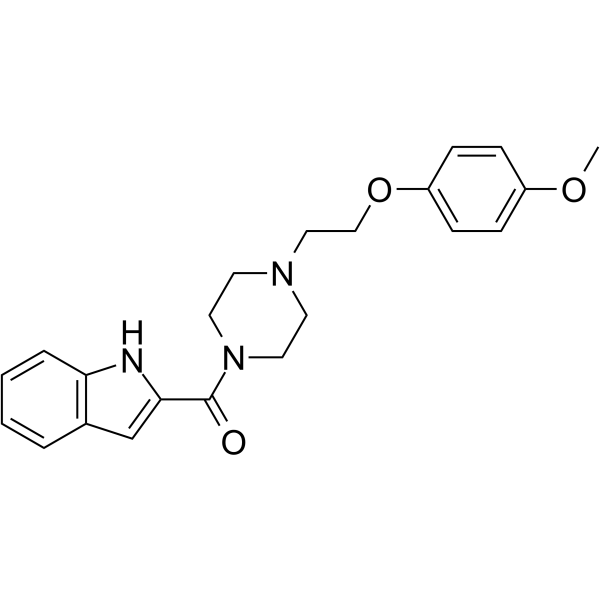
ML417 is a selective and brain penetrant D3 dopamine receptor (D3R) agonist, with an EC50 of 38 nM. ML417 potently promotes D3R-mediated β-arrestin translocation, G protein mediated signaling, and pERK phosphorylation with minimal effects on other GPCR-mediated signaling. ML417 exhibits neuroprotection against toxin-induced neurodegeneration of dopaminergic neurons .
|
-
-
- HY-139308
-
T0467
1 Publications Verification
|
PINK1/Parkin
Mitochondrial Metabolism
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
T0467 activates parkin mitochondrial translocation in a PINK1-dependent manner in vitro. T0467 do not induce mitochondrial accumulation of PINK1in dopaminergic neurons. T0467 is a potential compound for PINK1-Parkin signaling activation, and can be used for parkinson's disease and related disorders research .
|
-
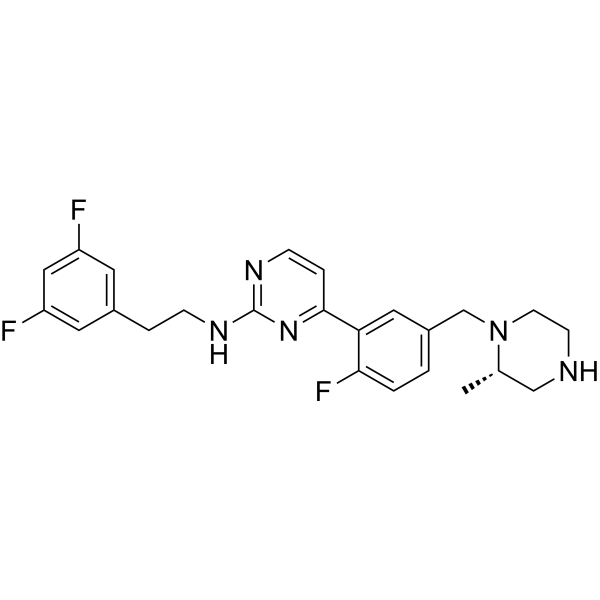
-
- HY-B1124
-
|
|
Adenylate Cyclase
Dopamine Transporter
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
Fipexide, a parachloro-phenossiacetic acid derivative, is an orally active nootropic agent. Fipexide reduces striatal adenylate cyclase activity. Fipexide has positive effect on cognitive performance by dopaminergic neurotransmission. Fipexide is used for senile dementia research. Fipexide acts as a chemical inducer in callus formation, shoot regeneration and Agrobacterium infection .
|
-
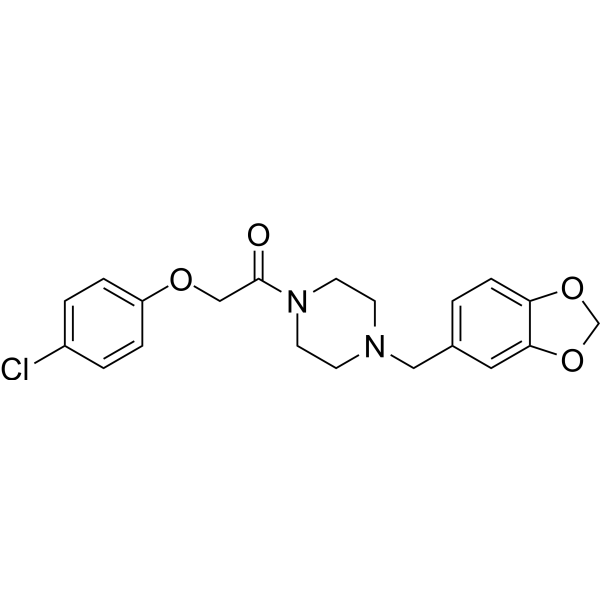
-
- HY-B1124A
-
|
|
Adenylate Cyclase
Dopamine Transporter
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
Fipexide hydrochloride, a parachloro-phenossiacetic acid derivative, is an orally active nootropic agent. Fipexide hydrochloride reduces striatal adenylate cyclase activity. Fipexide hydrochloride has positive effect on cognitive performance by dopaminergic neurotransmission. Fipexide hydrochloride is used for senile dementia research. Fipexide hydrochloride acts as a chemical inducer in callus formation, shoot regeneration and Agrobacterium infection .
|
-
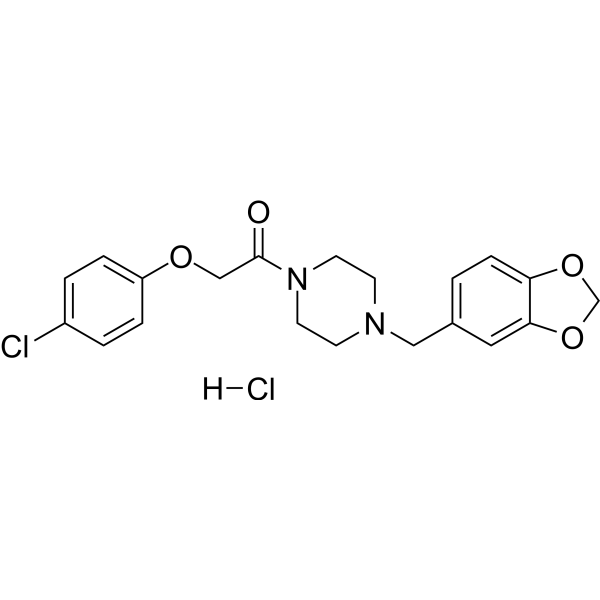
-
- HY-160426
-
|
|
Glucosidase
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
Gcase activator 3 (compound 9Q) is a glucosidase (Glucosidase, GCase) activator that can partially stabilize GCase and increase its activity. Gcase activator 3 reduces mutant GCase protein misfolding and degradation in fibroblasts and dopaminergic midbrain neurons. Gcase activator 3 can be used in the study of Parkinson's disease (PD) and related synucleinopathies .
|
-
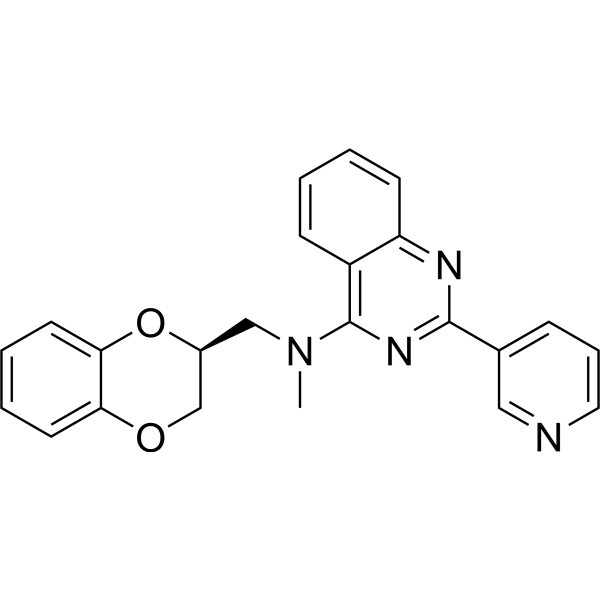
-
- HY-W152604
-
|
Cyclo(leu-gly)
|
Dopamine Receptor
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
Cyclo(glycyl-L-leucyl) (Cyclo(leu-gly)), a neuropeptide, down-regulates dopamine (DA) receptors and attenuates dopaminergic supersensitivity. Cyclo(glycyl-L-leucyl) inhibits the development of Morphine induced pain relief as well as dopamine receptor supersensitivity in rats. Cyclo(glycyl-L-leucyl) has the potential for the prevention of tardive and/or L-DOPA (HY-N0304)-induced dyskinesias .
|
-
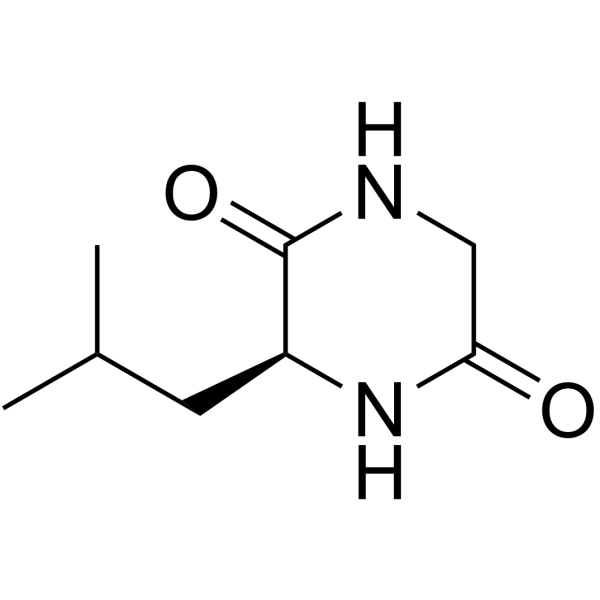
-
- HY-119857
-
|
SIRT2 Inhibitor,Inactive Control
|
Sirtuin
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
AGK7 is a potent inhibitor of sirtuin 2 (SIRT2). AGK7 rescues alpha-synuclein toxicity and modified inclusion morphology in a cellular model of Parkinson's disease. AGK7 protects against dopaminergic cell death both in vitro and in a Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease .
|
-
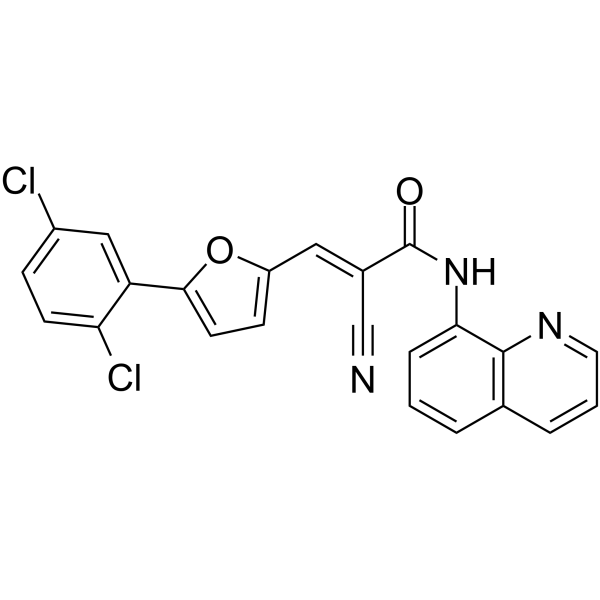
-
- HY-152171
-
|
|
Monoamine Transporter
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
GZ-11608 is a potent and selective vesicular monoamine transporter-2 (VMAT2) inhibitor with high affinity (Ki = 25 nM). GZ-11608 decreases methamphetamine-induced dopamine release from isolated synaptic vesicles from brain dopaminergic neurons. GZ-11608 exhibits rapid brain penetration and without neurotoxicity. GZ-11608 can be used for the research of methamphetamine use disorder .
|
-
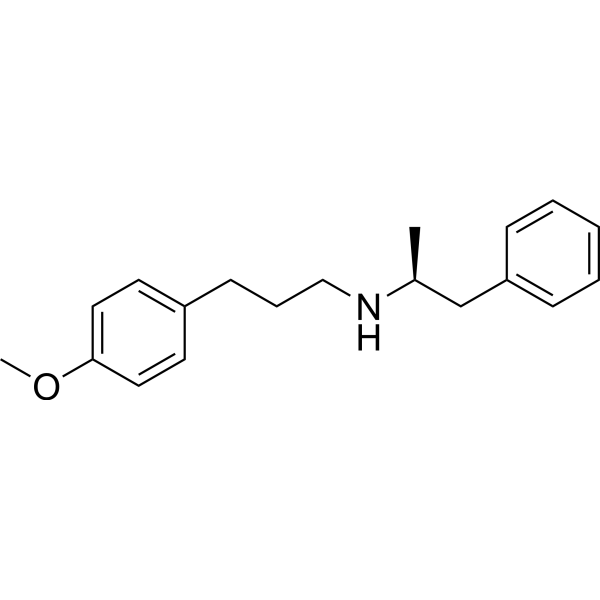
-
- HY-W001601
-
|
|
iGluR
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
Budipine is an anti-parkinson agent. Budipine also is a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp), is mediated the uptake into the brain by P-gp. Budipine also is N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) antagonist, and has indirect dopaminergic effects through an improved dopamine release, the inhibition of monoamine oxidase type B (MAO-B). Budipine can be used for the research of CNS disorders include Parkinson disease .
|
-
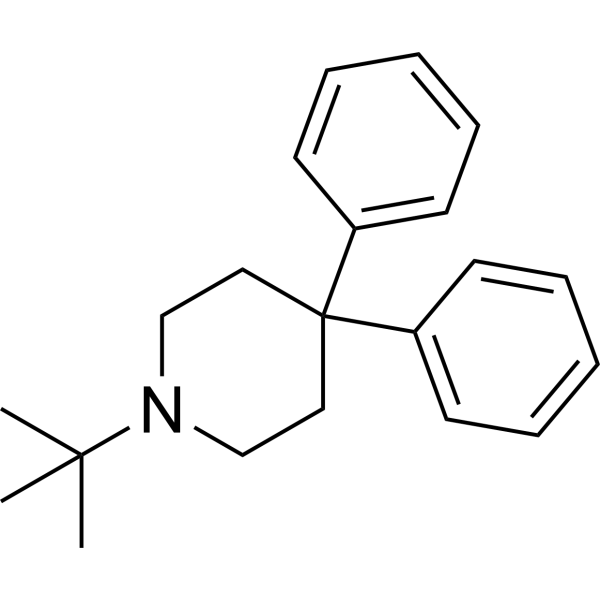
-
- HY-N0303
-
|
|
Mitochondrial Metabolism
Apoptosis
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
Idebenone, a well-appreciated mitochondrial protectant, exhibits protective efficacy against neurotoxicity and can be used for the research of Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease. Idebenone (oxidised form) has a dose-dependent inhibitory effect on the enzymatic metabolism of arachidonic acid in astroglial homogenates (IC50=16.65 μM) . Idebenone, a coenzyme Q10 analog and an antioxidant, induces apoptotic cell death in the human dopaminergic neuroblastoma SHSY-5Y cells . Idebenone quickly crosses the blood-brain barrier.
|
-
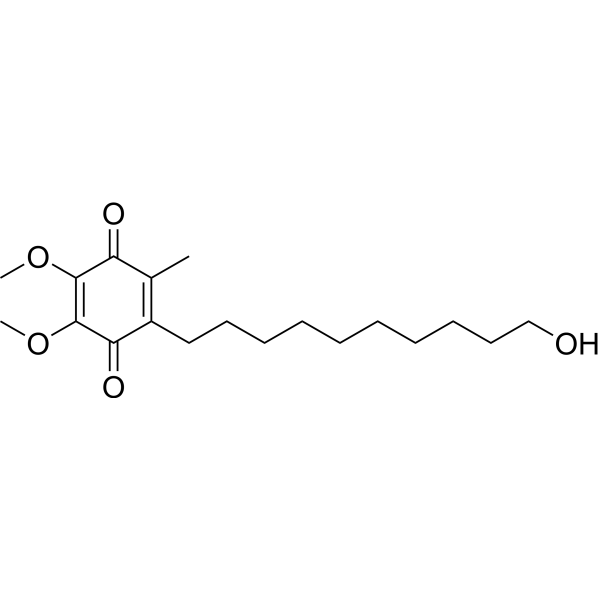
-
- HY-147319
-
|
|
Others
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
RTI-7470-44 is a potent, selective and blood-brain barrier (BBB) penetrant human trace amine-associated receptor subtype 1 (hTAAR1) antagonist with an IC50 value of 8.4 nM and a Ki value of 0.3 nM. RTI-7470-44 has moderate metabolic stability, and a favorable preliminary off-target profile. RTI-7470-44 can increase the spontaneous firing rate of mouse ventral tegmental area (VTA) dopaminergic neurons. RTI-7470-44 can be used for researching schizophrenia, agent addiction, and Parkinson’s disease (PD) .
|
-
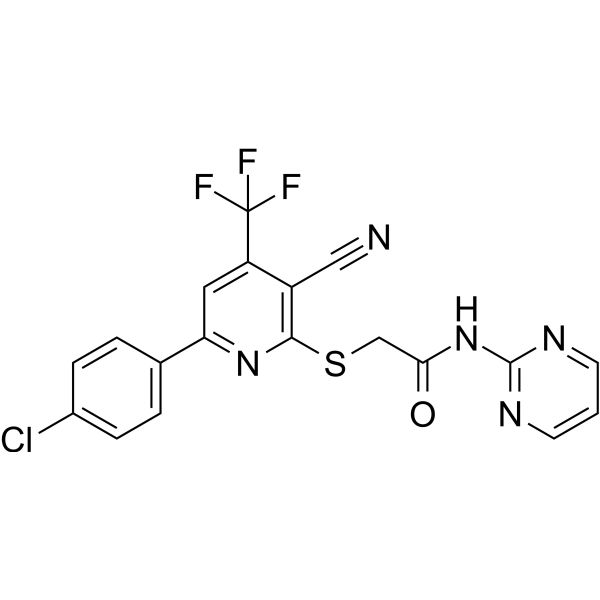
-
- HY-W016498
-
-
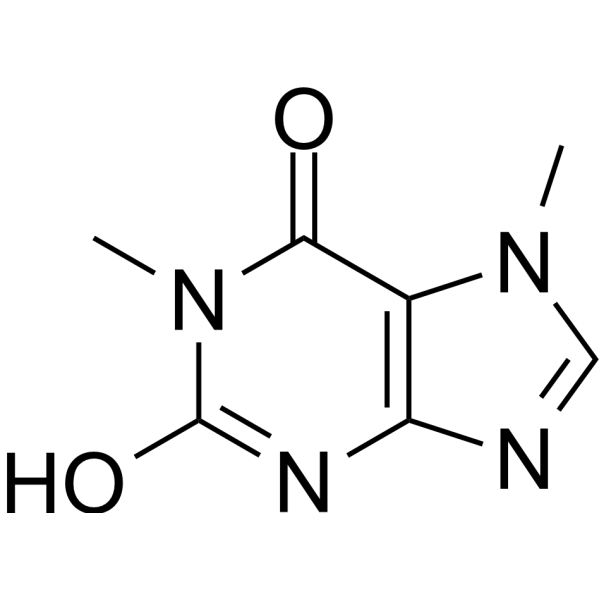
-
- HY-113356
-
-
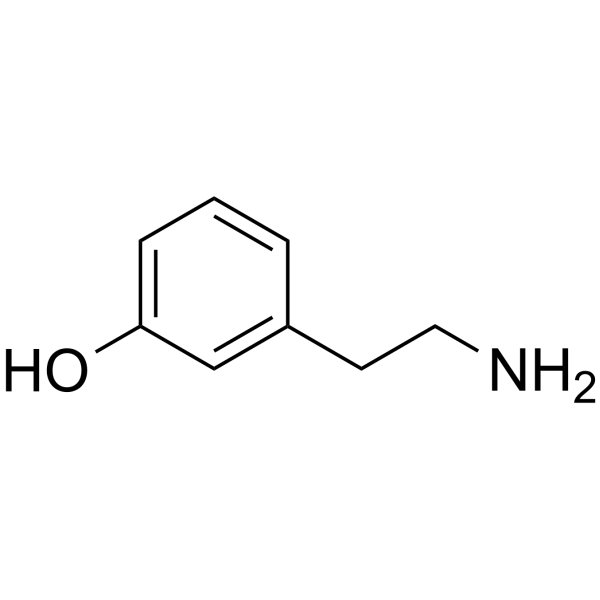
-
- HY-128975
-
-
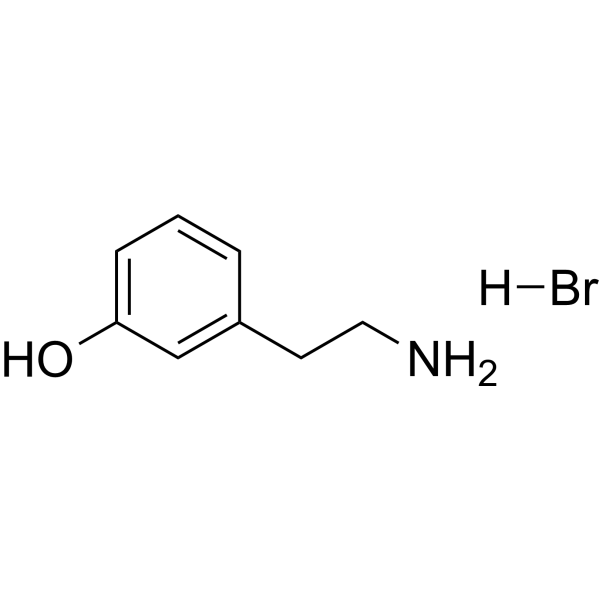
-
- HY-W016498S
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
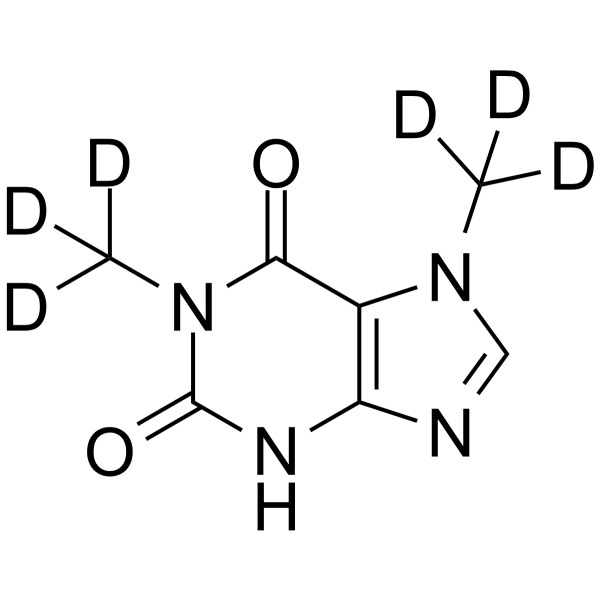
Paraxanthine-d6 is the deuterium labeled Paraxanthine. Paraxanthine, a caffeine metabolite, provides protection against Dopaminergic cell death via stimulation of Ryanodine Receptor Channels.
|
-
-
- HY-W008719S
-
|
|
Mitochondrial Metabolism
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
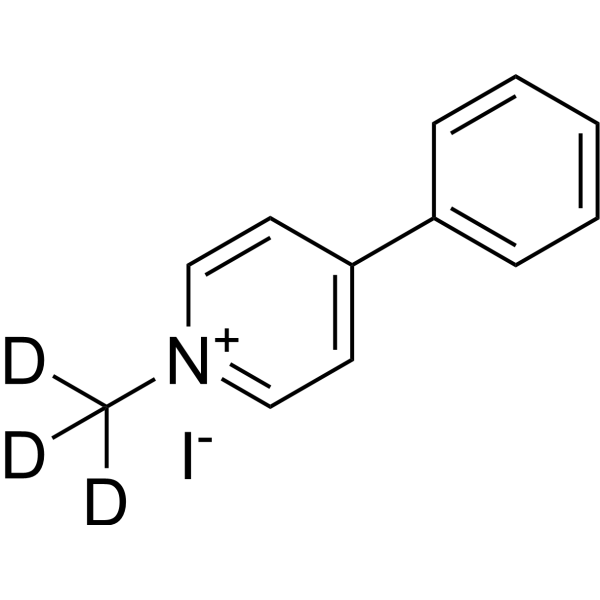
MPP+-d3 (iodide) is deuterium labeled MPP+ (iodide). MPP+ iodide, a toxic metabolite of the neurotoxin MPTP, causes symptom of Parkinson's disease in animal models by selectively destroying dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra. MPP+ iodide is taken up by the dopamine transporter into dopaminergic neurons where it exerts its neurotoxic action on mitochondria by affecting complex I of the respiratory chain. MPP+ iodide is also a high affinity substrate for the serotonin transporter (SERT)[1][2].
|
-
-
- HY-116578
-
|
EXP999; RP9965
|
Others
|
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
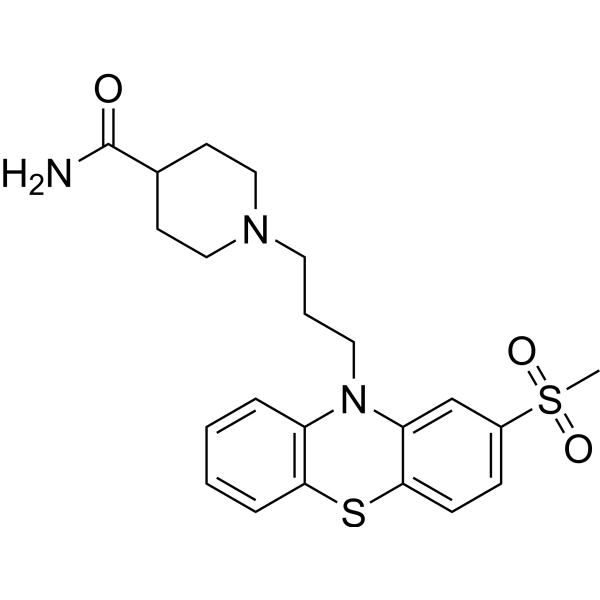
Metopimazine (EXP999) is a phenothiazine derivative used to prevent emesis during chemotherapy. Metopimazine belongs to the anti-dopaminergic anti-emetics (ADA) class. Metopimazine can be used for the research of gastroenteritis (GE) .
|
-
-
- HY-155206
-
|
|
5-HT Receptor
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
(+)-OSU6162 is an stabilizer on dopaminergic and serotonergic brain signaling. (+)-OSU6162 is a partial agonist of 5-HT2A receptor. (+)-OSU6162 can be used for neurological research .
|
-
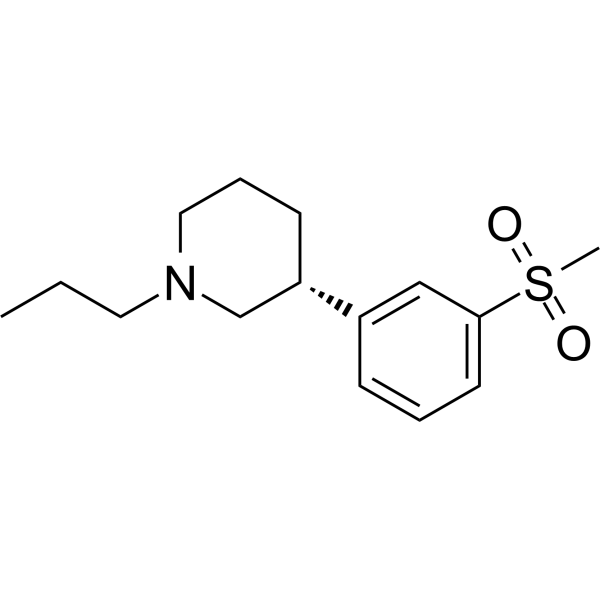
-
- HY-124876
-
|
SC-D
|
α-synuclein
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
SynuClean-D (SC-D) is an inhibitor of α-synuclein aggregation, disrupts mature amyloid fibrils, prevents fibril propagation, and abolishes the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease .
|
-
-
- HY-19489S1
-
-
-
- HY-123506
-
|
|
Src
|
Neurological Disease
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
Fenlean, a natural squamosamide derivative, is a Src tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Fenlean can inhibit over-activated microglia and protect dopaminergic neurons. Fenlean can attenuate neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease models .
|
-
-
- HY-B0282
-
|
ACh chloride
|
nAChR
Calcium Channel
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Neurological Disease
Cancer
|
|
Acetylcholine chloride (ACh chloride), a neurotransmitter, is a potent cholinergic agonist. Acetylcholine chloride is a modulator of the activity of dopaminergic (DAergic) neurons through the stimulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) . Acetylcholine chloride inhibits p53 mutant peptide aggregation in vitro .
|
-
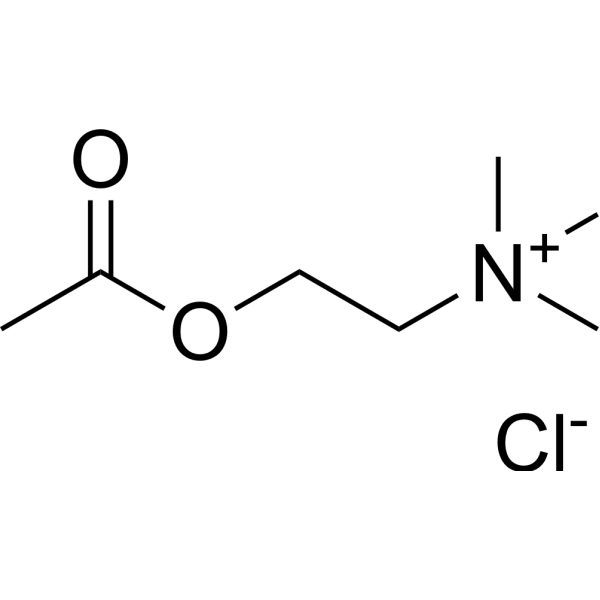
-
- HY-N0109
-
Salidroside
Maximum Cited Publications
20 Publications Verification
Rhodioloside
|
PINK1/Parkin
mTOR
Apoptosis
Prolyl Endopeptidase (PREP)
|
Cancer
|
|
Salidroside (Rhodioloside) is a prolyl endopeptidase inhibitor. Salidroside alleviates cachexia symptoms in mouse models of cancer cachexia via activating mTOR signalling. Salidroside protects dopaminergic neurons by enhancing PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy.
|
-
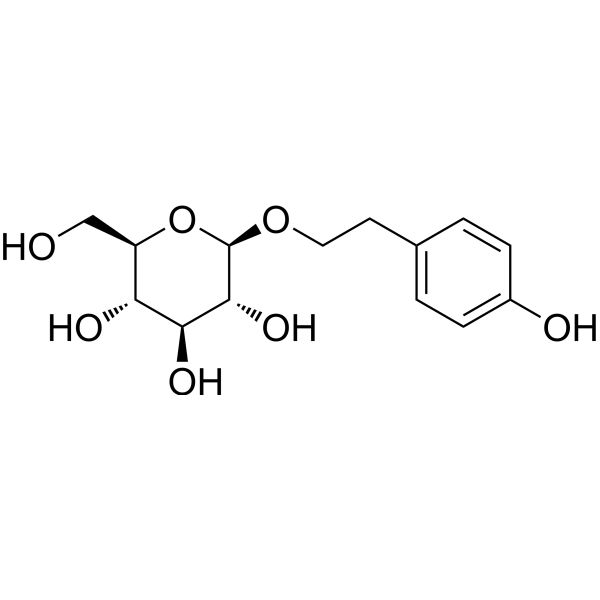
-
- HY-W016498S1
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
Paraxanthine- 13C4, 15N3 is the 13C-labeled and 15N-labeled Paraxanthine. Paraxanthine, a caffeine metabolite, provides protection against Dopaminergic cell death via stimulation of Ryanodine Receptor Channels.
|
-
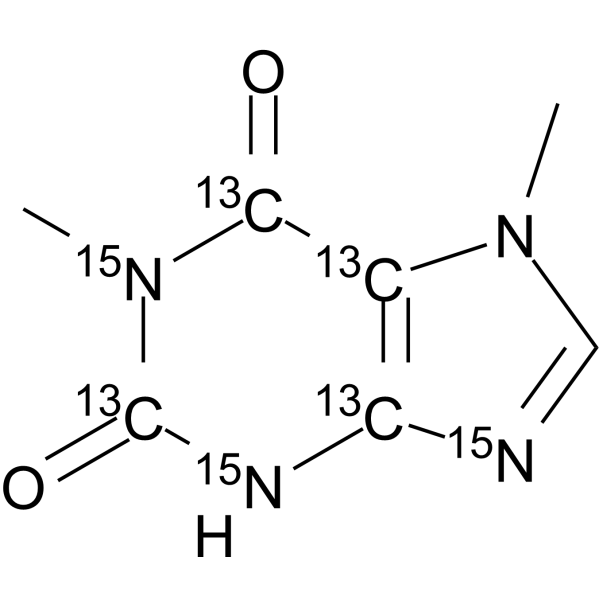
-
- HY-B1693
-
|
Methotrimeprazine
|
|
|
|
Levomepromazine (Methotrimeprazine) is an orally available neuroleptic agent, which is commonly used to relieve nausea and vomiting in palliative care settings. Levomepromazine has antagonist actions at multiple neurotransmitter receptor sites, including dopaminergic, cholinergic, serotonin and histamine receptors .
|
-
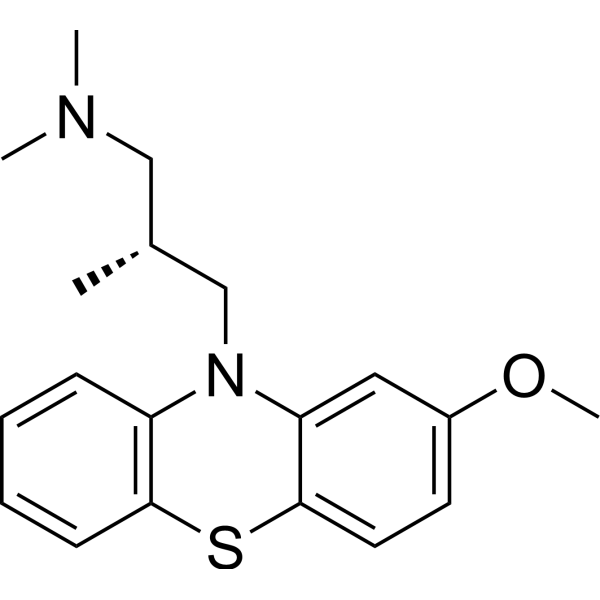
-
- HY-U00280
-
|
|
Others
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
Potassium Channel Activator 1 is an agent for treating, one or more disorders or conditions wherein the dopaminergic system is disrupted, such as one or more disorders or conditions independently selected from the group consisting of: schizophrenia and other psychotic states; mood disorders ADHD; aggression; movement disorders.
|
-
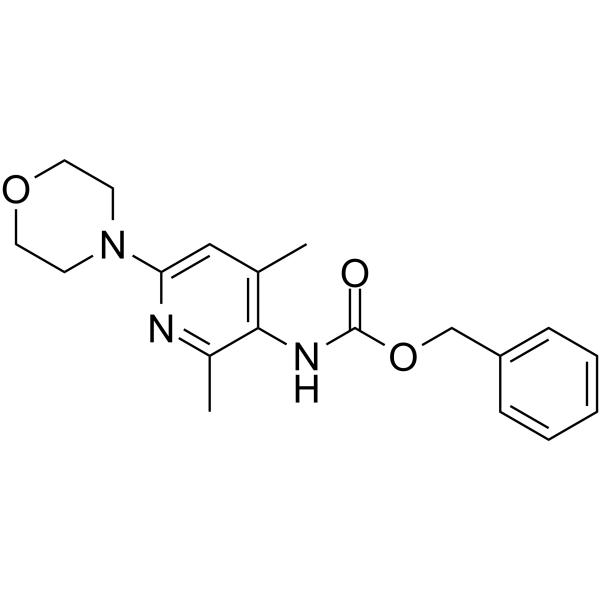
-
- HY-N12657
-
|
|
Others
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
Retinestatin, a new polyol polyketide, can protect SH-SY5Y dopaminergic cells from MPP + (HY-W008719)-induced cytotoxicity. Retinestatin shows neuroprotective effects in an in vitro model of Parkinson’s disease .
|
-
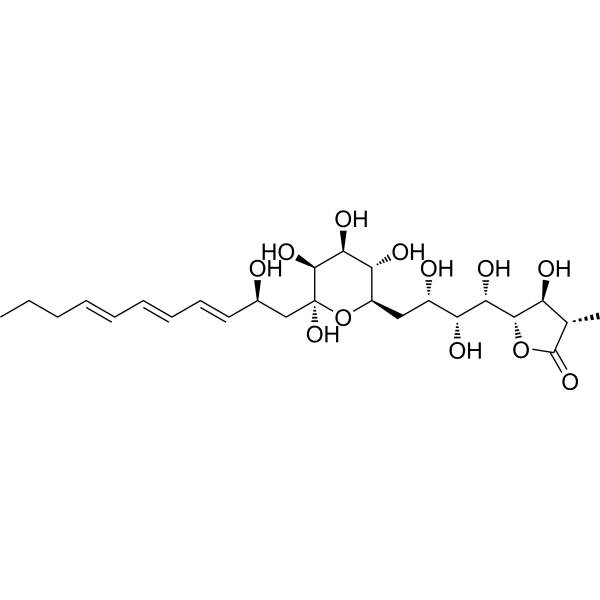
-
- HY-14608S
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
iGluR
Ferroptosis
Apoptosis
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
L-Glutamic acid- 13C is the 13C-labeled L-Glutamic acid. L-Glutamic acid acts as an excitatory transmitter and an agonist at all subtypes of glutamate receptors (metabotropic, kainate, NMDA, and AMPA). L-Glutamic acid shows a direct activating effect on the release of DA from dopaminergic terminals.
|
-
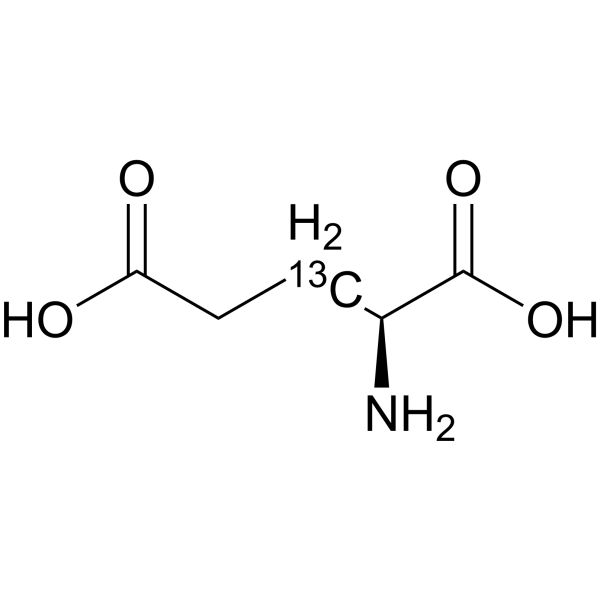
-
- HY-14608S7
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
iGluR
Ferroptosis
Apoptosis
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
L-Glutamic acid-d5 is the deuterium labeled L-Glutamic acid. L-Glutamic acid acts as an excitatory transmitter and an agonist at all subtypes of glutamate receptors (metabotropic, kainate, NMDA, and AMPA). L-Glutamic acid shows a direct activating effect on the release of DA from dopaminergic terminals.
|
-
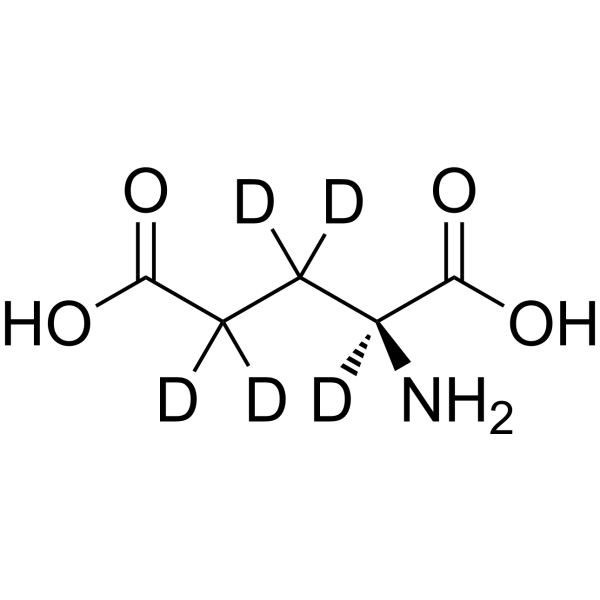
-
- HY-14608S8
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
iGluR
Ferroptosis
Apoptosis
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
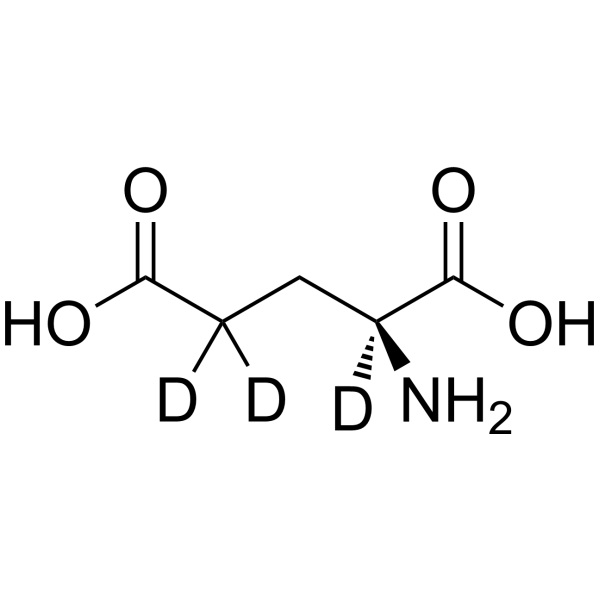
L-Glutamic acid-d3 is the deuterium labeled L-Glutamic acid. L-Glutamic acid acts as an excitatory transmitter and an agonist at all subtypes of glutamate receptors (metabotropic, kainate, NMDA, and AMPA). L-Glutamic acid shows a direct activating effect on the release of DA from dopaminergic terminals.
|
-
-
- HY-14608S5
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
iGluR
Ferroptosis
Apoptosis
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
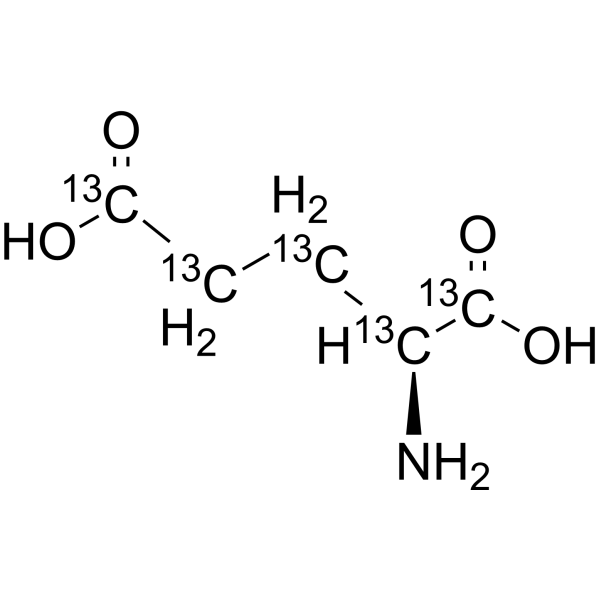
L-Glutamic acid- 13C5 is the 13C-labeled L-Glutamic acid. L-Glutamic acid acts as an excitatory transmitter and an agonist at all subtypes of glutamate receptors (metabotropic, kainate, NMDA, and AMPA). L-Glutamic acid shows a direct activating effect on the release of DA from dopaminergic terminals.
|
-
-
- HY-14608S2
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
iGluR
Ferroptosis
Apoptosis
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
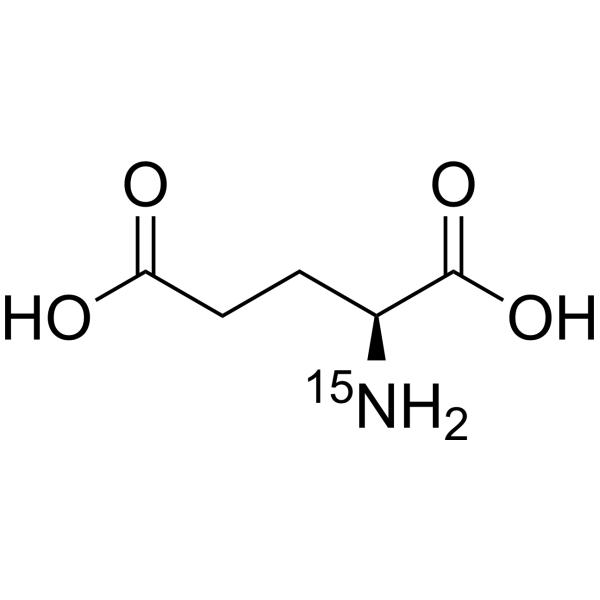
L-Glutamic acid- 15N is the 15N-labeled L-Glutamic acid. L-Glutamic acid acts as an excitatory transmitter and an agonist at all subtypes of glutamate receptors (metabotropic, kainate, NMDA, and AMPA). L-Glutamic acid shows a direct activating effect on the release of DA from dopaminergic terminals[1].
|
-
-
- HY-14608
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
iGluR
Ferroptosis
Apoptosis
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
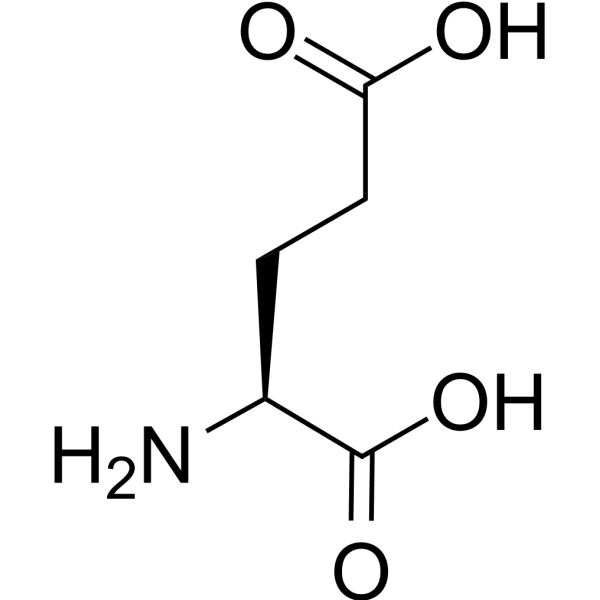
L-Glutamic acid is an excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter that acts as an agonist for all subtypes of glutamate receptors (metabolic rhodophylline, NMDA, and AMPA). L-Glutamic acid has an agonist effect on the release of DA from dopaminergic nerve endings. L-Glutamic acid can be used in the study of neurological diseases .
|
-
-
- HY-B0282S
-
|
ACh-d4 (chloride)
|
nAChR
Calcium Channel
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Neurological Disease
Cancer
|
|
Acetylcholine-d4 (chloride) is the deuterium labeled Acetylcholine chloride. Acetylcholine chloride (ACh chloride), a neurotransmitter, is a potent cholinergic agonist. Acetylcholine chloride is a modulator of the activity of dopaminergic (DAergic) neurons through the stimulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs)[1][2]. Acetylcholine chloride inhibits p53 mutant peptide aggregation in vitro[5].
|
-
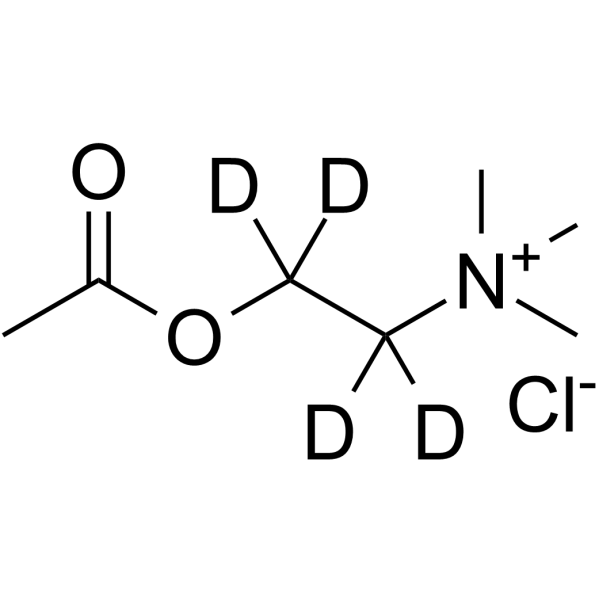
-
- HY-14608S1
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
iGluR
Ferroptosis
Apoptosis
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
L-Glutamic acid-1- 13C is the 13C-labeled L-Glutamic acid. L-Glutamic acid acts as an excitatory transmitter and an agonist at all subtypes of glutamate receptors (metabotropic, kainate, NMDA, and AMPA). L-Glutamic acid shows a direct activating effect on the release of DA from dopaminergic terminals.
|
-
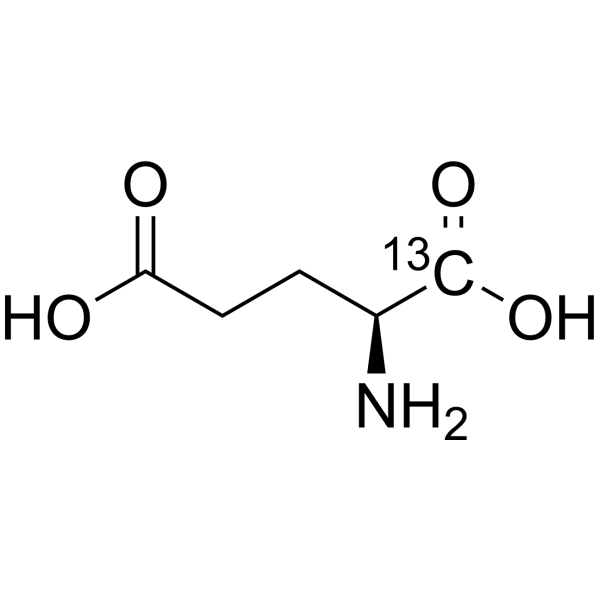
-
- HY-B0282S1
-
|
ACh-d9(chloride)
|
nAChR
Calcium Channel
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Neurological Disease
Cancer
|
|
Acetylcholine-d9 (chloride) is the deuterium labeled Acetylcholine chloride. Acetylcholine chloride (ACh chloride), a neurotransmitter, is a potent cholinergic agonist. Acetylcholine chloride is a modulator of the activity of dopaminergic (DAergic) neurons through the stimulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs)[1][2]. Acetylcholine chloride inhibits p53 mutant peptide aggregation in vitro[5].
|
-
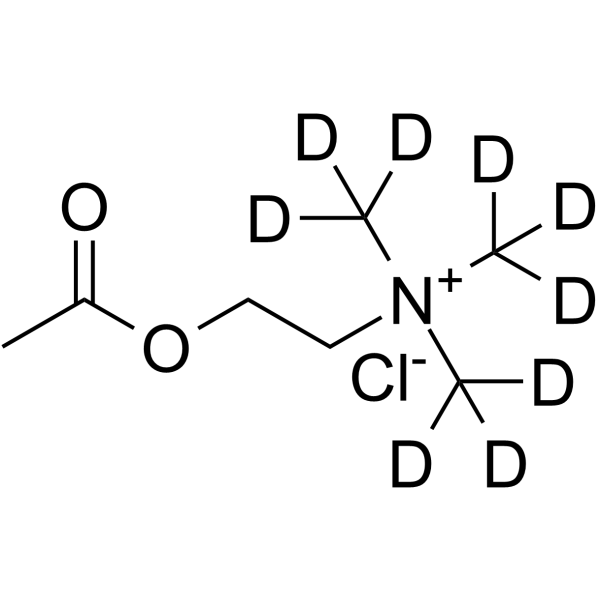
-
- HY-14608S6
-
-
-
- HY-103414
-
|
|
Dopamine Receptor
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
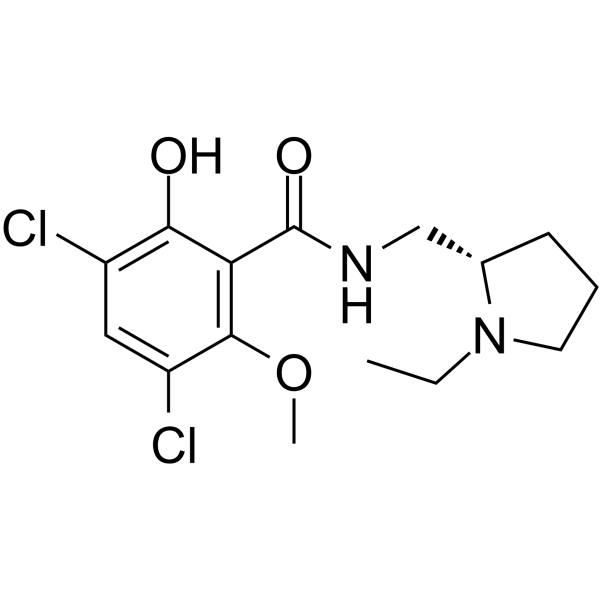
Raclopride is a dopamine D2/D3 receptor antagonist with potential antipsychotic effects. Raclopride binds to D2 and D3 receptors with Kis of 1.8 nM and 3.5 nM, respectively .
|
-
-
- HY-108976
-
|
|
Dopamine Receptor
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
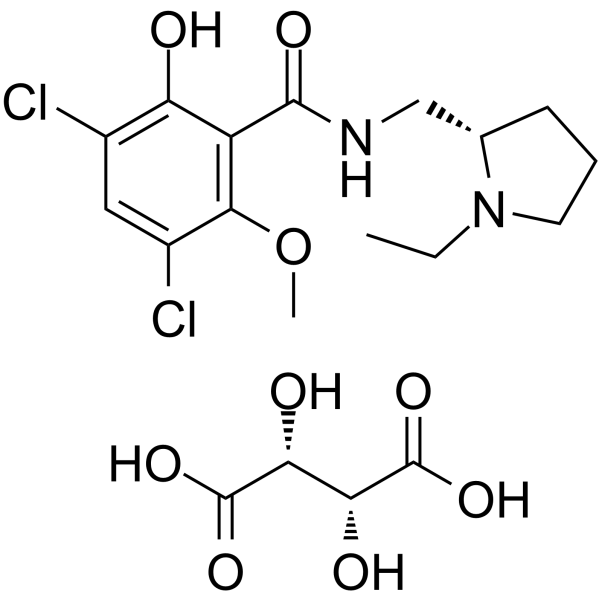
Raclopride tartrate is a selective dopamine D2/D3 receptor antagonist with potential antipsychotic effects. Raclopride tartrate binds to D2 and D3 receptors with Kis of 1.8 nM and 3.5 nM, respectively .
|
-
-
- HY-P10019
-
|
NLY01
|
GCGR
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
Pegsebrenatide (NLY01) is a long-acting GLP-1R agonist. Pegsebrenatide has an extended half-life and favorable blood-brain barrier penetration. Pegsebrenatide can block A1 astrocyte transformation, reducing dopaminergic cell death, and improving motor symptoms in mouse models of PD .
|
-
-
- HY-14608A
-
|
|
iGluR
Apoptosis
Ferroptosis
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
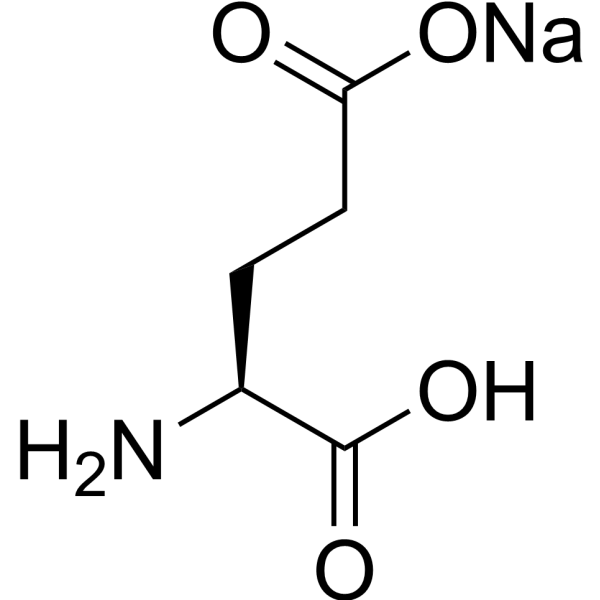
L-Glutamic acid monosodium salt is an excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter that acts as an agonist for all subtypes of glutamate receptors (metabolic rhodophylline, NMDA, and AMPA). L-Glutamic acid monosodium salt has an agonist effect on the release of DA from dopaminergic nerve endings. L-Glutamic acid monosodium salt can be used in the study of neurological diseases .
|
-
-
- HY-14608S3
-
-
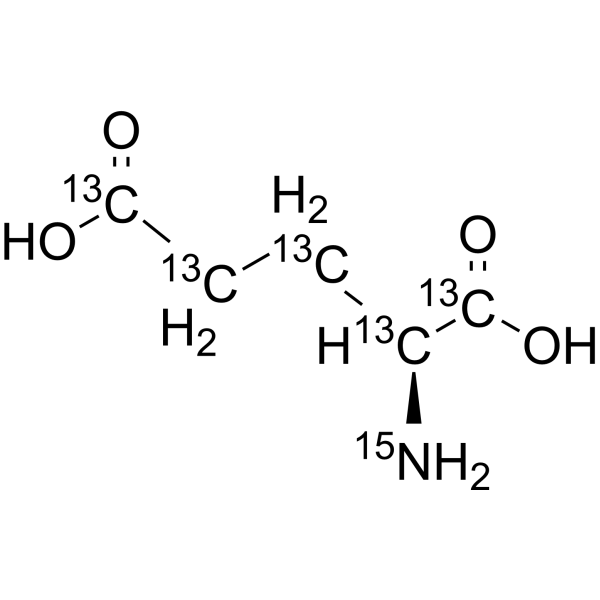
-
- HY-14608S9
-
-
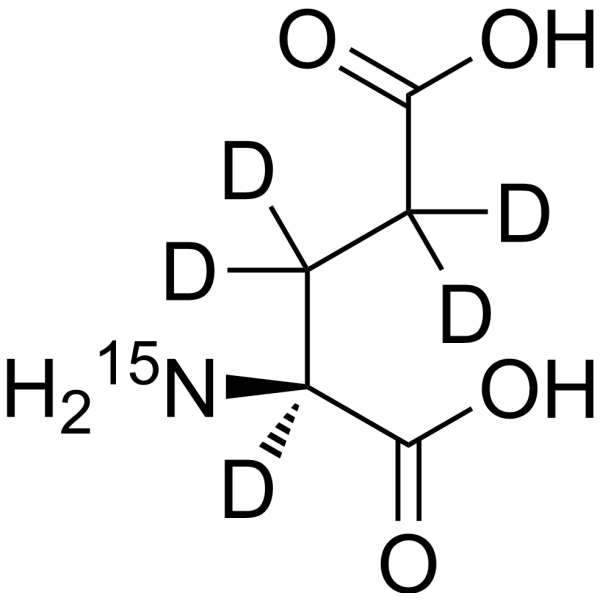
-
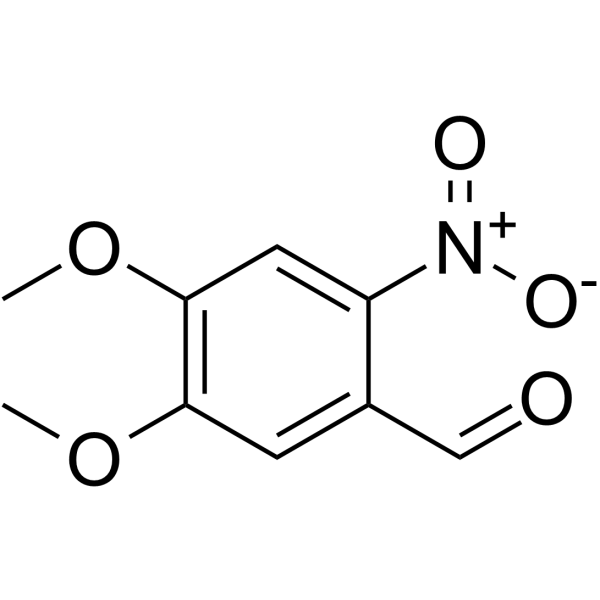
- HY-100705
-
|
6-Nitroveratraldehyde
|
|
|
|
DMNB (6-Nitroveratraldehyde), a precursor, can be used for the synthesis no-carrier-added 6-[ 18F]fluoro-L-DOPA (6-FDOPA). No-Carrier-Added (NCA) 6-[18F]fluoro-L-dopa (6-FDOPA) is being produced routinely for PET investigations of dopaminergic systems .
|
-
-
- HY-14608S10
-
|
|
Apoptosis
iGluR
Ferroptosis
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
L-Glutamic acid- 13C2 is the 13C labeled L-Glutamic acid[1]. L-Glutamic acid acts as an excitatory transmitter and an agonist at all subtypes of glutamate receptors (metabotropic, kainate, NMDA, and AMPA). L-Glutamic acid shows a direct activating effect on the release of DA from dopaminergic terminals[2].
|
-
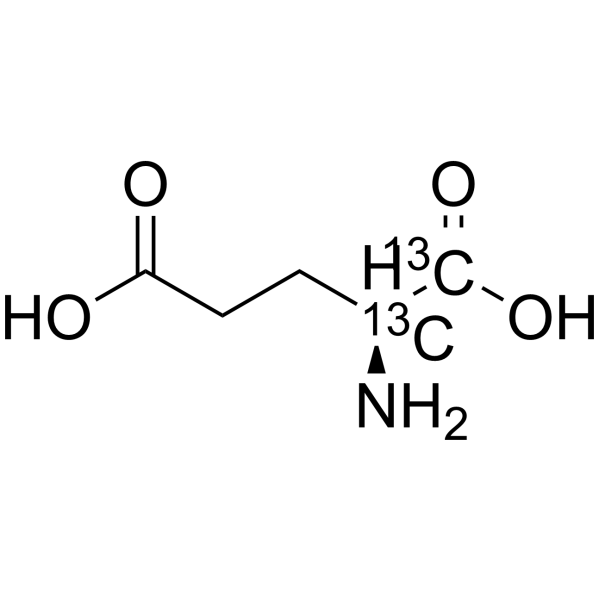
-
- HY-125693
-
|
|
Fungal
|
Infection
Neurological Disease
|
|
L685818 is a specific immunophilin ligand. L685818 was neuroregenerative and non-neuroprotective in primary brain cultures. L685818 protects dopaminergic neurons from toxic inhibition of MPP+ and 6-OHDA, reduces tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) loss, and promotes neuronal process regeneration. L685818 is also an antifungal reagent for Cryptococcus neoformans .
|
-
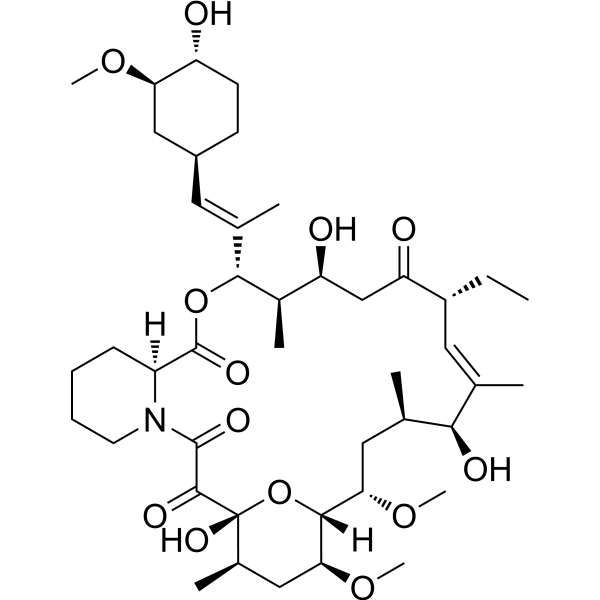
-
- HY-14608S4
-
-
-
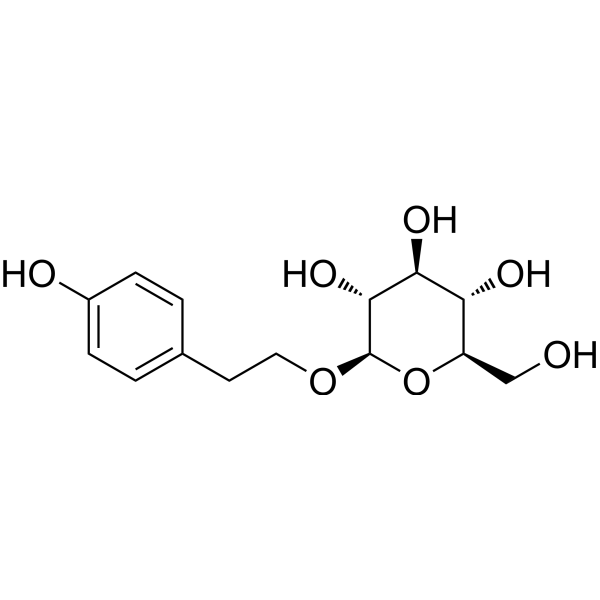
- HY-N0109R
-
|
Rhodioloside (Standard)
|
Prolyl Endopeptidase (PREP)
mTOR
Apoptosis
PINK1/Parkin
|
Cancer
|
|
Salidroside (Standard) is the analytical standard of Salidroside. This product is intended for research and analytical applications. Salidroside (Rhodioloside) is a prolyl endopeptidase inhibitor. Salidroside alleviates cachexia symptoms in mouse models of cancer cachexia via activating mTOR signalling. Salidroside protects dopaminergic neurons by enhancing PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy .
|
-
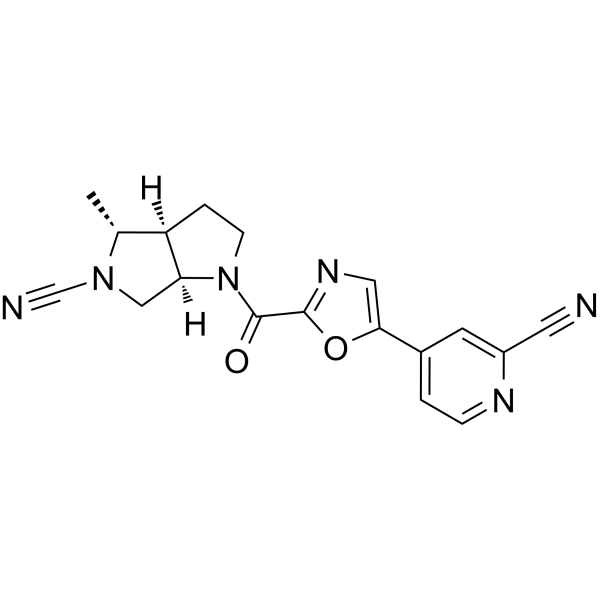
- HY-160019
-
|
|
Deubiquitinase
Mitophagy
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
MTX115325 (Example 1) is an orally active, brain-penetrating USP30 inhibitor (IC50=12 nM) with neuroprotective activity. MTX115325 increases ubiquitination (EC50=32 nM) of the mitochondrial outer membrane protein TOM20 (a USP30 substrate), increasing mitophagy. MTX115325 prevents dopaminergic neuron loss and preserves striatal dopamine .
|
-
- HY-117512
-
|
|
Dopamine Transporter
Serotonin Transporter
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
UWA-101 hydrochloride is a selective and non-cytotoxic DAT/SERT inhibitor, with EC50 values of 3.6 µM and 2.3 µM for inhibiting DAT and SERT, respectively. UWA-101 hydrochloride can alleviate the side effects of dopaminergic agents (such as L-DOPA), such as motor disorders, and lacks psychotropic activity. UWA-101 hydrochloride can be used for research on neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's disease .
|
-
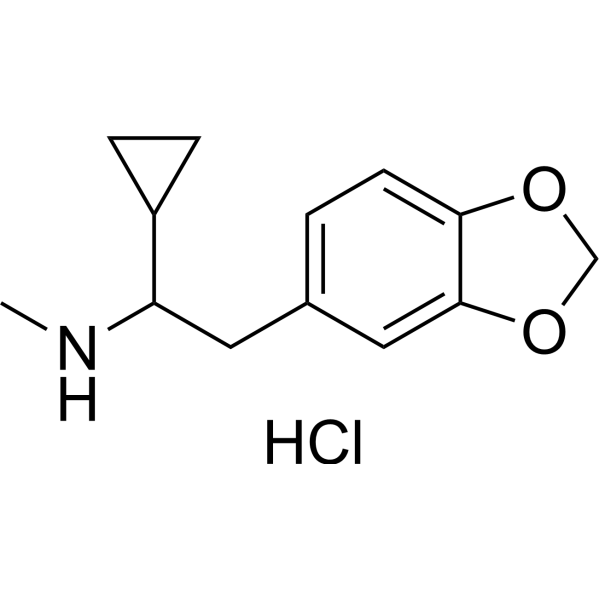
- HY-103129A
-
|
|
5-HT Receptor
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
SB-200646 is the first selective 5-HT2B/2C over 5-HT2A receptor antagonist with pKi values of 7.5, 6.9 and 5.2 for 5-HT2B, 5-HT2C and 5-HT2A, respectively. SB-200646 is orally active and has electrophysiological and anxiolytic properties in vivo .
|
-
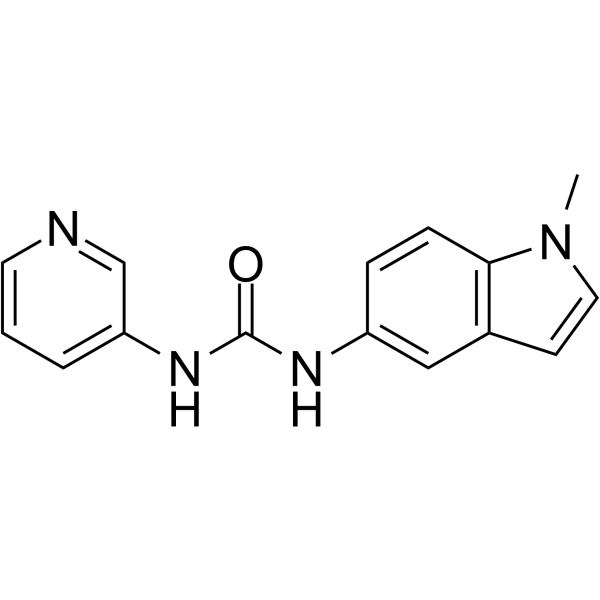
- HY-103129
-
|
|
5-HT Receptor
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
SB-200646A is the first selective 5-HT2B/2C over 5-HT2A receptor antagonist with pKi values of 7.5, 6.9 and 5.2 for 5-HT2B, 5-HT2C and 5-HT2A, respectively. SB-200646A is orally active and has electrophysiological and anxiolytic properties in vivo .
|
-
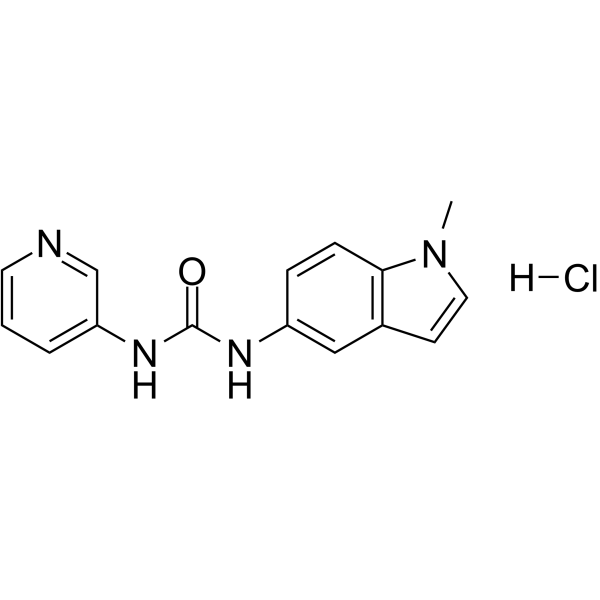
- HY-19225A
-
|
KA-672; Anseculin
|
iGluR
5-HT Receptor
Adrenergic Receptor
Dopamine Receptor
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
Ensaculin free base (KA-672) is a NMDA antagonist and have high affinities to serotonergic 5-HT1A and 5-HT7 receptors, adrenergic α1, and dopaminergic D2 and D3 receptors. Ensaculin free base is a memory-enhancing agent. Ensaculin free base has the potential as an antidementia agent acting on various transmitter systems .
|
-
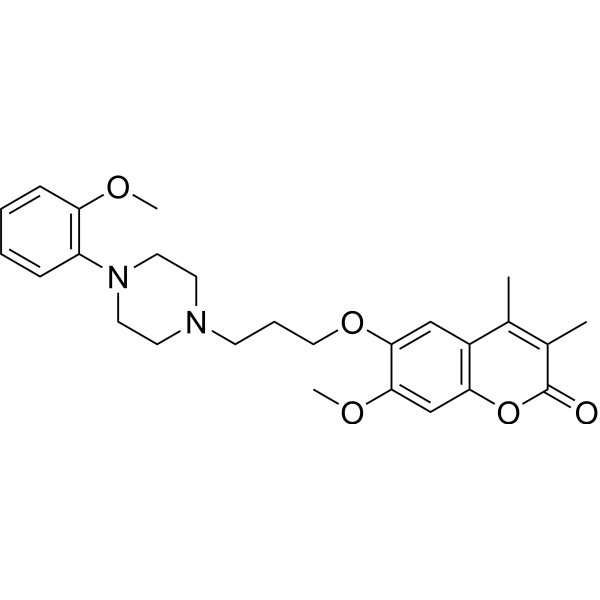
- HY-B1081
-
|
6-Hydroxydopamine hydrochloride; 6-OHDA hydrochloride
|
Dopamine Receptor
Autophagy
Mitophagy
COX
PGE synthase
Interleukin Related
p38 MAPK
Apoptosis
Caspase
|
Neurological Disease
Cancer
|
|
Oxidopamine (6-OHDA) hydrochloride is an antagonist of the neurotransmitter dopamine. Oxidopamine hydrochloride is a widely used neurotoxin and selectively destroys dopaminergic neurons. Oxidopamine hydrochloride promotes COX-2 activation, leading to PGE2 synthesis and pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1β secretion. Oxidopamine hydrochloride can be used for the research of Parkinson’s disease (PD), attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and Lesch-Nyhan syndrome .
|
-
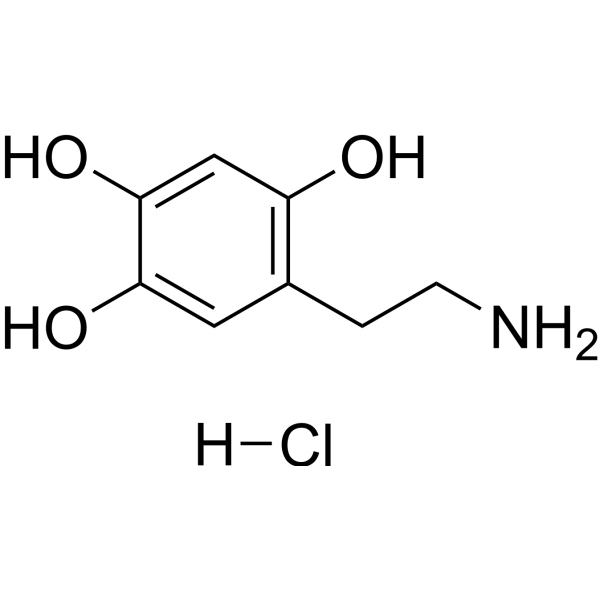
- HY-B1081A
-
|
6-Hydroxydopamine hydrobromide; 6-OHDA hydrobromide
|
Dopamine Receptor
Autophagy
Mitophagy
COX
PGE synthase
Interleukin Related
p38 MAPK
Apoptosis
Caspase
|
Neurological Disease
Cancer
|
|
Oxidopamine (6-OHDA) hydrobromide is an antagonist of the neurotransmitter dopamine. Oxidopamine hydrobromide is a widely used neurotoxin and selectively destroys dopaminergic neurons. Oxidopamine hydrobromide promotes COX-2 activation, leading to PGE2 synthesis and pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1β secretion. Oxidopamine hydrobromide can be used for the research of Parkinson’s disease (PD), attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and Lesch-Nyhan syndrome .
|
-
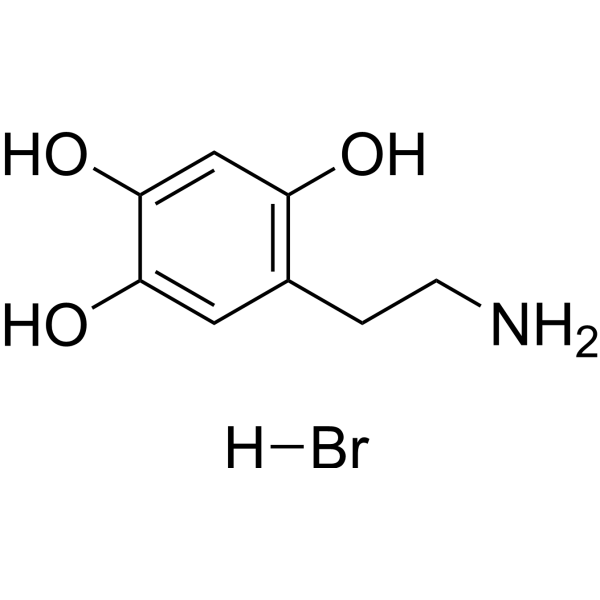
- HY-148502
-
|
|
mAChR
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
VU6019650 is a potent and selective orthosteric antagonist of M5 mAChR (IC50=36 nM), can be used for opioid use disorder (OUD) relief. VU6019650 can cross blood brain barrier, potentially modulates the mesolimbic dopaminergic reward circuitry. VU6019650 blocks Oxotremorine M iodide (HY-101372A) induced increases of neuronal firing rates of midbrain dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) .
|
-
- HY-110105
-
|
|
Potassium Channel
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
NS8593 hydrochloride is a potent and selective small conductance Ca 2+-activated K + channels (SK channels) inhibitor. NS8593 hydrochloride reversibly inhibits SK3-mediated currents with a Kd value of 77 nM. NS8593 hydrochloride inhibits all the SK1-3 subtypes Ca 2+-dependently (Kds of 0.42, 0.60, and 0.73 μM, respectively, at 0.5 μM Ca 2+), and does not affect the Ca 2+-activated K + channels of intermediate and large conductance (hIK and hBK channels, respectively) .
|
-
- HY-149483
-
|
|
nAChR
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
CVN417 is an orally active α6 subunit-containing nAChR antagonist, modulating phasic dopaminergic neurotransmission in an impulse-dependent manner. CVN417 inhibits Ca(2+) effluents mediated by nAChR subunits with IC50s of 0.086 μM (α6), 2.56 μM (α3) and 0.657 μM (α4), respectively. CVN417 attenuates resting tremor in Rodent models, displays the potential to improve movement dysfunction, in conditions such as Parkinson's disease .
|
-
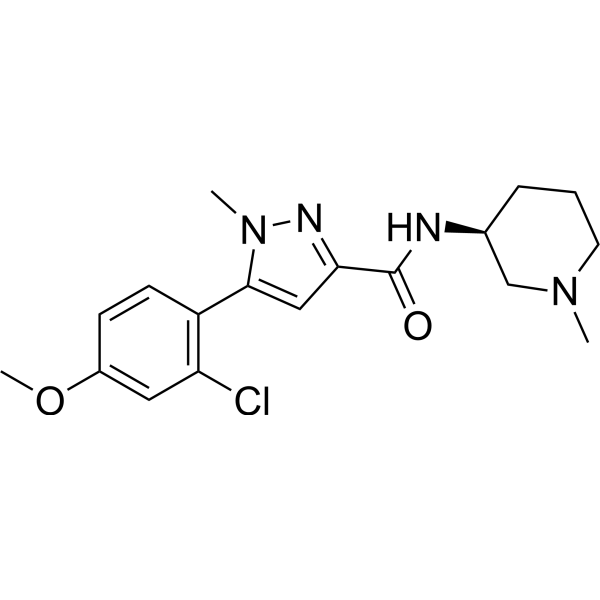
- HY-145848
-
|
|
Estrogen Receptor/ERR
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
ERRγ agonist-1 is a potent ERRγ agonist. ERRγ agonist-1 increases transcriptional activities of ERRγ. ERRγ agonist-1 has the potential for the research of neuropsychological disorders .
|
-
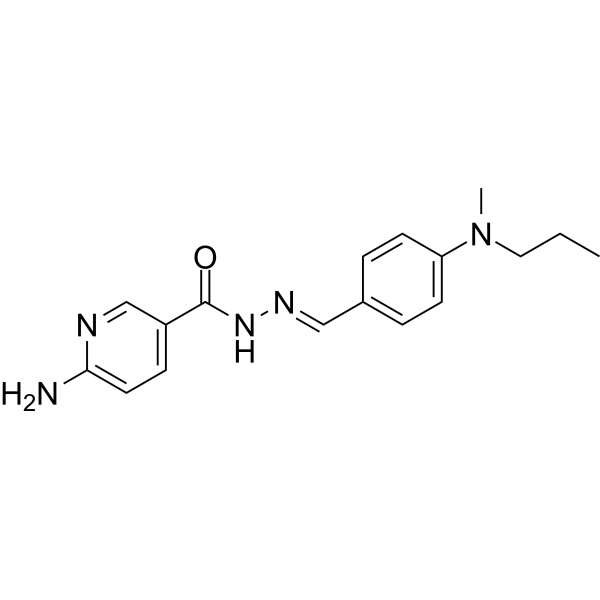
- HY-13409
-
|
|
5-HT Receptor
|
Neurological Disease
Metabolic Disease
|
|
SB 242084 is a selective, competitive and high-affinity (pKi=9.0) 5-HT2C receptor antagonist (crosses the blood-brain barrier). SB 242084 increases basal activity of dopaminergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) of the midbrain and dopamine release in the vomeronasal nucleus. SB 242084 also increases mitochondrial gene expression and oxidative metabolism via 5-HT2A receptor. SB 242084 has good research potential in the negative symptoms of anxiety, depression and schizophrenia, as well as in acute organ damage .
|
-
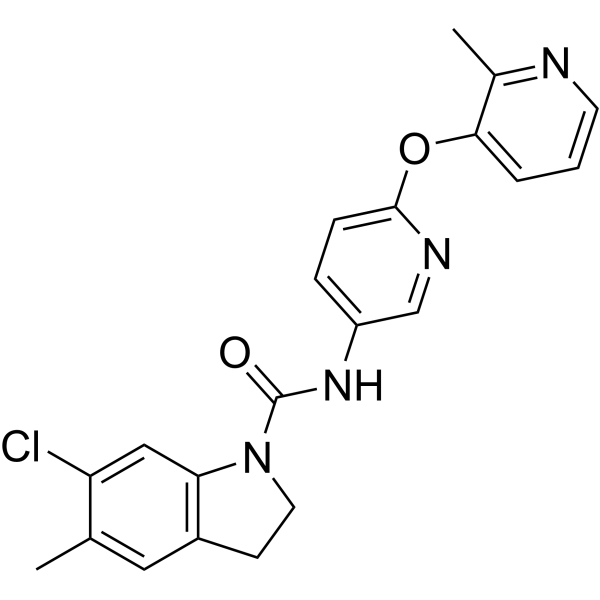
- HY-13409A
-
|
|
5-HT Receptor
|
Neurological Disease
Metabolic Disease
|
|
SB 242084 dihydrochloride is a selective, competitive and high-affinity (pKi=9.0) 5-HT2C receptor antagonist (crosses the blood-brain barrier). SB 242084 dihydrochloride increases basal activity of dopaminergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) of the midbrain and dopamine release in the vomeronasal nucleus. SB 242084 dihydrochloride also increases mitochondrial gene expression and oxidative metabolism via 5-HT2A receptor. SB 242084 dihydrochloride has good research potential in the negative symptoms of anxiety, depression and schizophrenia, as well as in acute organ damage .
|
-
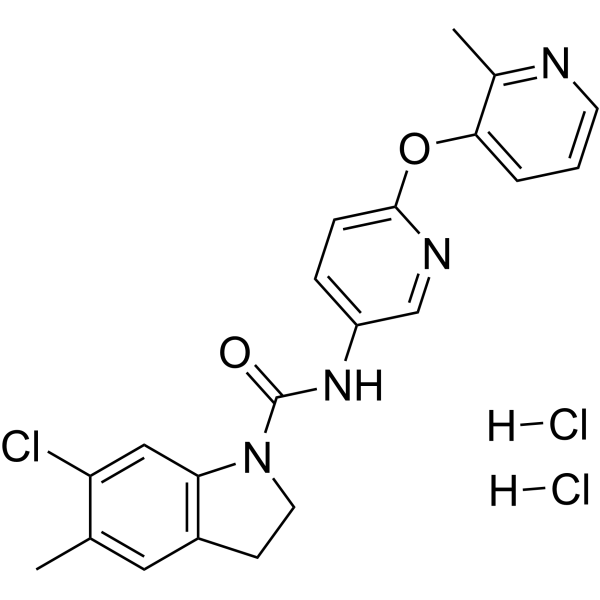
- HY-162363
-
|
|
PARP
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
MD6a is a melatonin derivative with inhibitroy activity towards PARP-1, which maintains proteins hemostasis and improves mitochondrial function through TOR/HSF-1 signaling. MD6a a neuroprotective effect .
|
-
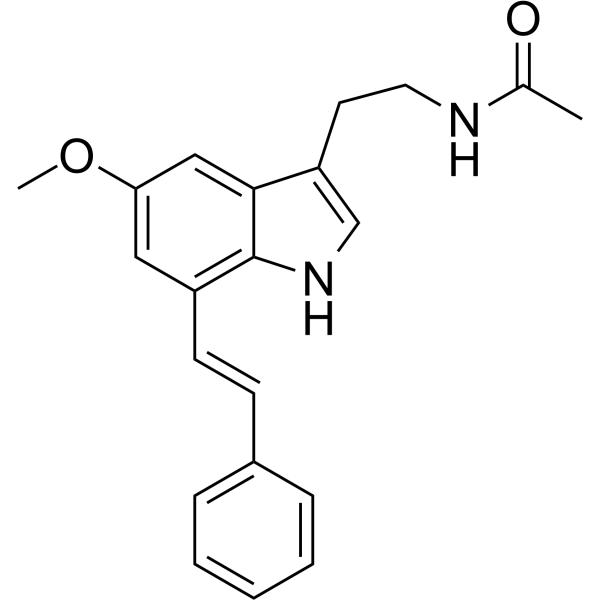
- HY-12583
-
A-366
2 Publications Verification
|
Histone Methyltransferase
Epigenetic Reader Domain
|
Cancer
|
|
A-366 is a potent, highly selective, peptide-competitive histone methyltransferase G9a inhibitor with IC50s of 3.3 and 38 nM for G9a and GLP (EHMT1), respectively. A-366 shows >1000-fold selectivity over 21 other methyltransferases. A-366 is also a potent, nanomolar inhibitor of the Spindlin1-H3K4me3-interaction (IC50=182.6 nM). A-366 displays high affinity at human histamine H3 receptor (Ki=17 nM) and shows subtype selectivity among subsets of the histaminergic and dopaminergic receptor families .
|
-
-
-
HY-L085
-
|
|
1339 compounds
|
|
Parkinson’s disease (PD), the second most common age-associated neurodegenerative disorder, is characterized by the loss of dopaminergic (DA) neurons and the presence of α-synuclein-containing aggregates in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc). Motor features such as tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia and postural instability are common traits of PD. To date, there is no treatment to stop or at least slow down the progression of the disease. The etiology and pathogenesis of PD is still elusive, however, a large body of evidence suggests a prominent role of oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, mitochondrial dysfunction and proteasome dysfunction in the pathogenesis of PD.
MCE offers a unique collection of 1339 compounds with anti- Parkinson’s Disease activities or targeting the unique targets of PD. MCE Anti- Parkinson's Disease Compound Library is a useful tool for exploring the mechanism of PD and discovering new drugs for PD.
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Area |
-
- HY-W152604
-
|
Cyclo(leu-gly)
|
Dopamine Receptor
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
Cyclo(glycyl-L-leucyl) (Cyclo(leu-gly)), a neuropeptide, down-regulates dopamine (DA) receptors and attenuates dopaminergic supersensitivity. Cyclo(glycyl-L-leucyl) inhibits the development of Morphine induced pain relief as well as dopamine receptor supersensitivity in rats. Cyclo(glycyl-L-leucyl) has the potential for the prevention of tardive and/or L-DOPA (HY-N0304)-induced dyskinesias .
|
-
- HY-P10019
-
|
NLY01
|
GCGR
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
Pegsebrenatide (NLY01) is a long-acting GLP-1R agonist. Pegsebrenatide has an extended half-life and favorable blood-brain barrier penetration. Pegsebrenatide can block A1 astrocyte transformation, reducing dopaminergic cell death, and improving motor symptoms in mouse models of PD .
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Category |
Target |
Chemical Structure |
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Chemical Structure |
-
- HY-W016498S
-
|
|
|
Paraxanthine-d6 is the deuterium labeled Paraxanthine. Paraxanthine, a caffeine metabolite, provides protection against Dopaminergic cell death via stimulation of Ryanodine Receptor Channels.
|
-

-
- HY-W008719S
-
|
|
|
MPP+-d3 (iodide) is deuterium labeled MPP+ (iodide). MPP+ iodide, a toxic metabolite of the neurotoxin MPTP, causes symptom of Parkinson's disease in animal models by selectively destroying dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra. MPP+ iodide is taken up by the dopamine transporter into dopaminergic neurons where it exerts its neurotoxic action on mitochondria by affecting complex I of the respiratory chain. MPP+ iodide is also a high affinity substrate for the serotonin transporter (SERT)[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-W016498S1
-
|
|
|
Paraxanthine- 13C4, 15N3 is the 13C-labeled and 15N-labeled Paraxanthine. Paraxanthine, a caffeine metabolite, provides protection against Dopaminergic cell death via stimulation of Ryanodine Receptor Channels.
|
-

-
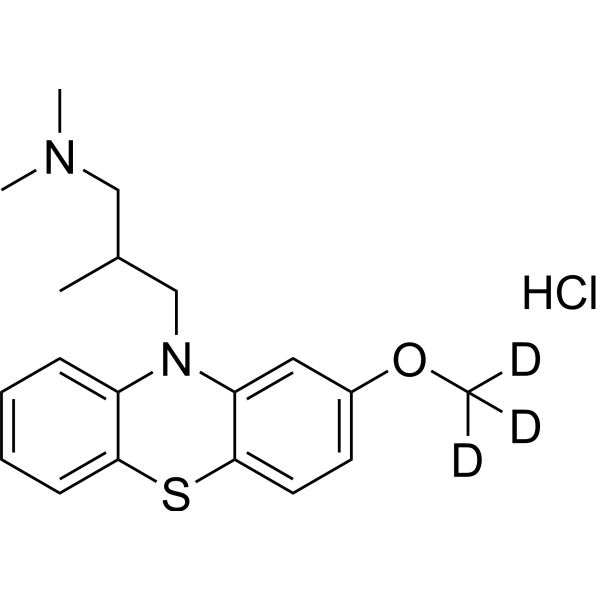
- HY-19489S1
-
|
|
|
(Rac)-Levomepromazine-d3 (hydrochloride) is a labelled racemic Methotrimeprazine, which is a phenothiazine which has antagonist actions at multiple neurotransmitter receptor sites, including dopaminergic, cholinergic, serotonin and histamine receptors[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-14608S
-
|
|
|
L-Glutamic acid- 13C is the 13C-labeled L-Glutamic acid. L-Glutamic acid acts as an excitatory transmitter and an agonist at all subtypes of glutamate receptors (metabotropic, kainate, NMDA, and AMPA). L-Glutamic acid shows a direct activating effect on the release of DA from dopaminergic terminals.
|
-

-
- HY-14608S7
-
|
|
|
L-Glutamic acid-d5 is the deuterium labeled L-Glutamic acid. L-Glutamic acid acts as an excitatory transmitter and an agonist at all subtypes of glutamate receptors (metabotropic, kainate, NMDA, and AMPA). L-Glutamic acid shows a direct activating effect on the release of DA from dopaminergic terminals.
|
-

-
- HY-14608S8
-
|
|
|
L-Glutamic acid-d3 is the deuterium labeled L-Glutamic acid. L-Glutamic acid acts as an excitatory transmitter and an agonist at all subtypes of glutamate receptors (metabotropic, kainate, NMDA, and AMPA). L-Glutamic acid shows a direct activating effect on the release of DA from dopaminergic terminals.
|
-

-
- HY-14608S5
-
|
|
|
L-Glutamic acid- 13C5 is the 13C-labeled L-Glutamic acid. L-Glutamic acid acts as an excitatory transmitter and an agonist at all subtypes of glutamate receptors (metabotropic, kainate, NMDA, and AMPA). L-Glutamic acid shows a direct activating effect on the release of DA from dopaminergic terminals.
|
-

-
- HY-14608S2
-
|
|
|
L-Glutamic acid- 15N is the 15N-labeled L-Glutamic acid. L-Glutamic acid acts as an excitatory transmitter and an agonist at all subtypes of glutamate receptors (metabotropic, kainate, NMDA, and AMPA). L-Glutamic acid shows a direct activating effect on the release of DA from dopaminergic terminals[1].
|
-

-
- HY-B0282S
-
|
|
|
Acetylcholine-d4 (chloride) is the deuterium labeled Acetylcholine chloride. Acetylcholine chloride (ACh chloride), a neurotransmitter, is a potent cholinergic agonist. Acetylcholine chloride is a modulator of the activity of dopaminergic (DAergic) neurons through the stimulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs)[1][2]. Acetylcholine chloride inhibits p53 mutant peptide aggregation in vitro[5].
|
-

-
- HY-14608S1
-
|
|
|
L-Glutamic acid-1- 13C is the 13C-labeled L-Glutamic acid. L-Glutamic acid acts as an excitatory transmitter and an agonist at all subtypes of glutamate receptors (metabotropic, kainate, NMDA, and AMPA). L-Glutamic acid shows a direct activating effect on the release of DA from dopaminergic terminals.
|
-

-
- HY-B0282S1
-
|
|
|
Acetylcholine-d9 (chloride) is the deuterium labeled Acetylcholine chloride. Acetylcholine chloride (ACh chloride), a neurotransmitter, is a potent cholinergic agonist. Acetylcholine chloride is a modulator of the activity of dopaminergic (DAergic) neurons through the stimulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs)[1][2]. Acetylcholine chloride inhibits p53 mutant peptide aggregation in vitro[5].
|
-

-
- HY-14608S6
-
|
|
|
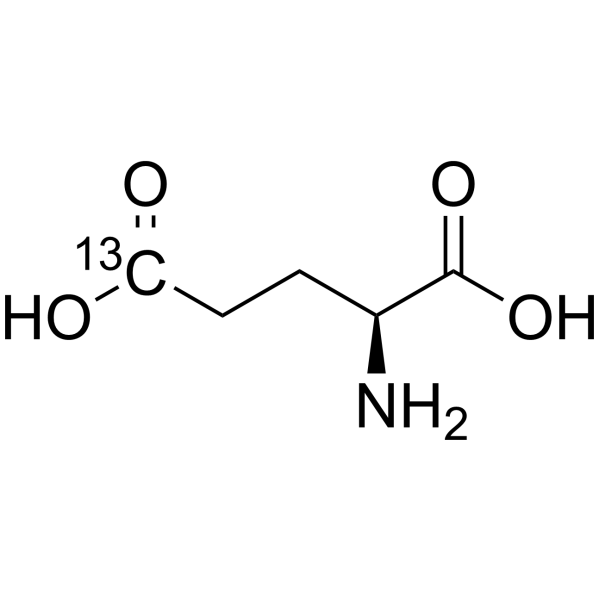
L-Glutamic acid-5- 13C is the 13C-labeled L-Glutamic acid. L-Glutamic acid acts as an excitatory transmitter and an agonist at all subtypes of glutamate receptors (metabotropic, kainate, NMDA, and AMPA). L-Glutamic acid shows a direct activating effect on the release of DA from dopaminergic terminals.
|
-

-
- HY-14608S3
-
|
|
|
L-Glutamic acid- 13C5, 15N is the 13C- and 15N-labeled L-Glutamic acid. L-Glutamic acid acts as an excitatory transmitter and an agonist at all subtypes of glutamate receptors (metabotropic, kainate, NMDA, and AMPA). L-Glutamic acid shows a direct activating effect on the release of DA from dopaminergic terminals.
|
-

-
- HY-14608S9
-
|
|
|
L-Glutamic acid- 15N,d5 is the deuterium and 15N-labeled L-Glutamic acid. L-Glutamic acid acts as an excitatory transmitter and an agonist at all subtypes of glutamate receptors (metabotropic, kainate, NMDA, and AMPA). L-Glutamic acid shows a direct activating effect on the release of DA from dopaminergic terminals.
|
-

-
- HY-14608S10
-
|
|
|
L-Glutamic acid- 13C2 is the 13C labeled L-Glutamic acid[1]. L-Glutamic acid acts as an excitatory transmitter and an agonist at all subtypes of glutamate receptors (metabotropic, kainate, NMDA, and AMPA). L-Glutamic acid shows a direct activating effect on the release of DA from dopaminergic terminals[2].
|
-

-
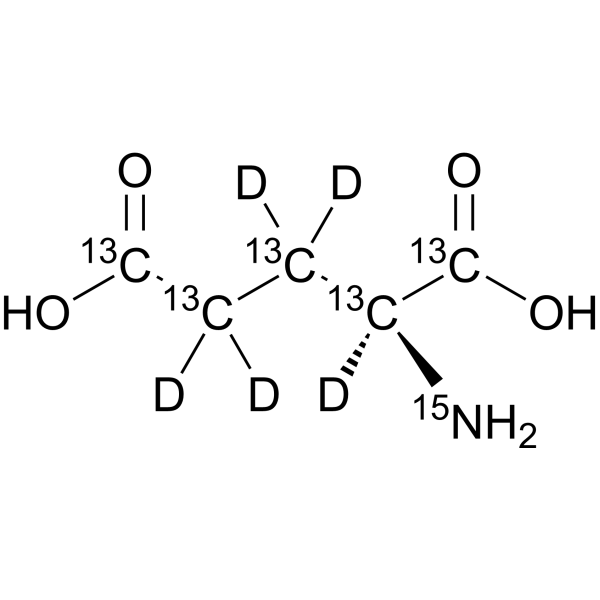
- HY-14608S4
-
|
|
|
L-Glutamic acid- 13C5, 15N,d5 is the deuterium, 13C-, and 15-labeled L-Glutamic acid. L-Glutamic acid acts as an excitatory transmitter and an agonist at all subtypes of glutamate receptors (metabotropic, kainate, NMDA, and AMPA). L-Glutamic acid shows a direct activating effect on the release of DA from dopaminergic terminals.
|
-

Your information is safe with us. * Required Fields.
Inquiry Information
- Product Name:
- Cat. No.:
- Quantity:
- MCE Japan Authorized Agent: