Search Result
Results for "
L-Phenylalanine-d
" in MedChemExpress (MCE) Product Catalog:
16
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Areas |
Chemical Structure |
-
- HY-N0215S12
-
|
|
Calcium Channel
iGluR
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
L-Phenylalanine-d5 is the deuterium labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-
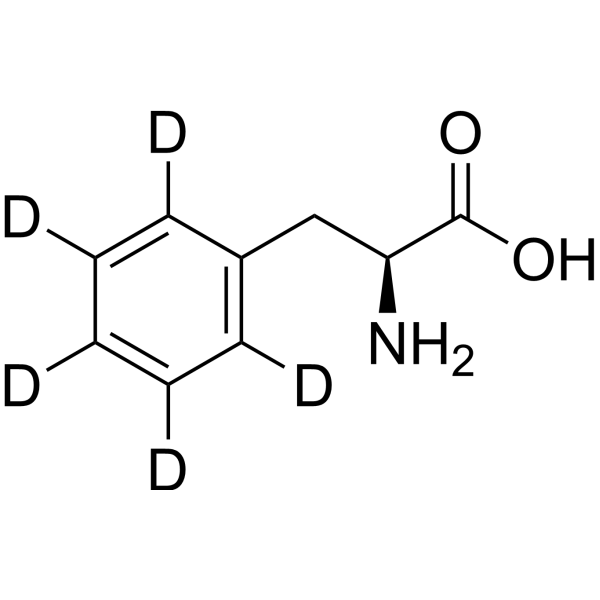
-
- HY-N0215S3
-
|
(S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid-d2
|
Calcium Channel
iGluR
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
L-Phenylalanine-d2 is the deuterium labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-
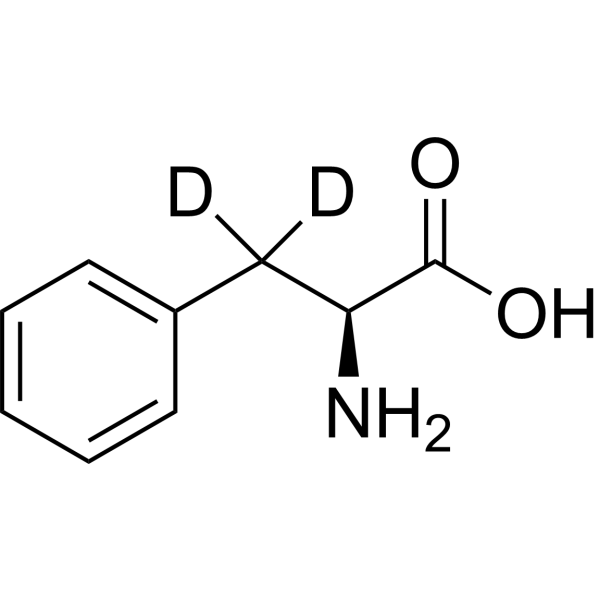
-
- HY-N0215S1
-
|
(S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid-d8
|
Calcium Channel
iGluR
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
L-Phenylalanine-d8 is the deuterium labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-
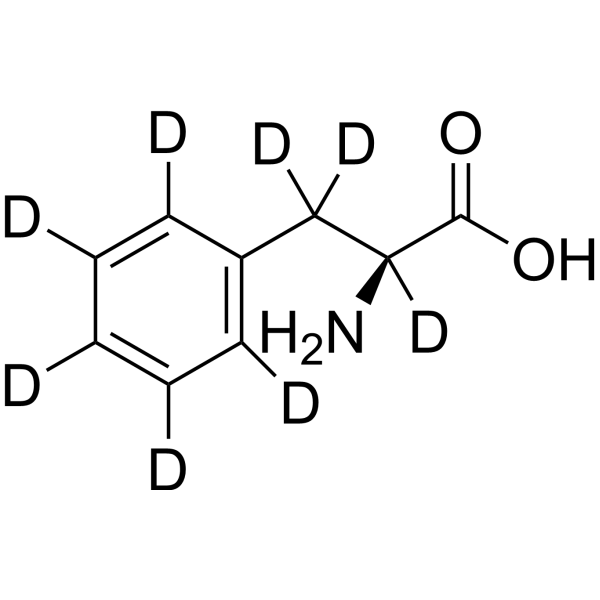
-
- HY-N0215S13
-
|
(S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid-d1
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Calcium Channel
iGluR
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
L-Phenylalanine-d is the deuterium labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-
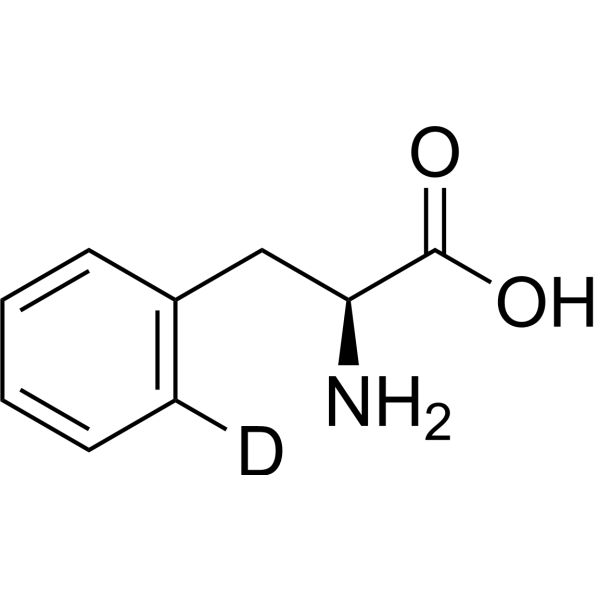
-
- HY-N0215S
-
|
(S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid-d7
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Calcium Channel
iGluR
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
L-Phenylalanine-d7 is the deuterium labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-
-
- HY-79096S1
-
-
-
- HY-79096S2
-
-
-
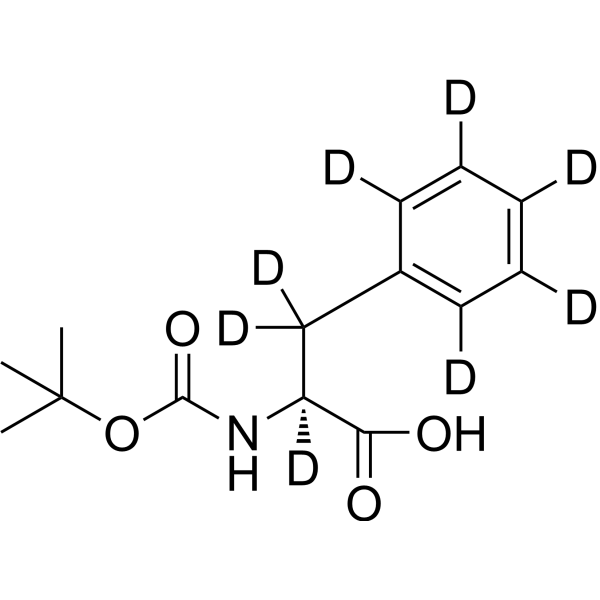
- HY-N0215S2
-
|
(S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid-13C
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Calcium Channel
iGluR
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
L-Phenylalanine- 13C is the 13C-labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-
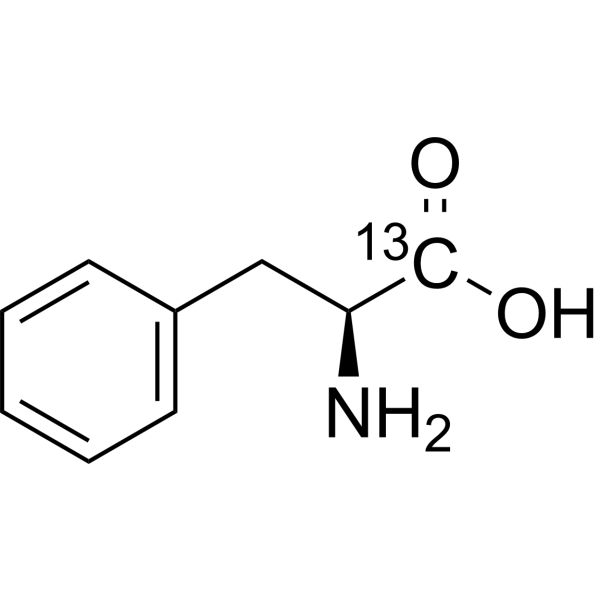
-
- HY-N0215S5
-
|
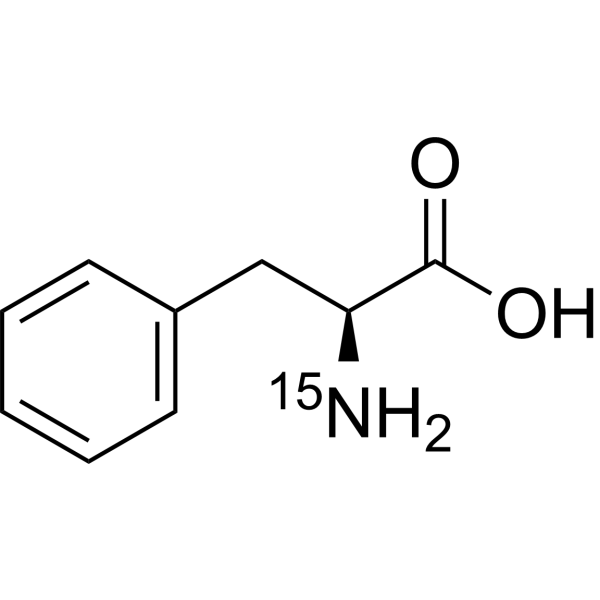
(S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid-15N
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Calcium Channel
iGluR
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
L-Phenylalanine- 15N is the 15N-labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-
-
- HY-N0215S10
-
|
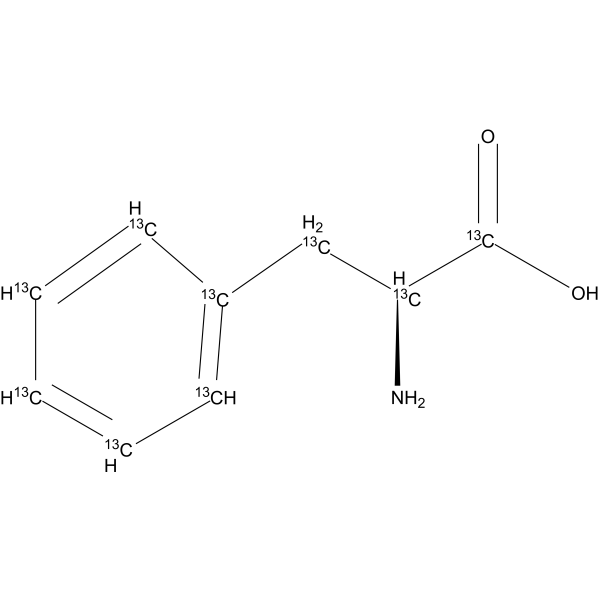
(S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid-13C9
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Calcium Channel
iGluR
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
L-Phenylalanine- 13C9 is the 13C-labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-
-
- HY-N0215S7
-
|
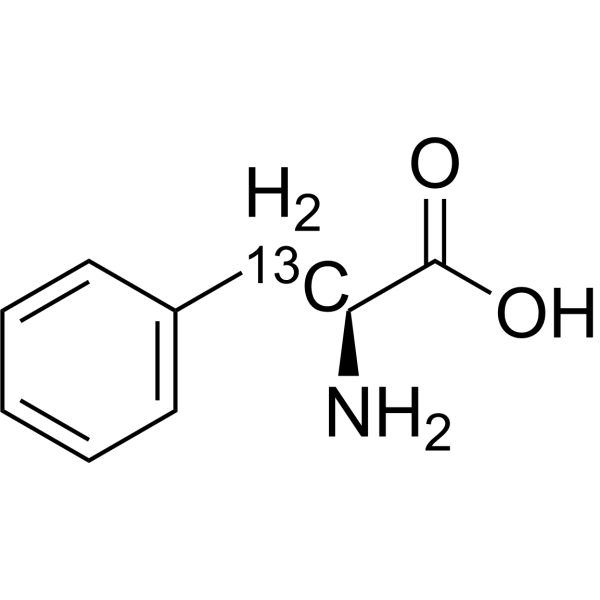
(S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid-3-13C
|
Calcium Channel
iGluR
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
L-Phenylalanine-3- 13C is the 13C-labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-
-
- HY-N0215S8
-
|
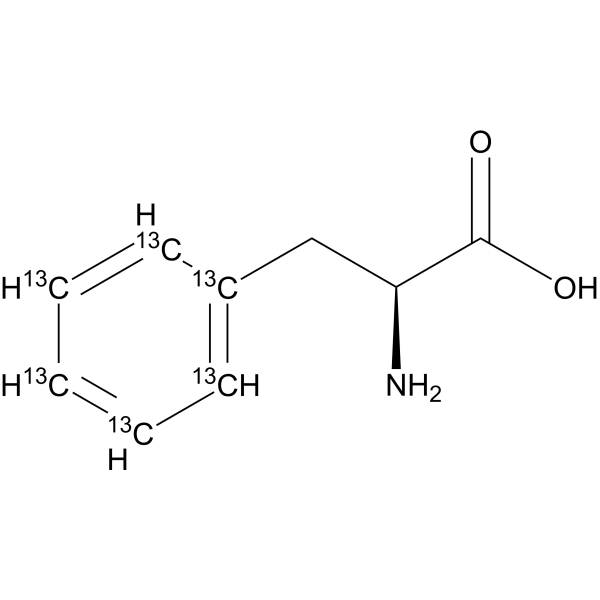
(S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid-13C6
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Calcium Channel
iGluR
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
L-Phenylalanine- 13C6 is the 13C-labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-
-
- HY-N0215S11
-
|
(S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid-13C9,15N
|
Calcium Channel
iGluR
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
L-Phenylalanine- 13C9, 15N is the 13C- and 15N-labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-
-
- HY-N0215S14
-
|
(S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid-15N,d8
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Calcium Channel
iGluR
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
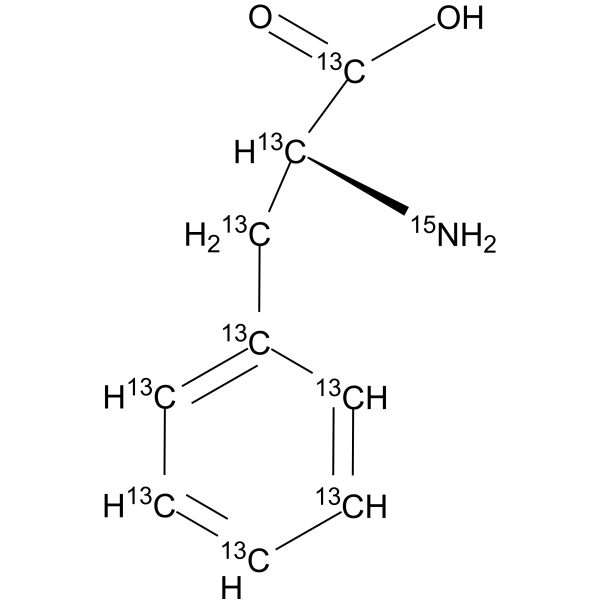
L-Phenylalanine- 15N,d8 is the deuterium and 15N-labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-
-
- HY-N0215S9
-
|
(S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid-13C9,15N,d8
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Calcium Channel
iGluR
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
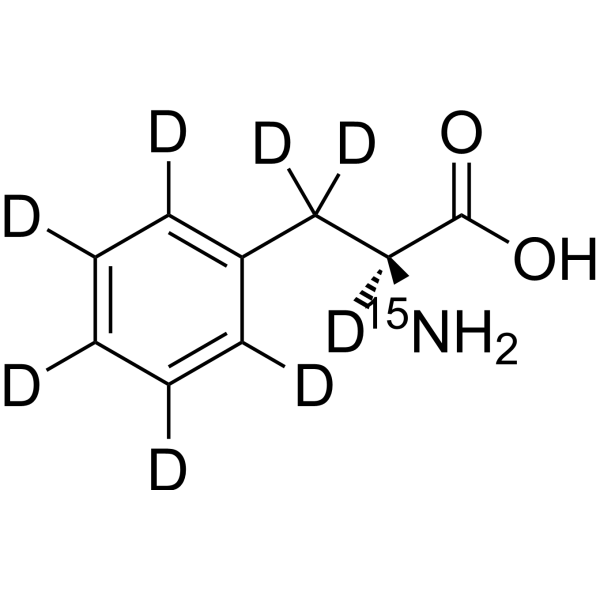
L-Phenylalanine- 13C9, 15N,d8 is the deuterium, 13C-, and 15-labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-
-
- HY-N0215
-
|
Phenylalanine
|
Calcium Channel
iGluR
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
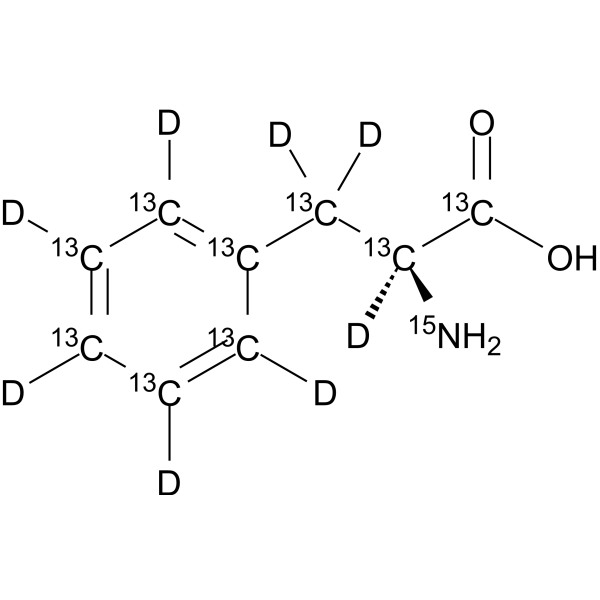
L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca + channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals .
|
-
-
- HY-N0215S6
-
|
2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid-d5 hydrochloride
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Calcium Channel
iGluR
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
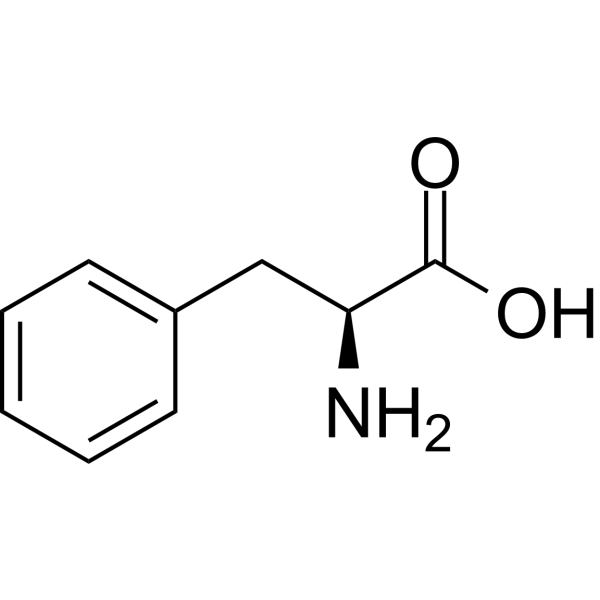
DL-Phenylalanine-d5 (hydrochloride) is the deuterium labeled DL-Phenylalanine hydrochloride. L-Phenylalanine hydrochloride is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine hydrochloride is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine hydrochloride is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine hydrochloride is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-
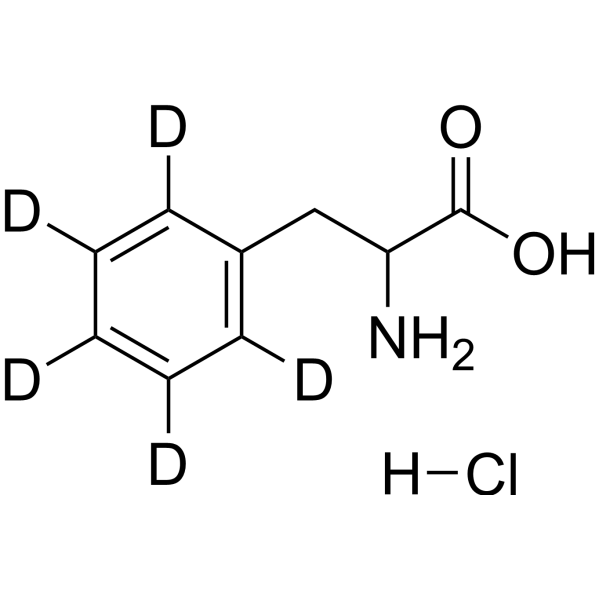
-
- HY-79908A
-
|
|
|
|
|
L-Phenylalanine benzyl ester (hydrochloride) is a phenylalanine derivative .
|
-
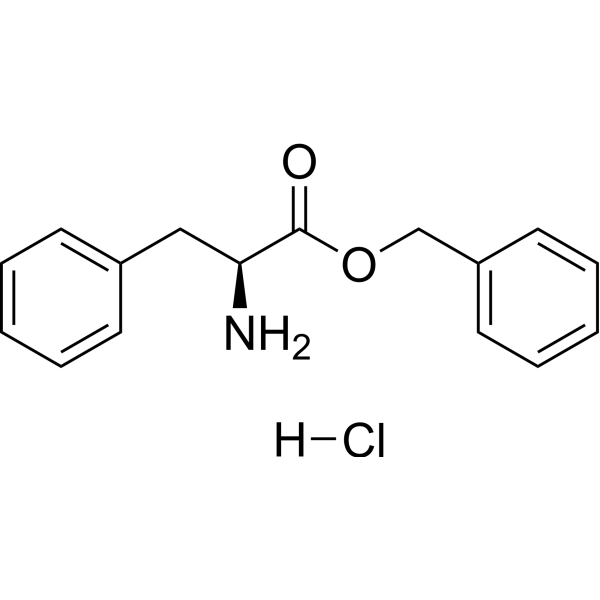
-
- HY-Y0068
-
|
N-AcetylPhenylalanine
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
N-Acetyl-L-phenylalanine (N-Acetylphenylalanine), the principal acylamino acid in Escherichia coli, is synthesized from L-phenylalanine and acetyl-CoA .
|
-
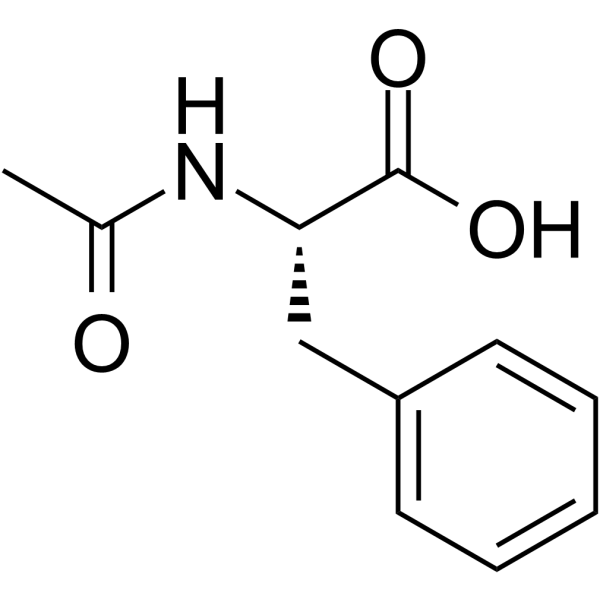
-
- HY-134230
-
|
L-α-aminooxy-β-phenylpropionic acid; AOPP
|
Others
|
Metabolic Disease
|
L-2-Aminooxy-3-phenylpropanoic acid is a potent inhibitor of L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase .
|
-
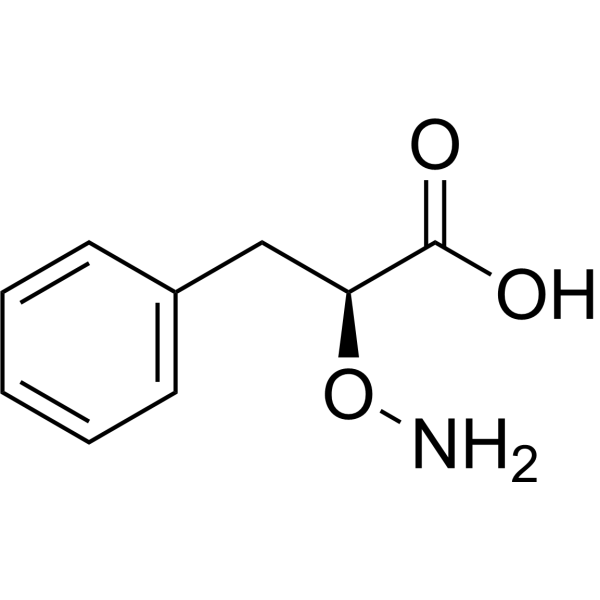
-
- HY-79909
-
|
|
|
|
|
L-Phenylalanine, N-[N-[(1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]-D-leucyl]-, phenylmethyl ester is a phenylalanine derivative .
|
-
![<em>L-Phenylalanine</em>, N-[N-[(1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]-D-leucyl]-, phenylmethyl ester](//file.medchemexpress.com/product_pic/hy-79909.gif)
-
- HY-134230A
-
|
L-α-aminooxy-β-phenylpropionic acid hydrobromide; AOPP hydrobromide
|
Others
|
Metabolic Disease
|
L-2-Aminooxy-3-phenylpropanoic acid hydrobromide is a potent inhibitor of L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase .
|
-
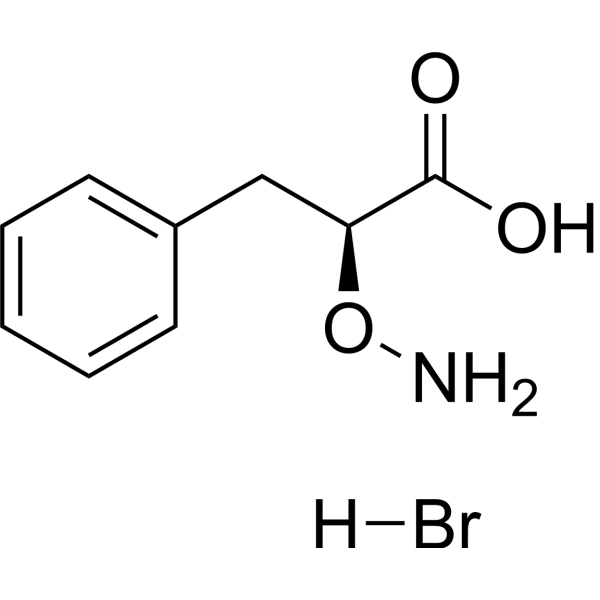
-
- HY-P3350
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
LS-BF1 is a stable and low toxic cationic antimicrobial peptide. LS-BF1 displays broad spectrum of antibacterial activity, including the challenging ESKAPE pathogens, by cell membrane disruptive mechanism. LS-BF1 shows good in vivo efficacy for elimination of bacteria in a mouse infection model[1].
|
-
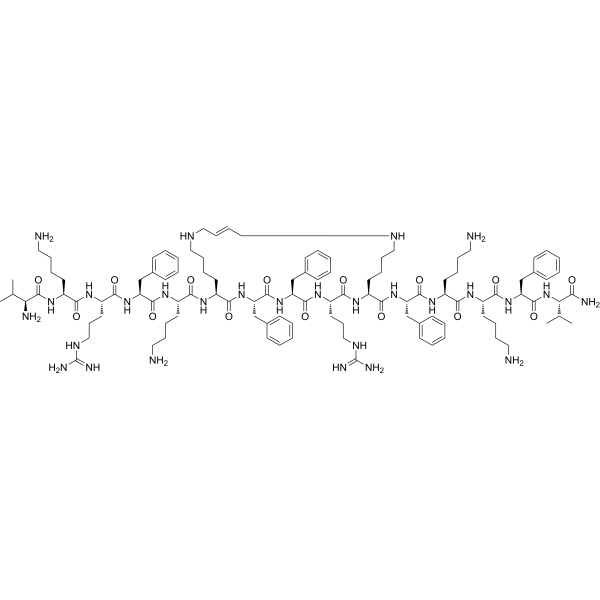
-
- HY-105168
-
|
|
Endothelin Receptor
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
TAK 044 is an antagonist of Endothelin Receptor. TAK 044 strongly inhibits ET-induced deterioration in various animal models. TAK 044 can be used in study ET-related diseases such as acute myocardial infarction,acute renal failure, acute hepatic malfunction, and subarachnoid hemorrhage .
|
-
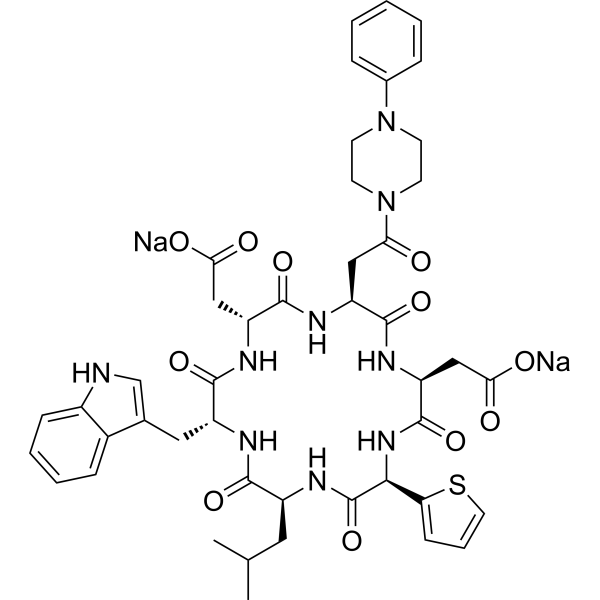
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Area |
-
- HY-P3350
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
LS-BF1 is a stable and low toxic cationic antimicrobial peptide. LS-BF1 displays broad spectrum of antibacterial activity, including the challenging ESKAPE pathogens, by cell membrane disruptive mechanism. LS-BF1 shows good in vivo efficacy for elimination of bacteria in a mouse infection model[1].
|
-
- HY-105168
-
|
|
Endothelin Receptor
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
TAK 044 is an antagonist of Endothelin Receptor. TAK 044 strongly inhibits ET-induced deterioration in various animal models. TAK 044 can be used in study ET-related diseases such as acute myocardial infarction,acute renal failure, acute hepatic malfunction, and subarachnoid hemorrhage .
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Category |
Target |
Chemical Structure |
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Chemical Structure |
-
- HY-N0215S12
-
|
|
|
L-Phenylalanine-d5 is the deuterium labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-

-
- HY-N0215S3
-
|
|
|
L-Phenylalanine-d2 is the deuterium labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-

-
- HY-N0215S1
-
|
|
|
L-Phenylalanine-d8 is the deuterium labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-

-
- HY-N0215S13
-
|
|
|
L-Phenylalanine-d is the deuterium labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-

-
- HY-N0215S
-
|
|
|
L-Phenylalanine-d7 is the deuterium labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-

-
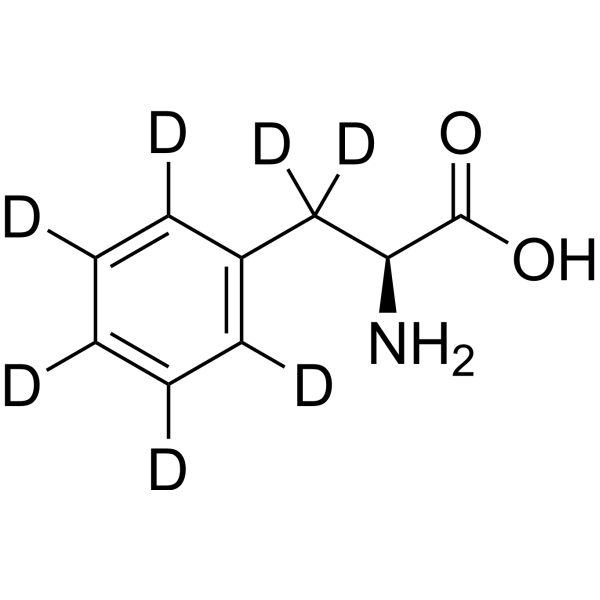
- HY-79096S1
-
|
|
|
BOC-L-phenylalanine-d5 is the deuterium labeled BOC-L-phenylalanine[1].
|
-

-
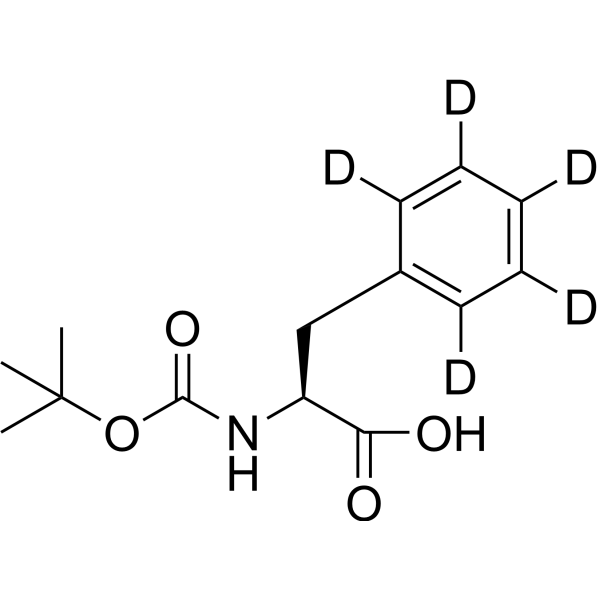
- HY-79096S2
-
|
|
|
BOC-L-phenylalanine-d8 is the deuterium labeled BOC-L-phenylalanine[1].
|
-

-
- HY-N0215S2
-
|
|
|
L-Phenylalanine- 13C is the 13C-labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-

-
- HY-N0215S5
-
|
|
|
L-Phenylalanine- 15N is the 15N-labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-

-
- HY-N0215S10
-
|
|
|
L-Phenylalanine- 13C9 is the 13C-labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-

-
- HY-N0215S7
-
|
|
|
L-Phenylalanine-3- 13C is the 13C-labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-

-
- HY-N0215S8
-
|
|
|
L-Phenylalanine- 13C6 is the 13C-labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-

-
- HY-N0215S11
-
|
|
|
L-Phenylalanine- 13C9, 15N is the 13C- and 15N-labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-

-
- HY-N0215S14
-
|
|
|
L-Phenylalanine- 15N,d8 is the deuterium and 15N-labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-

-
- HY-N0215S9
-
|
|
|
L-Phenylalanine- 13C9, 15N,d8 is the deuterium, 13C-, and 15-labeled L-Phenylalanine. L-Phenylalanine ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid) is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-

-
- HY-N0215S6
-
|
|
|
DL-Phenylalanine-d5 (hydrochloride) is the deuterium labeled DL-Phenylalanine hydrochloride. L-Phenylalanine hydrochloride is an essential amino acid isolated from Escherichia coli. L-Phenylalanine hydrochloride is a α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca+ channels antagonist with a Ki of 980 nM. L-phenylalanine hydrochloride is a competitive antagonist for the glycine- and glutamate-binding sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) (KB of 573 μM ) and non-NMDARs, respectively. L-Phenylalanine hydrochloride is widely used in the production of food flavors and pharmaceuticals[1][2][3][4].
|
-

Your information is safe with us. * Required Fields.
Inquiry Information
- Product Name:
- Cat. No.:
- Quantity:
- MCE Japan Authorized Agent:


























![<em>L-Phenylalanine</em>, N-[N-[(1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]-D-leucyl]-, phenylmethyl ester](http://file.medchemexpress.com/product_pic/hy-79909.gif)





