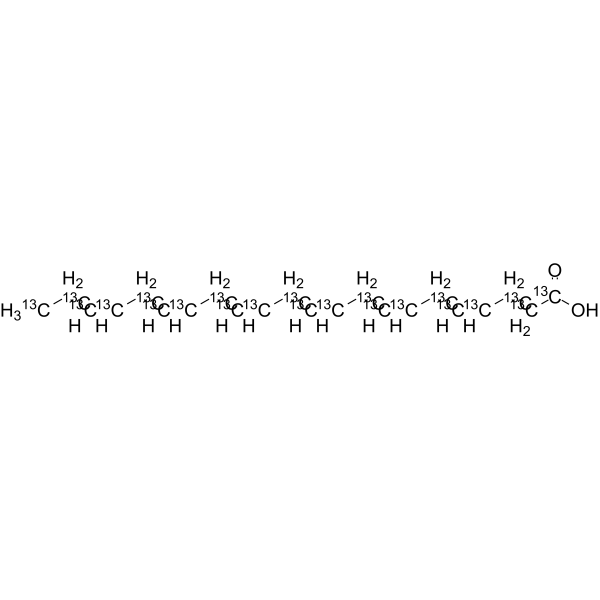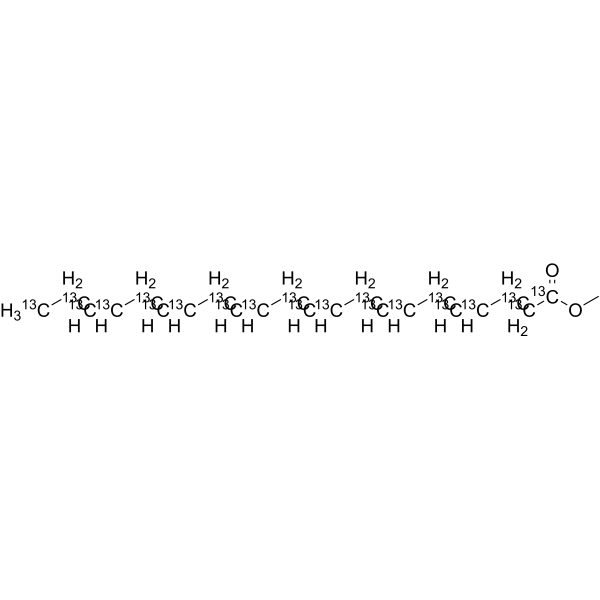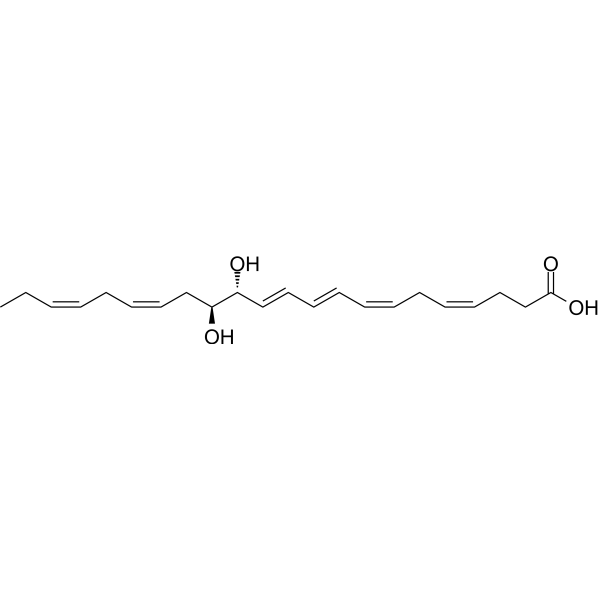Search Result
Results for "
docosahexaenoic
" in MedChemExpress (MCE) Product Catalog:
2
Biochemical Assay Reagents
11
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Areas |
Chemical Structure |
-
- HY-107343
-
|
Ethyl docosahexaenoate
|
Others
|
Neurological Disease
Metabolic Disease
|
|
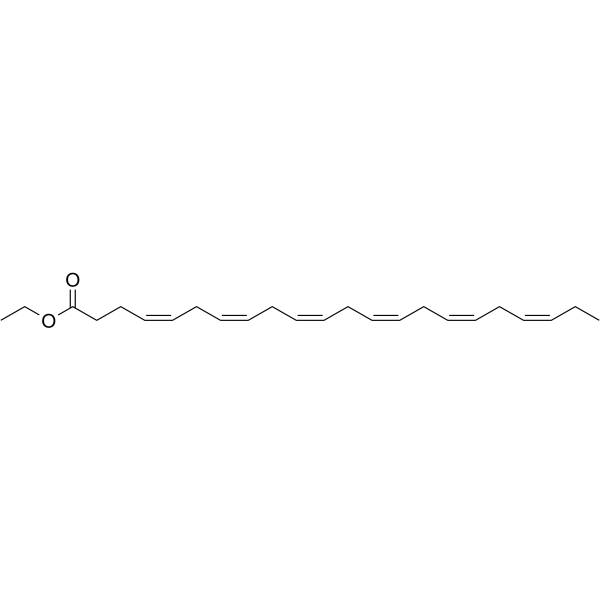
Docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester (Ethyl docosahexaenoate) is a 90% concentrated ethyl ester of docosahexaenoic acid manufactured from the microalgal oil. Docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester enhances 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neuronal damage by induction of lipid peroxidation in mouse striatum. Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is a key component of the cell membrane, and its peroxidation is inducible due to the double-bond chemical structure. Docosahexaenoic acid has neuroprotective effects .
|
-
-
- HY-101541
-
|
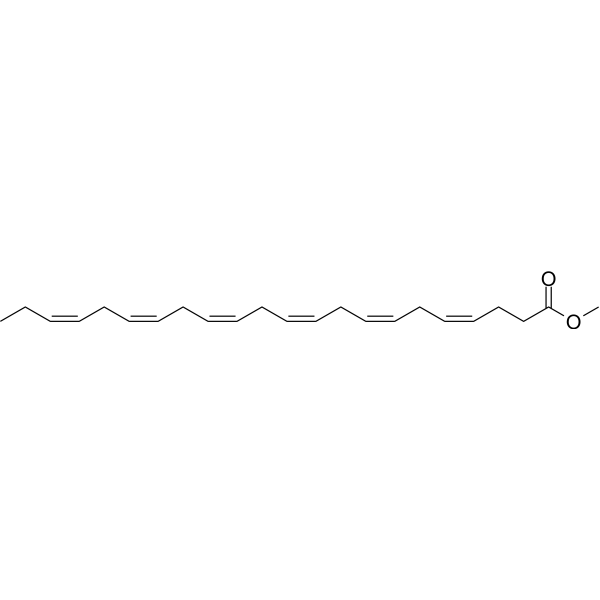
Methyl docosahexaenoate; all cis-DHA methyl ester
|
Others
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
Docosahexaenoic Acid methyl ester is a methylated docosahexaenoic acid analog which can be intercalated into membrane phospholipids without being oxidized or hydrolyzed.
|
-
-
- HY-B2167
-
|
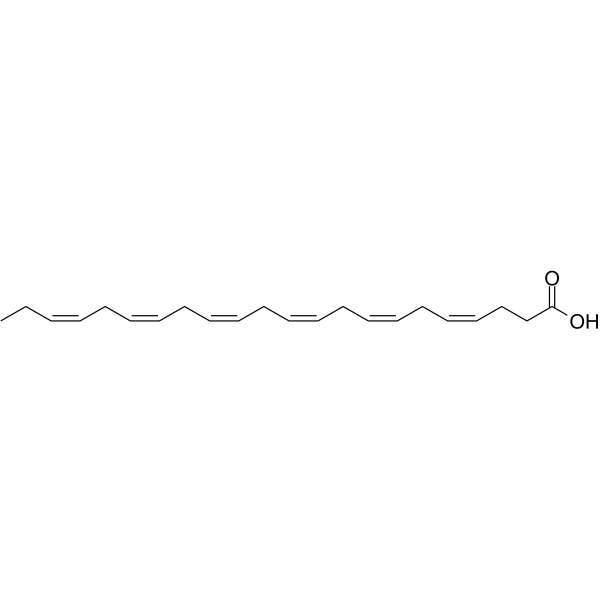
DHA; Cervonic acid
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) is an omega-3 fatty acid abundantly present brain and retina. It can be obtained directly from fish oil and maternal milk.
|
-
-
- HY-B2167S1
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
|
|
Docosahexaenoic acid- 13C22 is the 13C labeled Docosahexaenoic acid[1]. Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) is an omega-3 fatty acid abundantly present brain and retina. It can be obtained directly from fish oil and maternal milk[2][3][4][5][6].
|
-
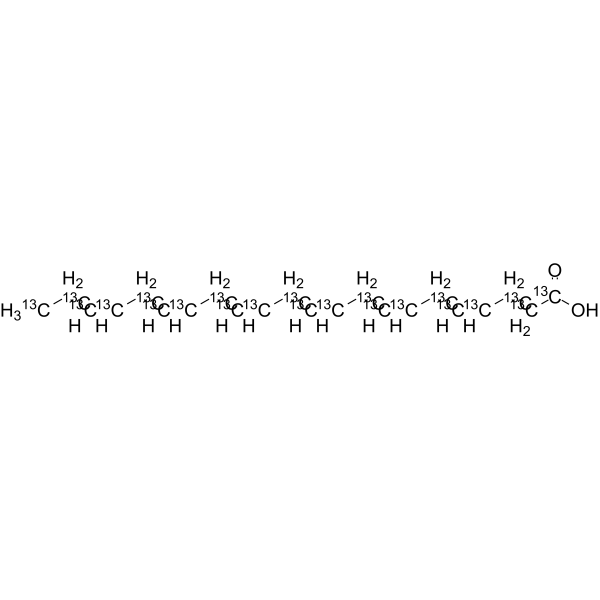
-
- HY-107343S
-
|
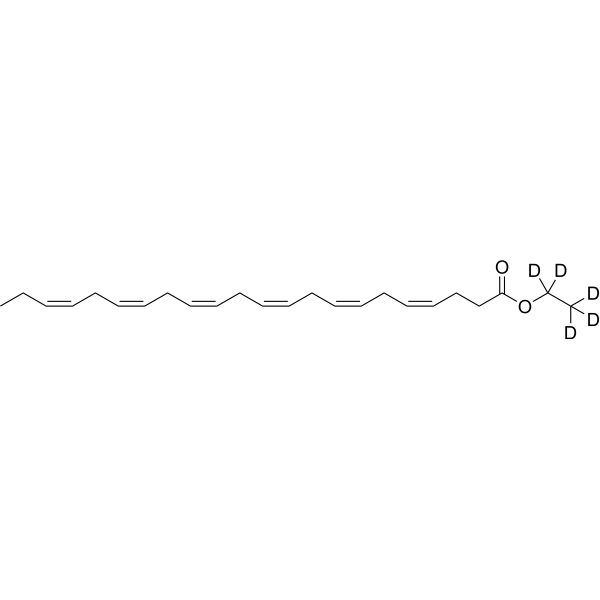
Ethyl docosahexaenoate-d5
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
|
Neurological Disease
Metabolic Disease
|
|
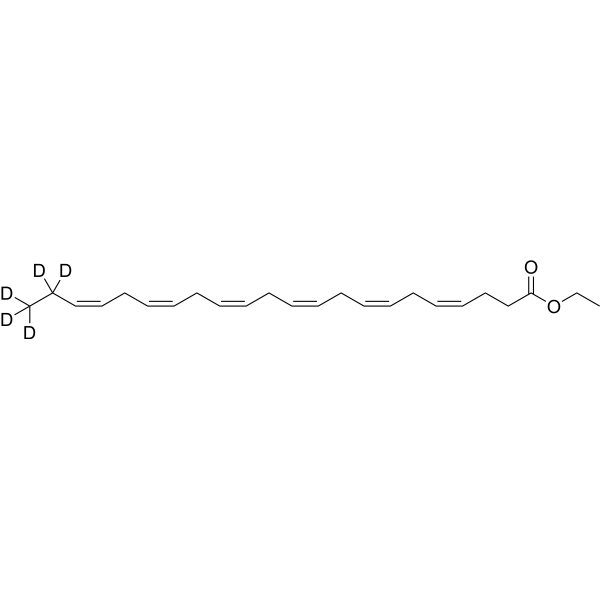
Docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester-d5 is the deuterium labeled Docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester. Docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester (Ethyl docosahexaenoate) is a 90% concentrated ethyl ester of docosahexaenoic acid manufactured from the microalgal oil. Docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester enhances 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neuronal damage by induction of lipid peroxidation in mouse striatum. Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is a key component of the cell membrane, and its peroxidation is inducible due to the double-bond chemical structure. Docosahexaenoic acid has neuroprotective effects[1][2].
|
-
-
- HY-107343S1
-
|
Ethyl docosahexaenoate-d5-1
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
|
Others
|
|
Docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester-d5-1 is the deuterium labeled Docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester. Docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester (Ethyl docosahexaenoate) is a 90% concentrated ethyl ester of docosahexaenoic acid manufactured from the microalgal oil. Docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester enhances 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neuronal damage by induction of lipid peroxidation in mouse striatum. Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is a key component of the cell membrane, and its peroxidation is inducible due to the double-bond chemical structure. Docosahexaenoic acid has neuroprotective effects[1][2][3].
|
-
-
- HY-B2167S
-
|
DHA-d5; Cervonic acid-d5
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
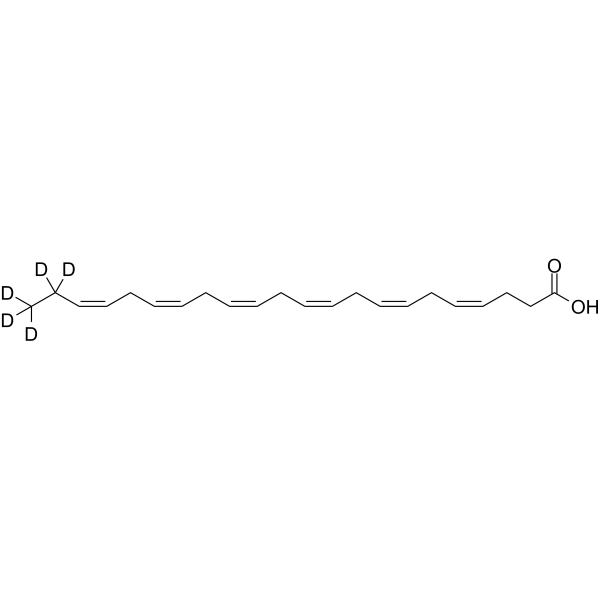
Docosahexaenoic acid-d5 is the deuterium labeled Docosahexaenoic Acid. Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) is an omega-3 fatty acid abundantly present brain and retina. It can be obtained directly from fish oil and maternal milk.
|
-
-
- HY-101541S
-
|
Methyl docosahexaenoate-d5; all cis-DHA methyl ester-d5
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
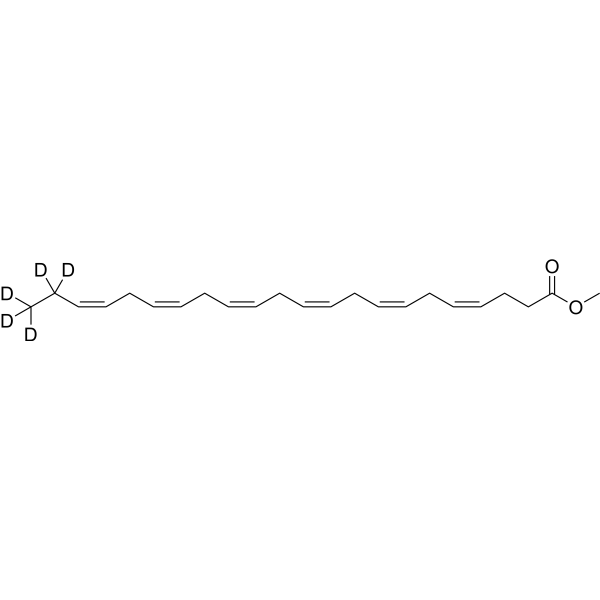
Docosahexaenoic acid-d5 methyl ester is the deuterium labeled Docosahexaenoic Acid methyl ester. Docosahexaenoic Acid methyl ester is a methylated docosahexaenoic acid analog which can be intercalated into membrane phospholipids without being oxidized or hydrolyzed[1][2].
|
-
-
- HY-101541S1
-
|
Methyl docosahexaenoate-13C22; all cis-DHA methyl ester-13C22
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
|
Others
|
|
Docosahexaenoic acid- 13C22 methyl ester is the 13C22 labeled Docosahexaenoic acid methyl ester (HY-101541)[1].
|
-
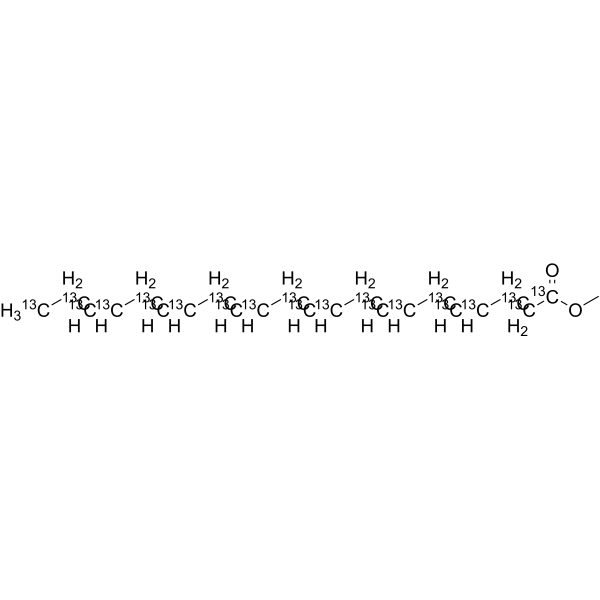
-
- HY-124019
-
-
-
- HY-130550
-
-

-
- HY-157690
-
|
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
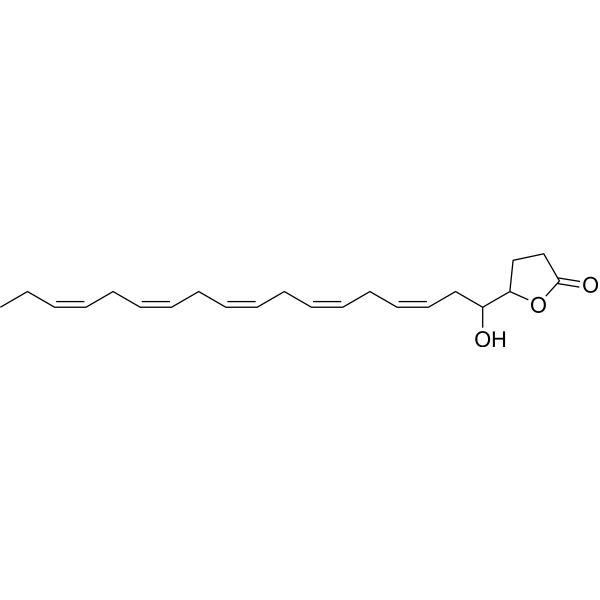
19(S),20(R)-EDP is an epoxidized metabolite of docosahexaenoic acid (HY-B2167) .
|
-
-
- HY-120178
-
|
|
Others
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
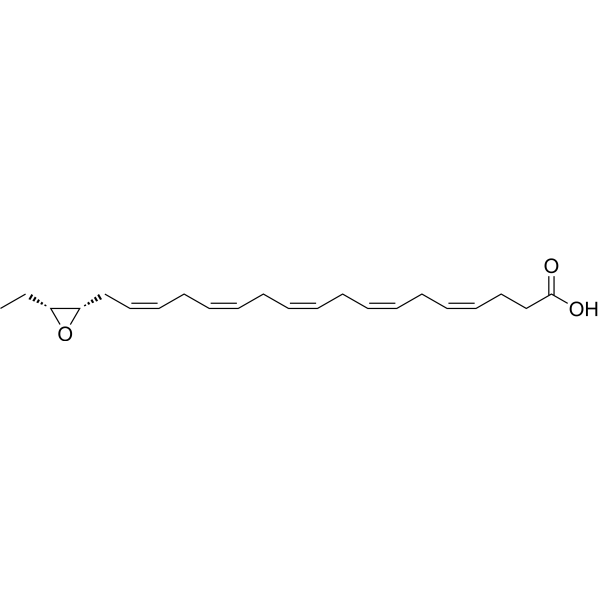
(±)7(8)-DiHDPA is a epoxygenase metabolite of docosahexaenoic acid (HY-B2167). (±)7(8)-DiHDPA inhibits platelet aggregation at concentrations below those affecting thromboxane synthesis .
|
-
-
- HY-120442
-
|
|
Others
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
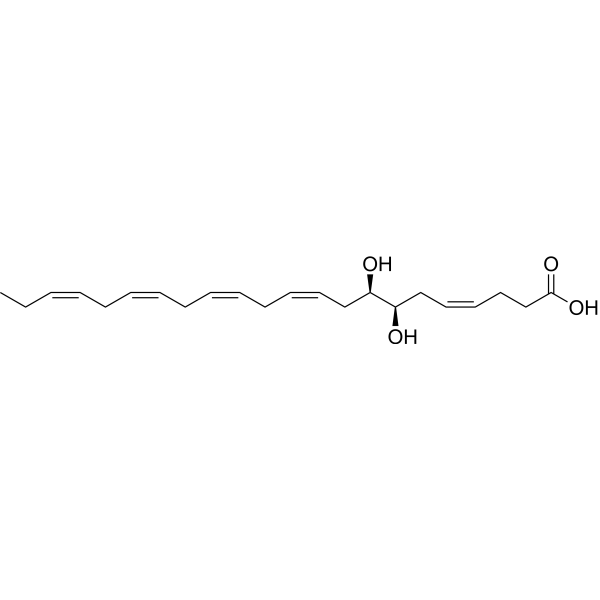
(±)16(17)-DiHDPA is a epoxygenase metabolite of docosahexaenoic acid (HY-B2167). (±)16(17)-DiHDPA inhibits platelet aggregation at concentrations below those affecting thromboxane synthesis .
|
-
-
- HY-157690A
-
|
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
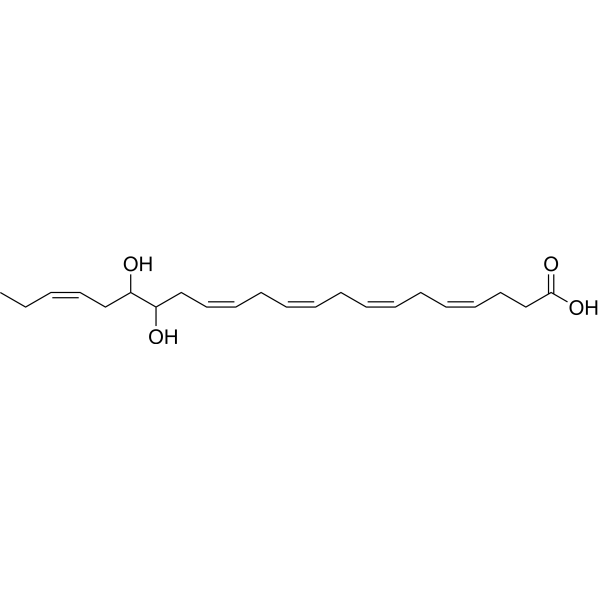
19(R),20(S)-EDP (compound 19(S),20(R)-2a) is an oxylipin and a metabolite of docosahexaenoic acid (HY-B2167) .
|
-

-
- HY-136540
-
|
RvD3
|
Others
|
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
Resolvin D3 (RvD3) is a docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) derived mediator. Resolvin D3 is dysregulated in arthritis and reduces arthritic inflammation .
|
-
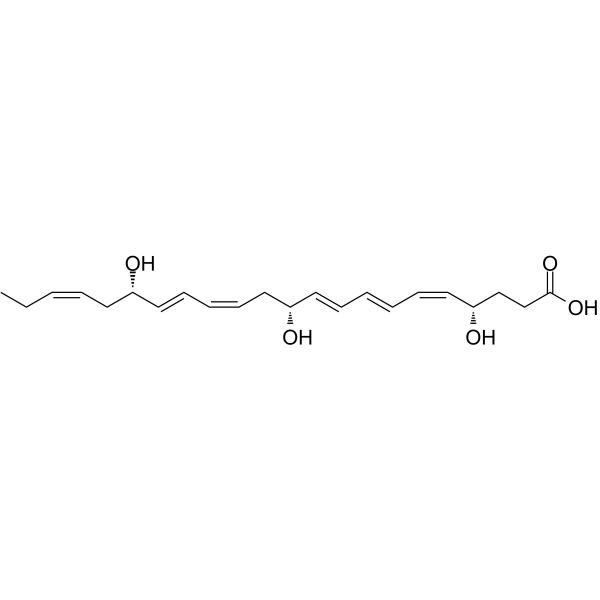
-
- HY-130419
-
|
13,14-EpDPE
|
Others
|
Cardiovascular Disease
Neurological Disease
|
|
(±)13(14)-EpDPA (13,14-EpDPE) is the product of the reaction of cytochrome P-450 epoxygenase with Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA).(±)13(14)-EpDPA has antihyperalgesic and vasorelaxative activities .
|
-
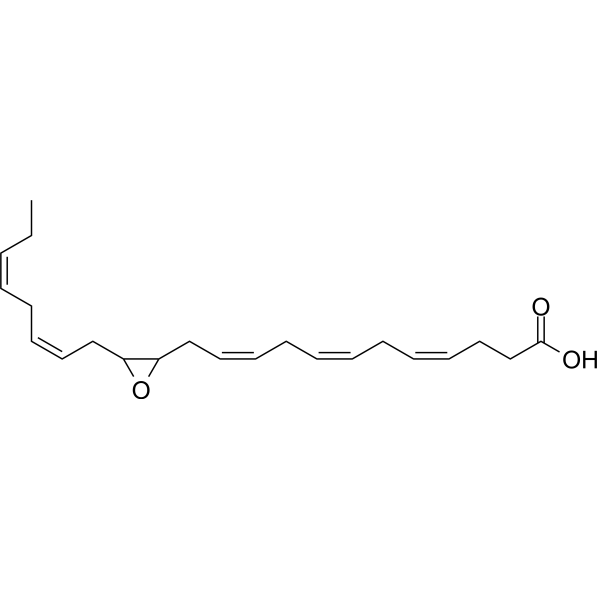
-
- HY-130413
-
|
Neuroprotectin D1; NPD1
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
Protectin D1, neuroprotectin D1 when generated by neural cells, is a member of a new family of bioactive products generated from docosahexaenoic acid. Protectin D1 is also a specialized pro-resolving mediator with potent pro-resolving and anti-inflammatory effects in vivo in several human disease models .
|
-
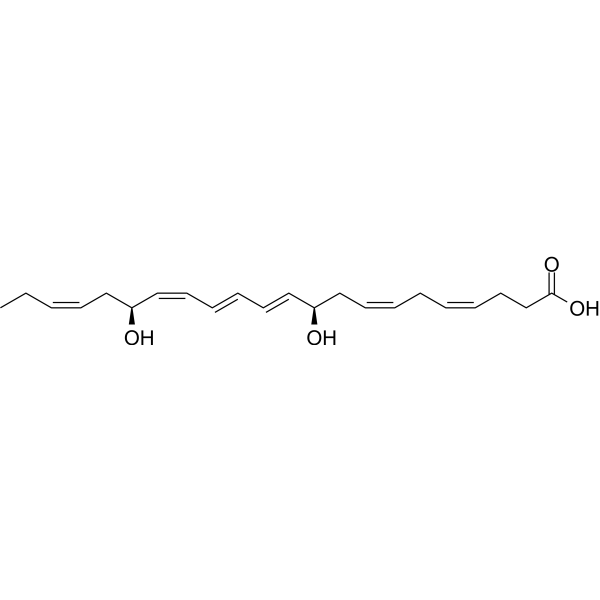
-
- HY-130239
-
|
14(S)-HDoHE
|
Drug Metabolite
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
14(S)-HDHA (14(S)-HDoHE) is an oxygenation product of Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). 14(S)-HDHA is a marker reflecting activation of a Docosahexaenoic acid carbon 14-lipoxygenation pathway .
|
-
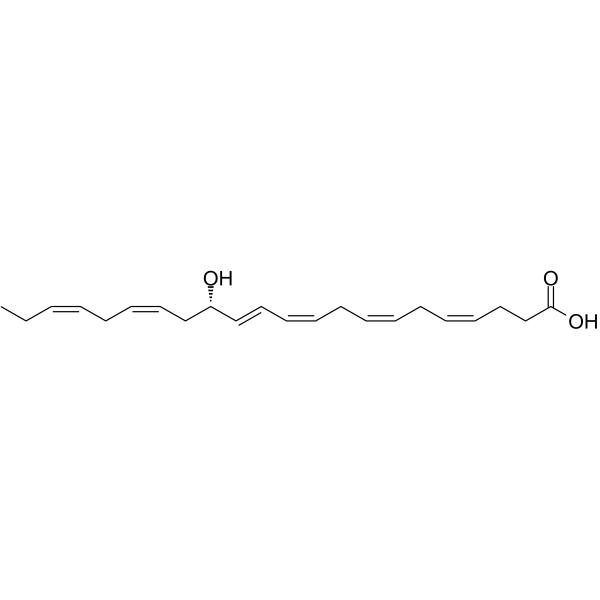
-
- HY-120312
-
|
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
PCTR3 is a Docosahexaenoic acid DHA (HY-B2167) derivative, which acts as a pro-resolving and tissue regeneration lipid mediator .
|
-
-
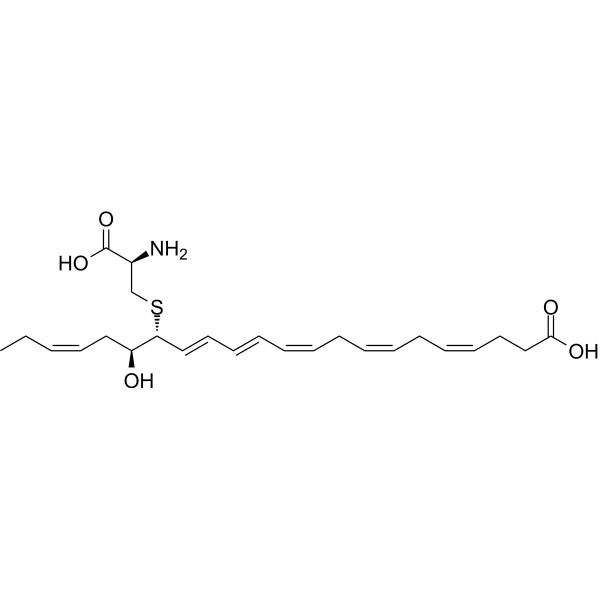
- HY-19886
-
|
|
|
|
|
F 16915, a Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA, HY-B2167) derivative, is a potent pro-agent of DHA. F 16915 can prevent heart failure-induced atrial fibrillation .
|
-
-
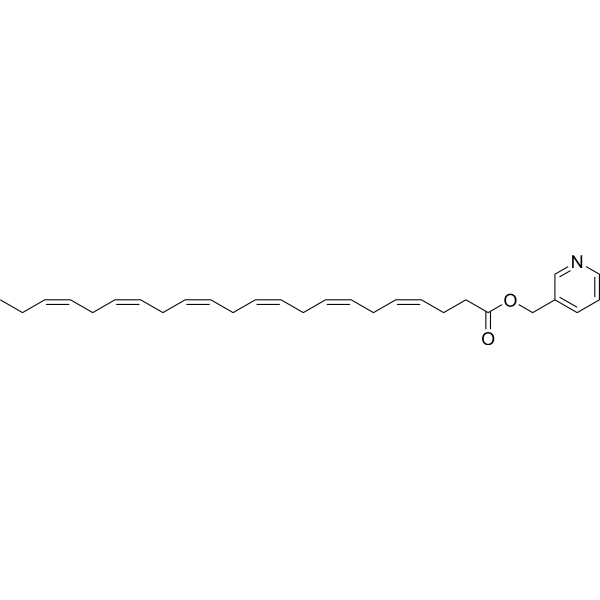
- HY-119684
-
|
|
Others
|
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
Maresin 2 is an anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving mediator from human macrophages. Maresins are a new family of anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving lipid mediators biosynthesized from docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) by macrophages .
|
-
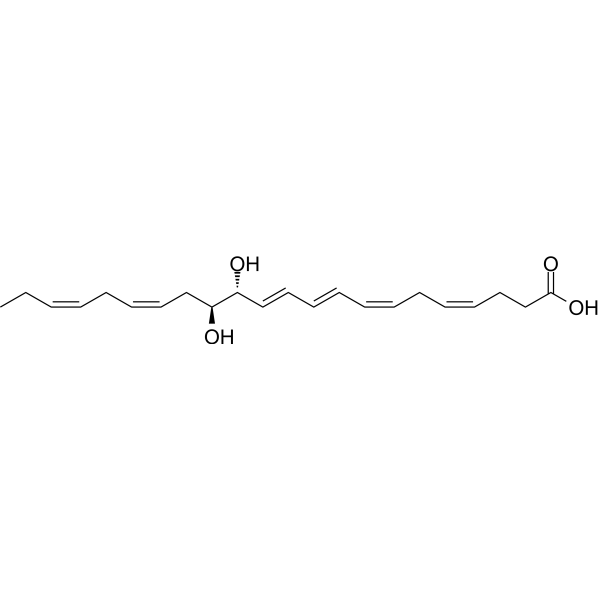
-
- HY-116663
-
|
(±)20-HDoHE
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
(±)20-HDHA ((±)20-HDoHE) is a racemic mixture and is an autoxidation product of Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). (±)20-HDHA is also formed by peroxidation process in human platelets and rat brain homogenate .
|
-
-
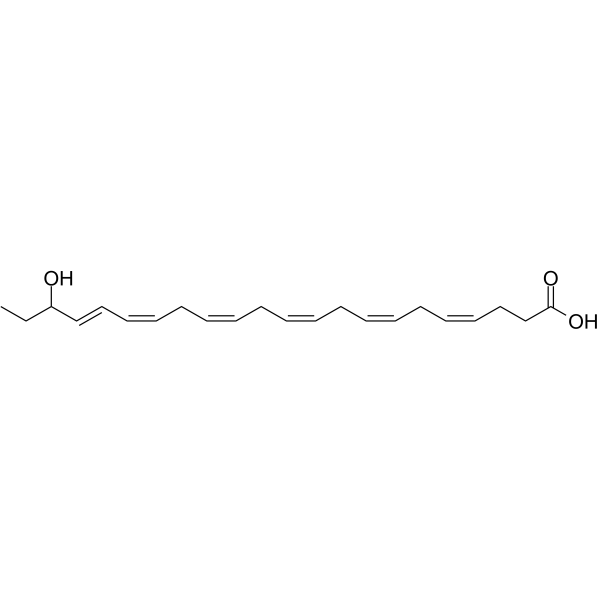
- HY-116429
-
|
|
Reactive Oxygen Species
|
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
Maresin 1, produced by human Mφs from endogenous docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and a specialized proresolving mediator, stimulates intracellular [Ca 2+] and secretion. Maresin 1 possesses anti-inflammatory activity .
|
-
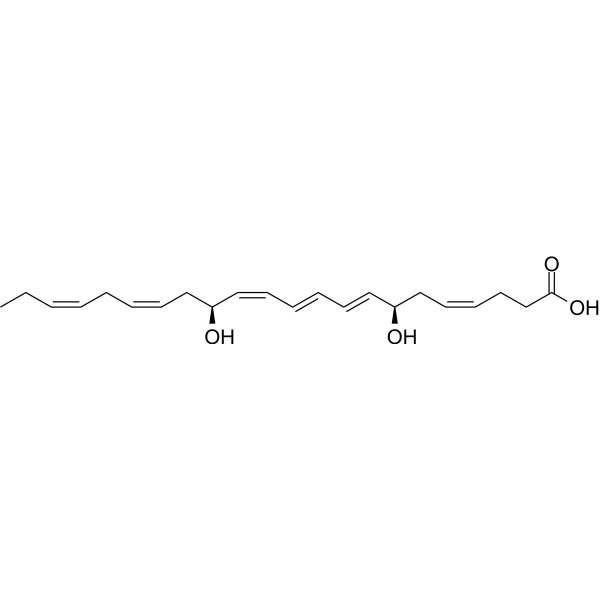
-
- HY-136540S
-
|
RvD3-d5
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
|
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
Resolvin D3-d5 is the deuterium labeled Resolvin D3. Resolvin D3 (RvD3) is a docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) derived mediator. Resolvin D3 is dysregulated in arthritis and reduces arthritic inflammation[1][2].
|
-
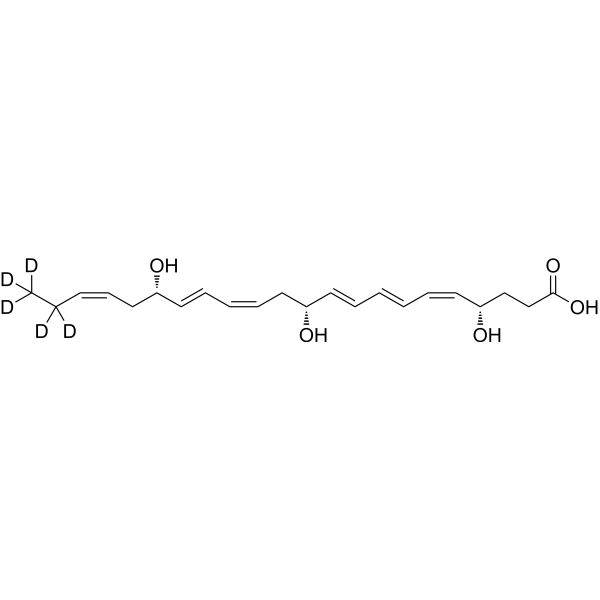
-
- HY-116429S
-
-
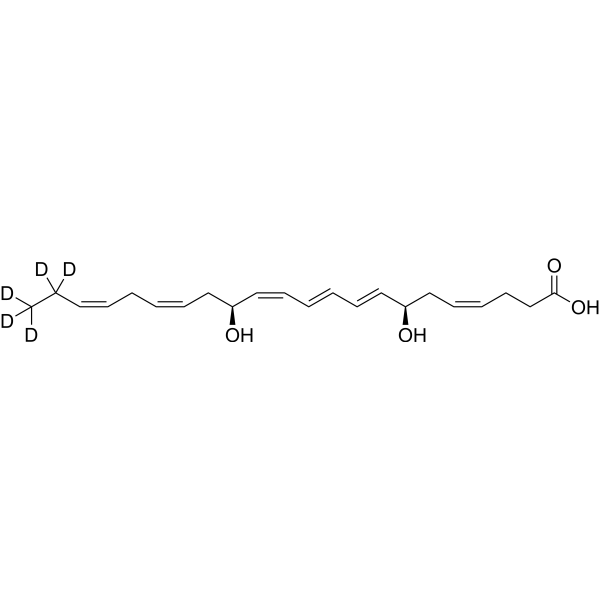
-
- HY-120255A
-
|
|
PPAR
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
17(S)-HDHA is a pro-resolving mediator (SPM). 17(S)-HDHA slightly activats PPARγ, PPARα and PPARδ .
|
-
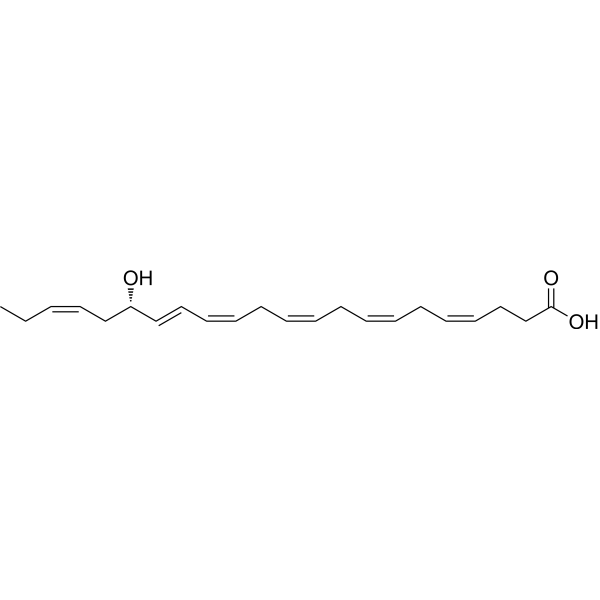
-
- HY-121636
-
|
RvD2
|
TRP Channel
|
Infection
Neurological Disease
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
Resolvin D2 is a metabolite of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), with anti-inflammatory, anti-infective activities. Resolvin D2 is a potent regulator of leukocytes and controls microbial sepsis. Resolvin D2 is a remarkably potent inhibitor of TRPV1 (IC50 = 0.1 nM) and TRPA1 (IC50 = 2 nM) in primary sensory neurons .
|
-
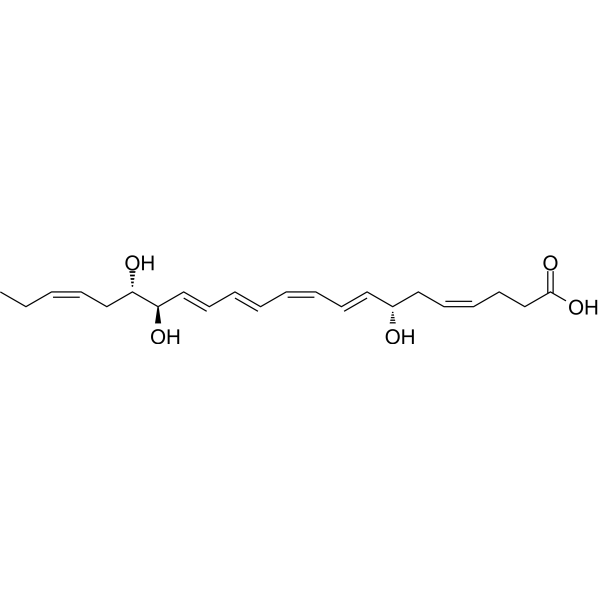
-
- HY-125527
-
|
RvD1
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
Resolvin D1 (RvD1), an endogenous pro-resolving mediator of inflammation, is derived from omega-3 docosahexaenoic acid during the resolution phase of acute inflammation. Resolvin D1 blocks proinflammatory neutrophil migration by regulating actin polymerization, reduces TNF-α–mediated inflammation in macrophages, and enhances phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by macrophages .
|
-
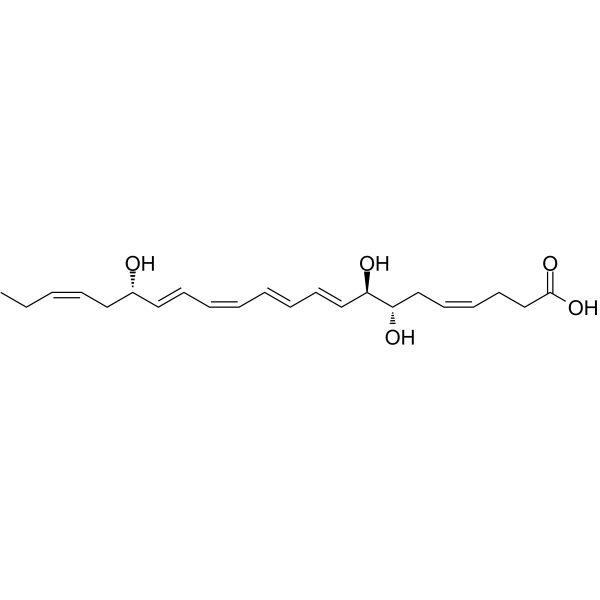
-
- HY-120255AS
-
-
-
- HY-116124
-
|
|
Lipoxygenase
|
Others
|
|
17(S)-HpDHA is the main 15-Lipoxygenase (LOX) isoenzyme: h15-LOX-1 and h15-LOX-2 and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). product. 17(S)-HpDHA negatively regulates epoxide synthesis via allosteric regulation. 17(S)-HpDHA also inhibits platelet aggregation with an EC50 of approximately 1 μM .
|
-

-
- HY-121636S
-
|
RvD2-d5
|
TRP Channel
|
Infection
Neurological Disease
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
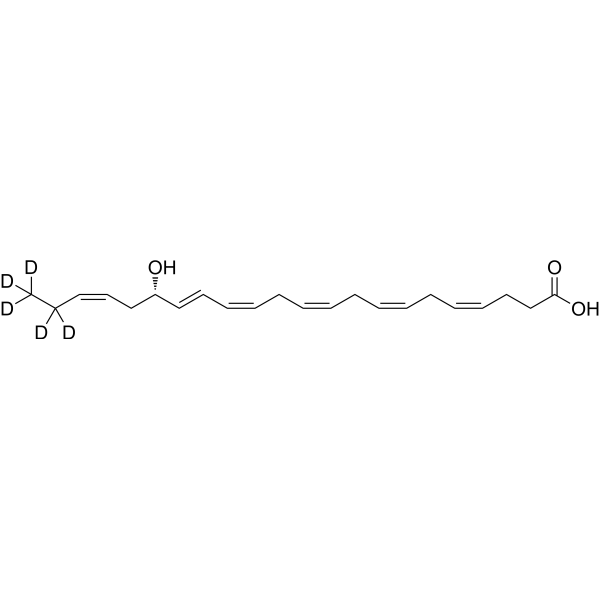
Resolvin D2-d5 is the deuterium labeled Resolvin D2. Resolvin D2 is a metabolite of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), with anti-inflammatory, anti-infective activities. Resolvin D2 is a potent regulator of leukocytes and controls microbial sepsis. Resolvin D2 is a remarkably potent inhibitor of TRPV1 (IC50 = 0.1 nM) and TRPA1 (IC50 = 2 nM) in primary sensory neurons[1][2][3].
|
-
-
- HY-125527S
-
|
RvD1-d5
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
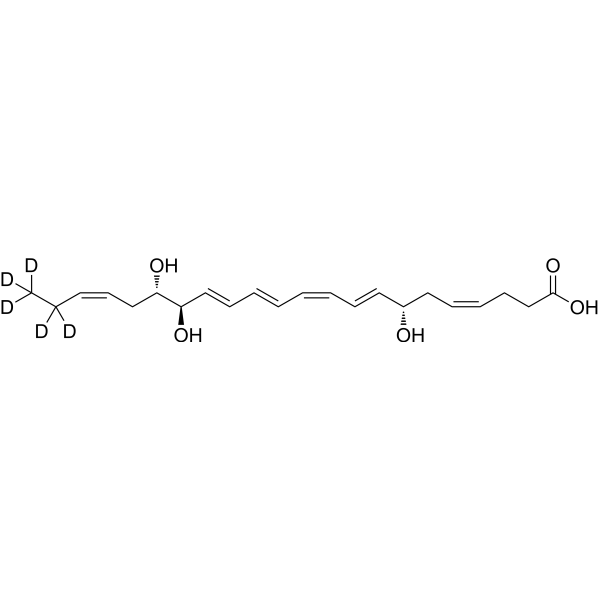
Resolvin D1-d5 is the deuterium labeled Resolvin D1. Resolvin D1 (RvD1), an endogenous pro-resolving mediator of inflammation, is derived from omega-3 docosahexaenoic acid during the resolution phase of acute inflammation. Resolvin D1 blocks proinflammatory neutrophil migration by regulating actin polymerization, reduces TNF-α–mediated inflammation in macrophages, and enhances phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by macrophages[1][2].
|
-
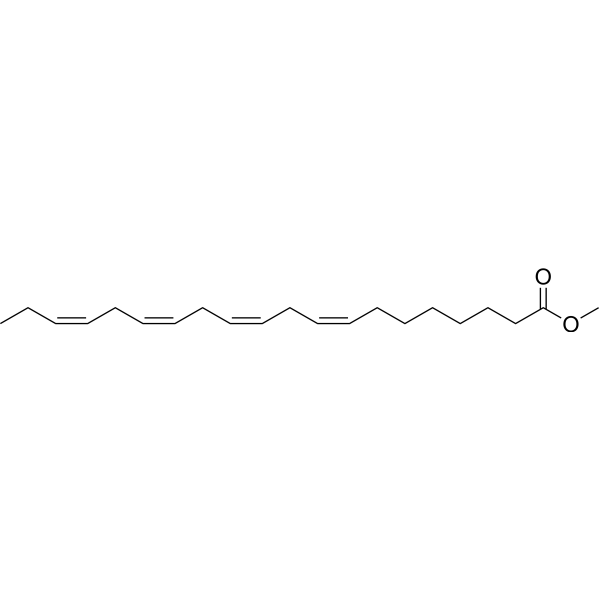
-
- HY-120978
-
|
ω-3 Arachidonic acid methyl ester; (all-Z)-8,11,14,17-Eicosatetraenoic acid methyl ester
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
omega-3 Arachidonic Acid methyl ester, mainly docosahexaenoic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid and α-Linoleic acid, represented by linoleic acid, is an essential dietary nutrient required for normal growth and development.Omega-3Methyl arachidonic acid is a rare fatty acid Omega-3Neutral fat-soluble form of arachidonic acid. Omega-3Fatty acids, as a group, were associated with reduced inflammation and autoimmune activity, as well as reduced thrombosis and platelet activation.
|
-
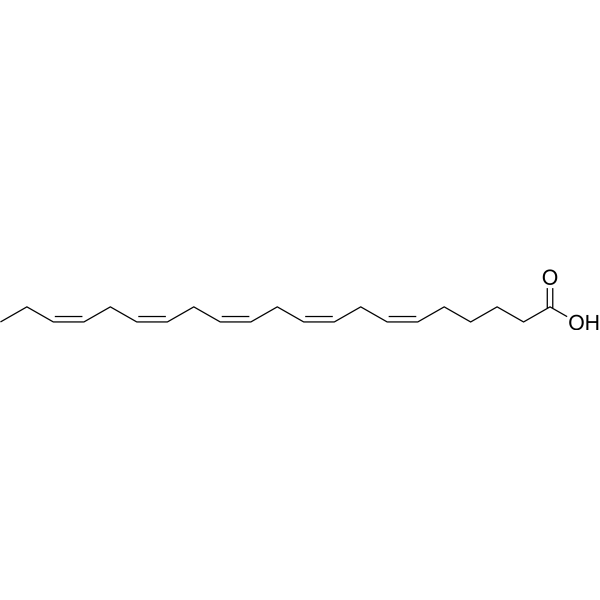
-
- HY-N7833
-
|
Heneicosapentaenoic acid
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Heneicosapentaenoic Acid (HPA) is a 21:5 omega-3 fatty acid found in trace amounts in the green alga B. pennata and in fish oils. Its chemical composition is similar to eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), except that a carbon is extended at the carboxy terminus, placing the first double bond at the δ6 position. HPA can be used to study the importance of double bond position in omega-3 fatty acids. It incorporates phospholipids and triacylglycerols in vivo with the same efficiency as EPA and docosahexaenoic acid, and exhibits a strong inhibitory effect on the synthesis of arachidonic acid from linoleic acid. HPA is a poor substrate for prostaglandin H synthase (PGHS) (cyclooxygenase) and 5-lipoxygenase, but retains the ability to rapidly inactivate PGHS.
|
-
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Type |
-
- HY-120978
-
|
ω-3 Arachidonic acid methyl ester; (all-Z)-8,11,14,17-Eicosatetraenoic acid methyl ester
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
omega-3 Arachidonic Acid methyl ester, mainly docosahexaenoic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid and α-Linoleic acid, represented by linoleic acid, is an essential dietary nutrient required for normal growth and development.Omega-3Methyl arachidonic acid is a rare fatty acid Omega-3Neutral fat-soluble form of arachidonic acid. Omega-3Fatty acids, as a group, were associated with reduced inflammation and autoimmune activity, as well as reduced thrombosis and platelet activation.
|
-
- HY-N7833
-
|
Heneicosapentaenoic acid
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Heneicosapentaenoic Acid (HPA) is a 21:5 omega-3 fatty acid found in trace amounts in the green alga B. pennata and in fish oils. Its chemical composition is similar to eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), except that a carbon is extended at the carboxy terminus, placing the first double bond at the δ6 position. HPA can be used to study the importance of double bond position in omega-3 fatty acids. It incorporates phospholipids and triacylglycerols in vivo with the same efficiency as EPA and docosahexaenoic acid, and exhibits a strong inhibitory effect on the synthesis of arachidonic acid from linoleic acid. HPA is a poor substrate for prostaglandin H synthase (PGHS) (cyclooxygenase) and 5-lipoxygenase, but retains the ability to rapidly inactivate PGHS.
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Category |
Target |
Chemical Structure |
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Chemical Structure |
-
- HY-B2167S
-
|
|
|
Docosahexaenoic acid-d5 is the deuterium labeled Docosahexaenoic Acid. Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) is an omega-3 fatty acid abundantly present brain and retina. It can be obtained directly from fish oil and maternal milk.
|
-

-
- HY-B2167S1
-
|
|
|
Docosahexaenoic acid- 13C22 is the 13C labeled Docosahexaenoic acid[1]. Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) is an omega-3 fatty acid abundantly present brain and retina. It can be obtained directly from fish oil and maternal milk[2][3][4][5][6].
|
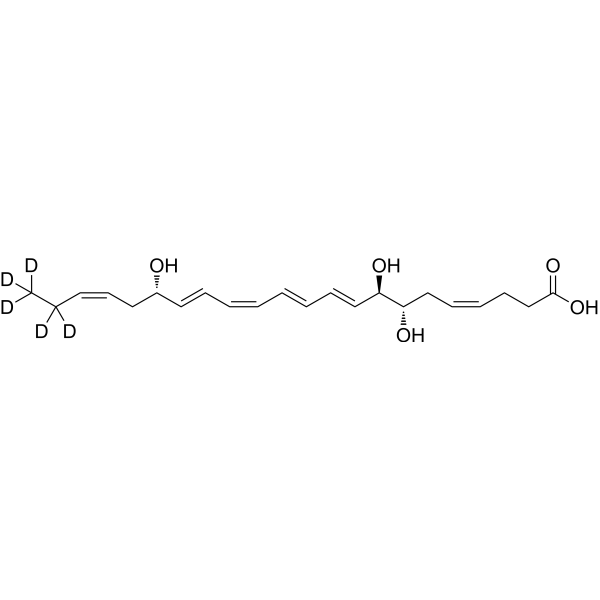
-
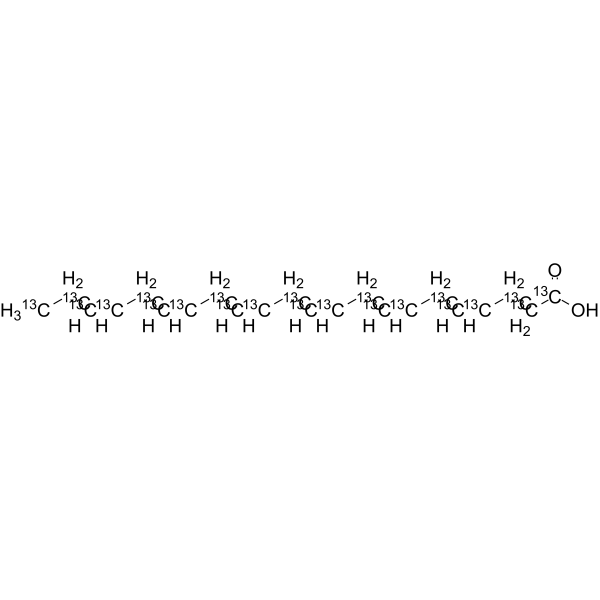
-
- HY-107343S
-
|
|
|
Docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester-d5 is the deuterium labeled Docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester. Docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester (Ethyl docosahexaenoate) is a 90% concentrated ethyl ester of docosahexaenoic acid manufactured from the microalgal oil. Docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester enhances 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neuronal damage by induction of lipid peroxidation in mouse striatum. Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is a key component of the cell membrane, and its peroxidation is inducible due to the double-bond chemical structure. Docosahexaenoic acid has neuroprotective effects[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-107343S1
-
|
|
|
Docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester-d5-1 is the deuterium labeled Docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester. Docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester (Ethyl docosahexaenoate) is a 90% concentrated ethyl ester of docosahexaenoic acid manufactured from the microalgal oil. Docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester enhances 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neuronal damage by induction of lipid peroxidation in mouse striatum. Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is a key component of the cell membrane, and its peroxidation is inducible due to the double-bond chemical structure. Docosahexaenoic acid has neuroprotective effects[1][2][3].
|
-

-
- HY-101541S
-
|
|
|
Docosahexaenoic acid-d5 methyl ester is the deuterium labeled Docosahexaenoic Acid methyl ester. Docosahexaenoic Acid methyl ester is a methylated docosahexaenoic acid analog which can be intercalated into membrane phospholipids without being oxidized or hydrolyzed[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-101541S1
-
|
|
|
Docosahexaenoic acid- 13C22 methyl ester is the 13C22 labeled Docosahexaenoic acid methyl ester (HY-101541)[1].
|
-
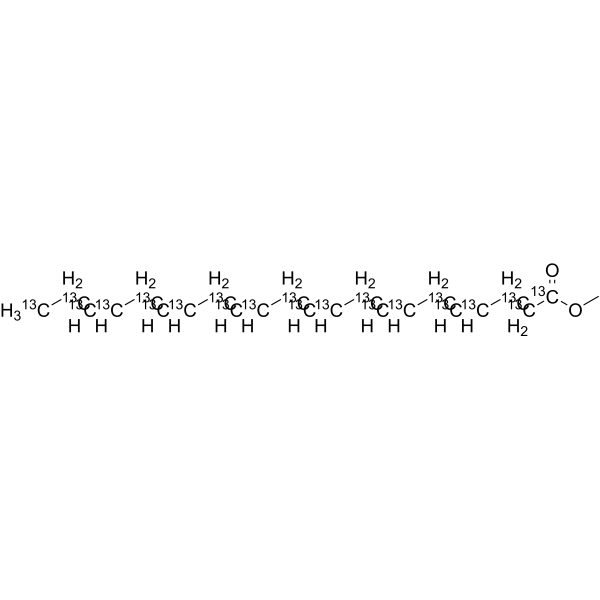
-
- HY-136540S
-
|
|
|
Resolvin D3-d5 is the deuterium labeled Resolvin D3. Resolvin D3 (RvD3) is a docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) derived mediator. Resolvin D3 is dysregulated in arthritis and reduces arthritic inflammation[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-116429S
-
|
|
|
Maresin 1-d5 is the deuterium labeled Maresin 1. Maresin 1, produced by human Mφs from endogenous docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and a specialized proresolving mediator, stimulates intracellular [Ca2+] and secretion. Maresin 1 possesses anti-inflammatory activity[1][2][3].
|
-

-
- HY-120255AS
-
|
|
|
17(S)-HDHA-d5 is the deuterium labeled 17(S)-HDHA[1].
|
-

-
- HY-121636S
-
|
|
|
Resolvin D2-d5 is the deuterium labeled Resolvin D2. Resolvin D2 is a metabolite of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), with anti-inflammatory, anti-infective activities. Resolvin D2 is a potent regulator of leukocytes and controls microbial sepsis. Resolvin D2 is a remarkably potent inhibitor of TRPV1 (IC50 = 0.1 nM) and TRPA1 (IC50 = 2 nM) in primary sensory neurons[1][2][3].
|
-

-
- HY-125527S
-
|
|
|
Resolvin D1-d5 is the deuterium labeled Resolvin D1. Resolvin D1 (RvD1), an endogenous pro-resolving mediator of inflammation, is derived from omega-3 docosahexaenoic acid during the resolution phase of acute inflammation. Resolvin D1 blocks proinflammatory neutrophil migration by regulating actin polymerization, reduces TNF-α–mediated inflammation in macrophages, and enhances phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by macrophages[1][2].
|
-

Your information is safe with us. * Required Fields.
Inquiry Information
- Product Name:
- Cat. No.:
- Quantity:
- MCE Japan Authorized Agent: