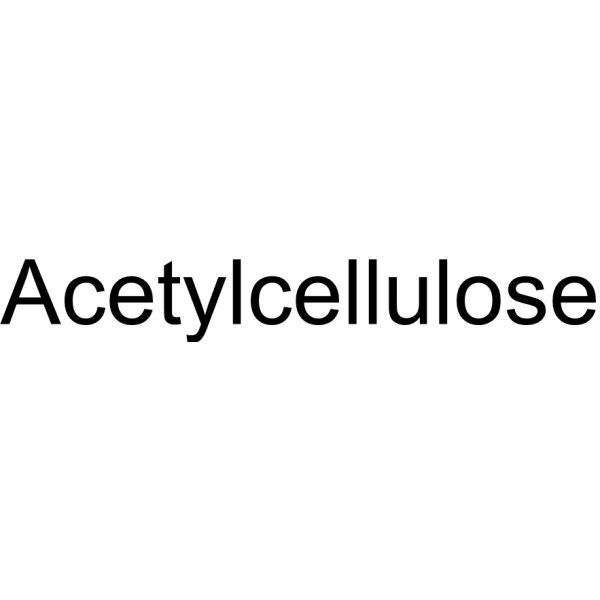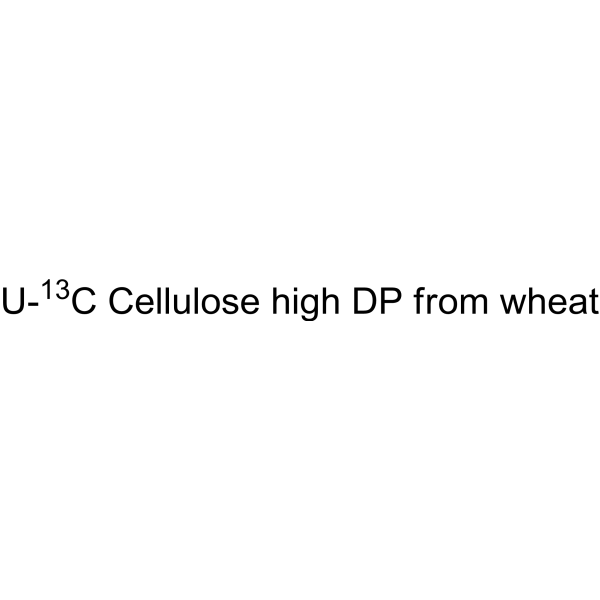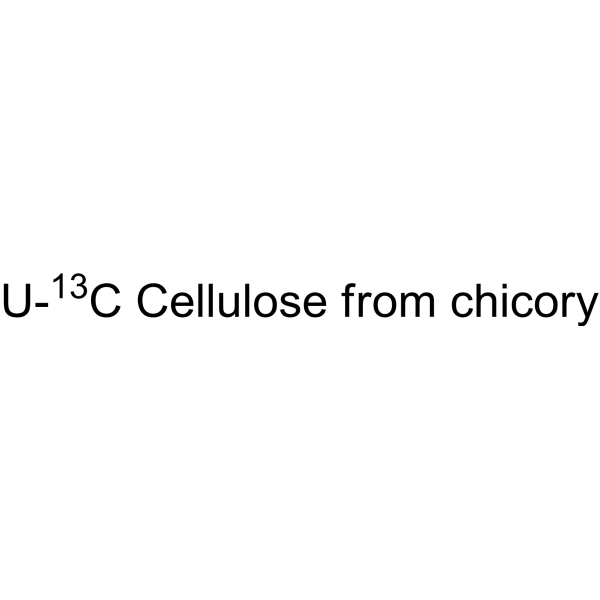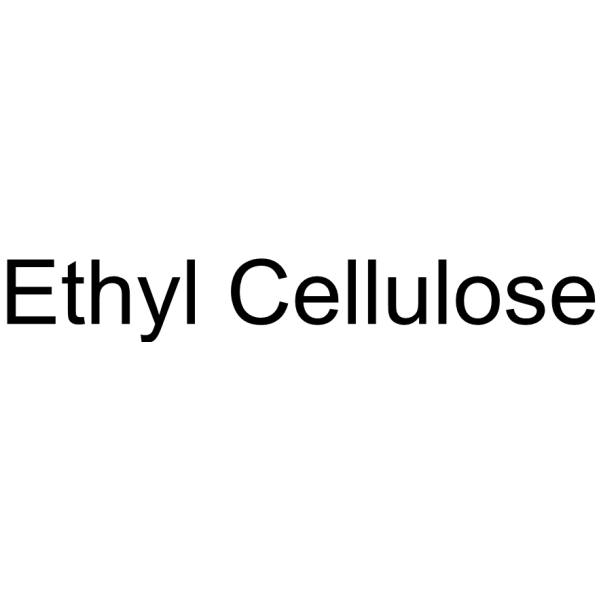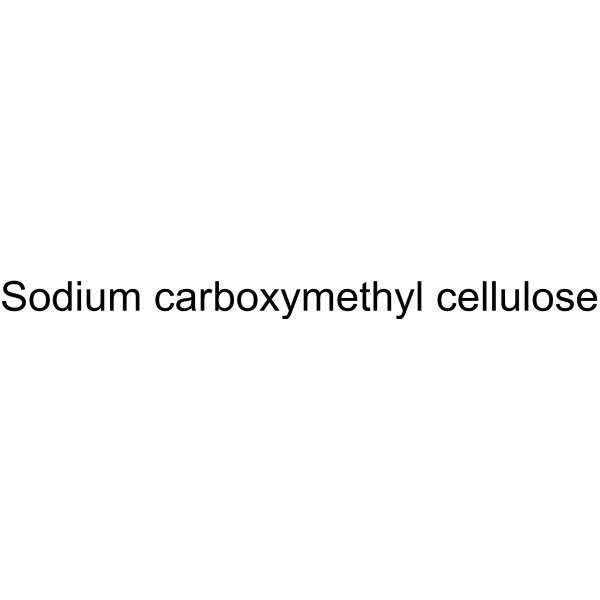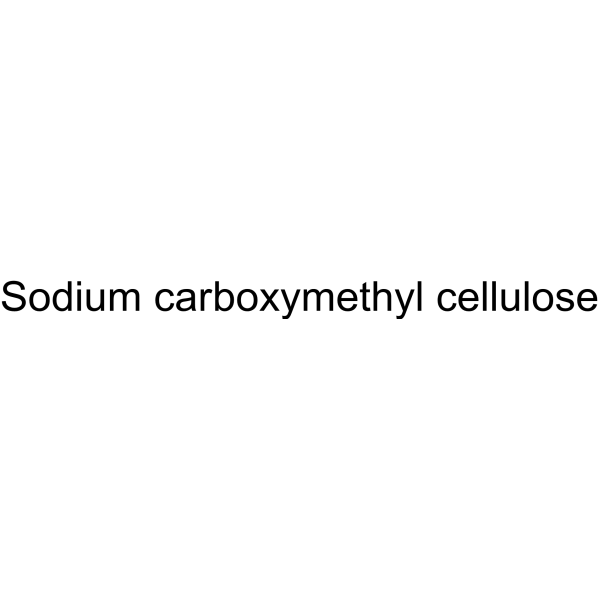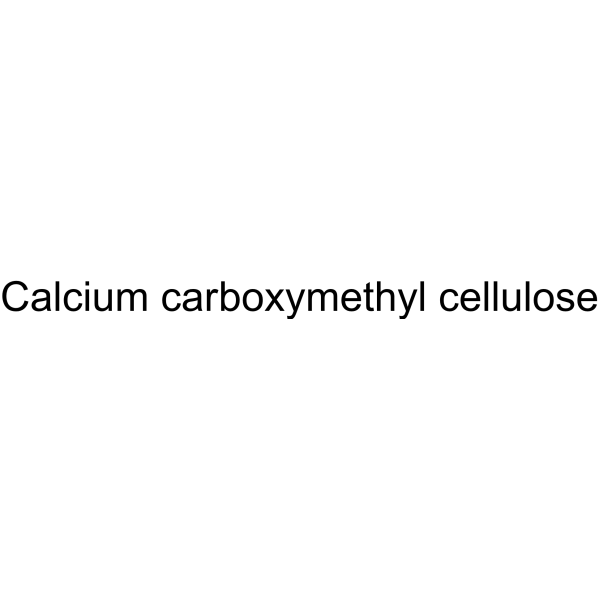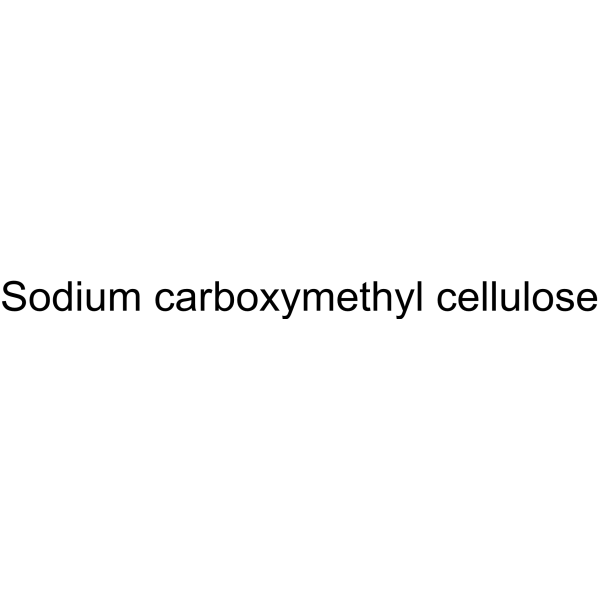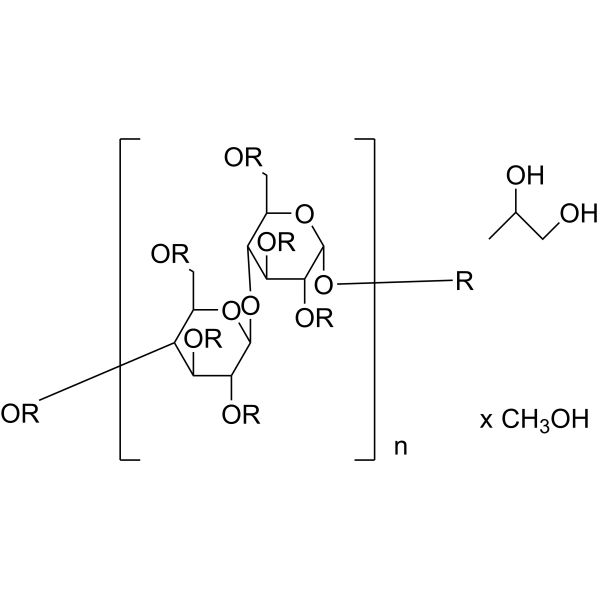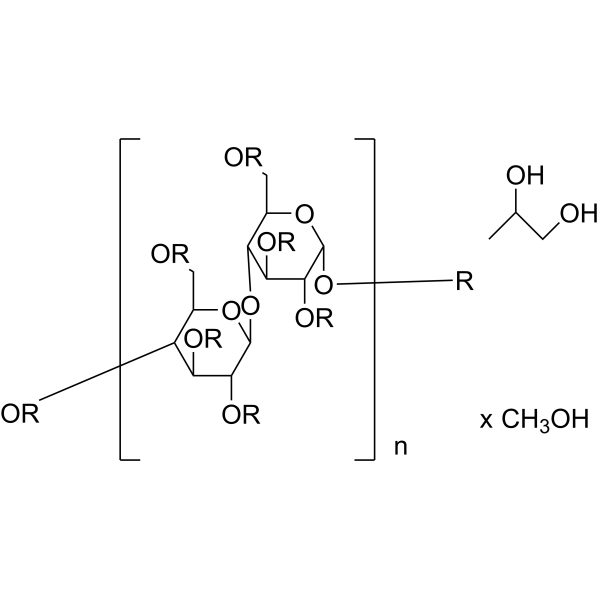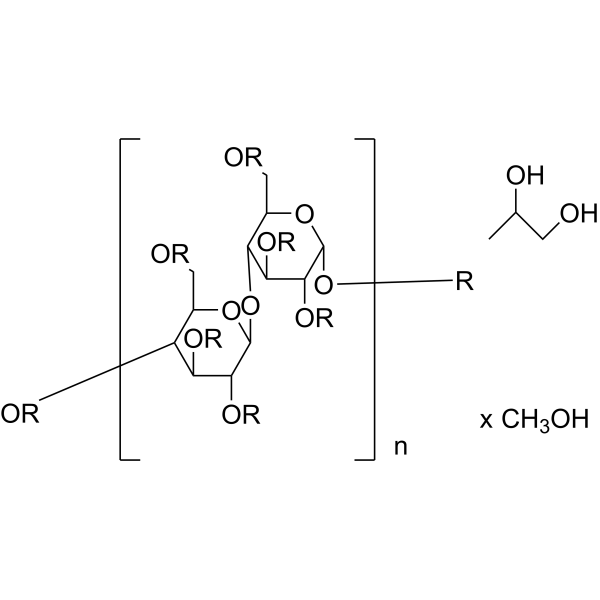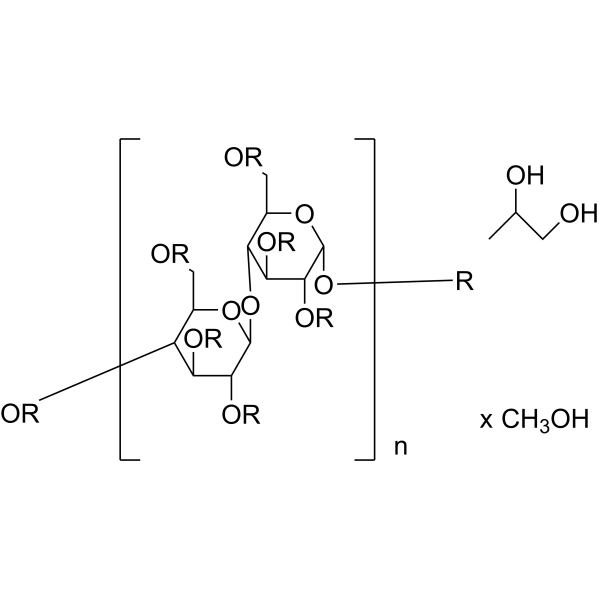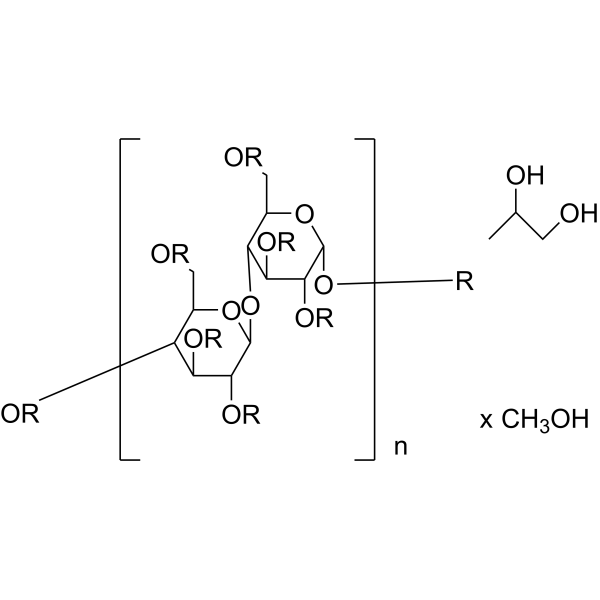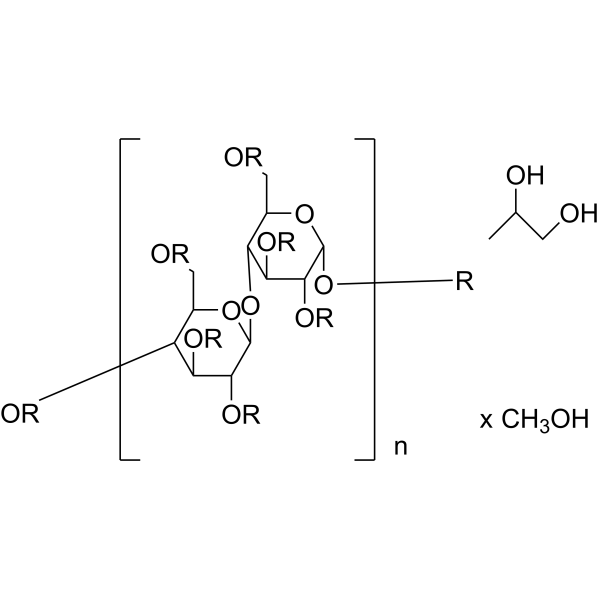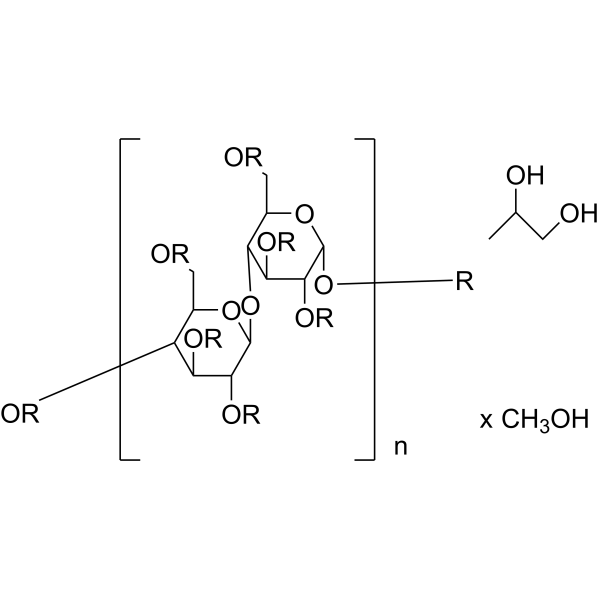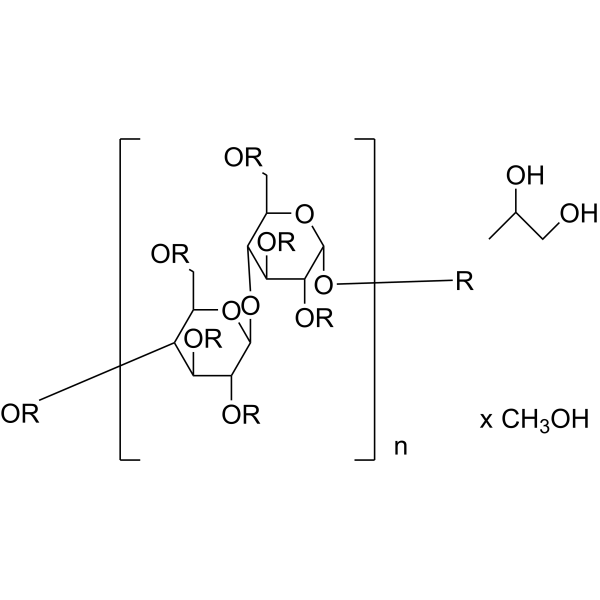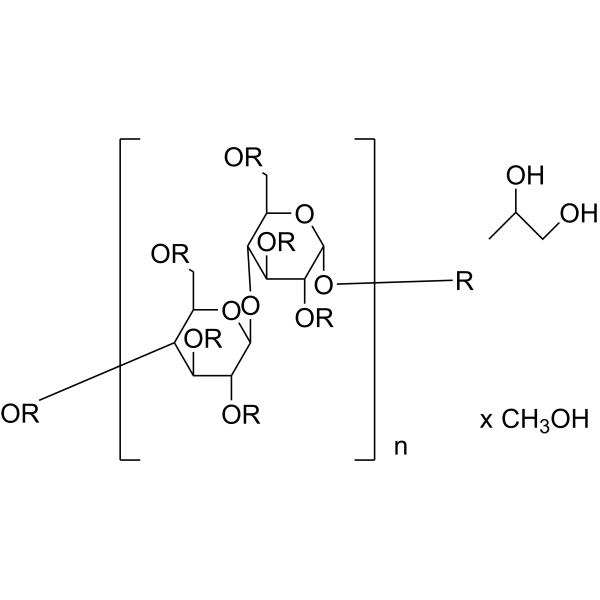Search Result
Results for "
cellulose
" in MedChemExpress (MCE) Product Catalog:
22
Biochemical Assay Reagents
8
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Areas |
Chemical Structure |
-
- HY-B2221
-
|
Pectin glycosidase
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
Cellulose (Pectin glycosidase) is a natural high molecular weight polysaccharide found in many plants and organisms. It is widely used in manufacturing industries, such as in paper making, textiles, food and medicine, etc. As a renewable resource, Cellulose is biodegradable and sustainable, and can also be used to manufacture chemicals such as Cellulose Esters, Cellulose Acetate and Cellulose Nitrate. In addition, Cellulose is often used as a food additive to increase the stability and quality of food.
|
-

-
- HY-W133892
-
|
cellulose monoacetate
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Acetylcellulose is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
-
- HY-B2221S5
-
|
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
U- 13C Cellulose from broccoli is the 13C labeled Cellulose (HY-B2221). Cellulose is a natural high molecular weight polysaccharide found in many plants and organisms. It is widely used in manufacturing industries, such as in paper making, textiles, food and medicine, etc. As a renewable resource, Cellulose is biodegradable and sustainable, and can also be used to manufacture chemicals such as Cellulose Esters, Cellulose Acetate and Cellulose Nitrate. In addition, Cellulose is often used as a food additive to increase the stability and quality of food .
|
-

-
- HY-B2221S4
-
-

-
- HY-B2221S2
-
|
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
|
Others
|
|
U-13C Cellulose high DP from wheat is the cellulose (HY-B2221) isolated from wheat, that is consist of abundant glucose and all the carbon atoms are labeled with isotope 13C .
|
-
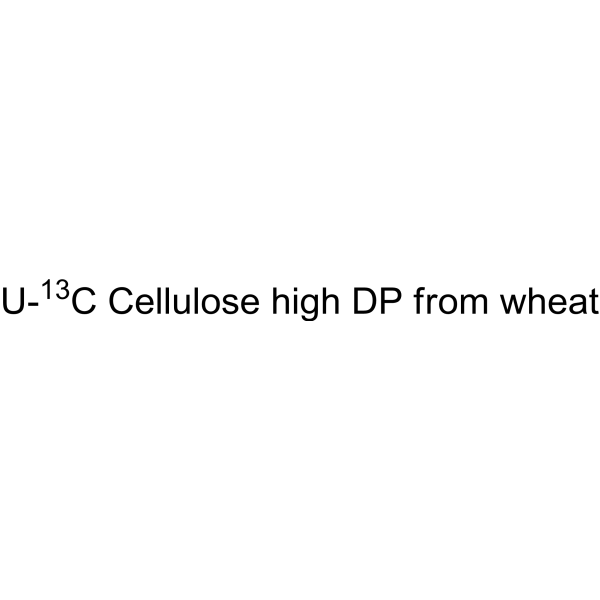
-
- HY-19964
-
|
Potassium clavulanate:cellulose (1:1)
|
Beta-lactamase
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Infection
|
|
Potassium clavulanate cellulose (Potassium clavulanate:cellulose (1:1)) is a mixture of potassium clavulanate and cellulose, is a bacterial β-lactamase inhibitor. Clavulanate potassium is a form of Clavulanic acid. Clavulanate potassium fights bacteria that resistant to penicillins and other antibiotics. Potassium clavulanate with the combination of amoxicillin can be used for the research of different infections caused by bacteria, such as sinusitis, pneumonia, ear infections, bronchitis, urinary tract infections, and infections of the skin .
|
-
-
- HY-B2221S1
-
|
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
U- 13C Cellulose from chicory is the 13C labeled Cellulose (HY-B2221). Cellulose (Pectin glycosidase) is a natural high molecular weight polysaccharide found in many plants and organisms. It is widely used in manufacturing industries, such as in paper making, textiles, food and medicine, etc. As a renewable resource, Cellulose is biodegradable and sustainable, and can also be used to manufacture chemicals such as Cellulose Esters, Cellulose Acetate and Cellulose Nitrate. In addition, Cellulose is often used as a food additive to increase the stability and quality of food .
|
-
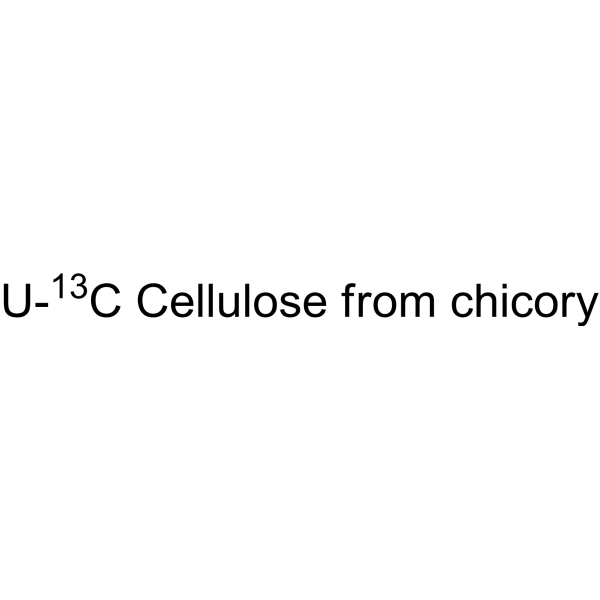
-
- HY-W115746
-
|
Ethyl cellulose N-200
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Ethyl cellulose is a derivative of cellulose. Ethyl cellulose serves as a non-toxic and biodegradable polymer, with unique properties such as oleogel formation, delivery of active component, and film-forming ability in the food and pharmaceutical sectors. Ethyl cellulose can be used as an excipient, such as coating agent, flavoring agent, tablet filler. Pharmaceutical excipients, or pharmaceutical auxiliaries, refer to other chemical substances used in the pharmaceutical process other than pharmaceutical ingredients. Pharmaceutical excipients generally refer to inactive ingredients in pharmaceutical preparations, which can improve the stability, solubility and processability of pharmaceutical preparations. Pharmaceutical excipients also affect the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination (ADME) processes of co-administered drugs .
|
-
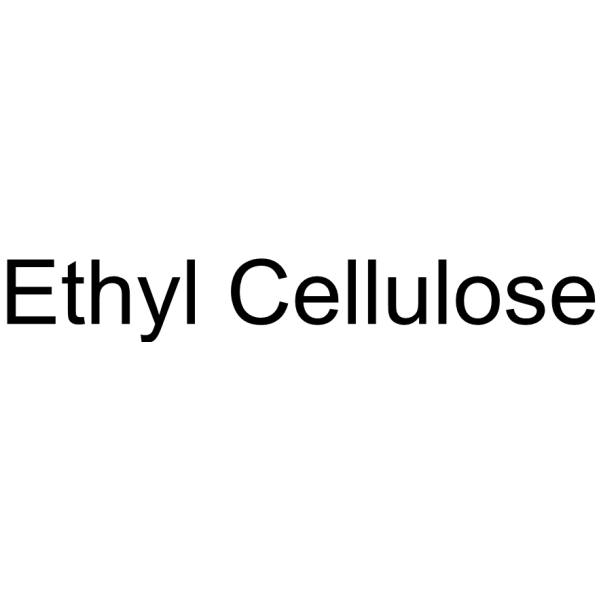
-
- HY-B2221B
-
|
Hydroxyethyl pectin glycosidase
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Hydroxyethyl cellulose is a non-ionic, modified cellulose polymer used as a thickening agent for aqueous cosmetic and personal care formulations.
|
-
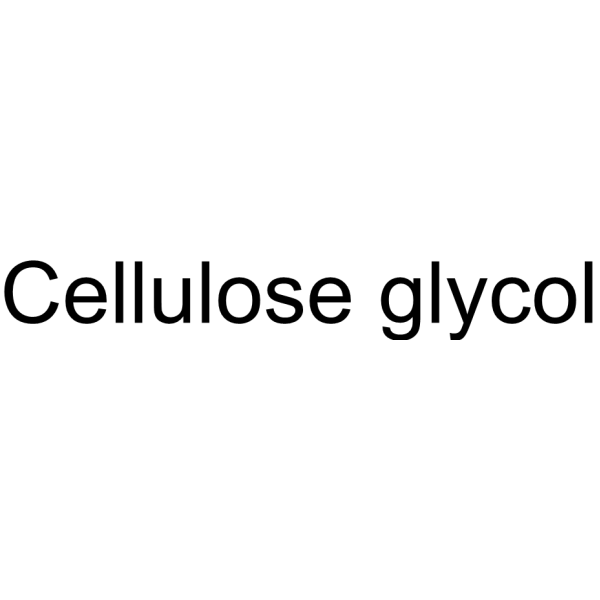
-
- HY-B2221S
-
|
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
U- 13C Cellulose high DP from potato is the 13C labeled Cellulose (HY-B2221). Cellulose (Pectin glycosidase) is a natural high molecular weight polysaccharide found in many plants and organisms. It is widely used in manufacturing industries, such as in paper making, textiles, food and medicine, etc. As a renewable resource, Cellulose is biodegradable and sustainable, and can also be used to manufacture chemicals such as Cellulose Esters, Cellulose Acetate and Cellulose Nitrate. In addition, Cellulose is often used as a food additive to increase the stability and quality of food .
|
-

-
- HY-B2221S3
-
|
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
U- 13C Cellulose high DP from maize is the 13C labeled Cellulose (HY-B2221). Cellulose (Pectin glycosidase) is a natural high molecular weight polysaccharide found in many plants and organisms. It is widely used in manufacturing industries, such as in paper making, textiles, food and medicine, etc. As a renewable resource, Cellulose is biodegradable and sustainable, and can also be used to manufacture chemicals such as Cellulose Esters, Cellulose Acetate and Cellulose Nitrate. In addition, Cellulose is often used as a food additive to increase the stability and quality of food .
|
-

-
- HY-B2221C
-
|
Carboxymethyl cellulose CM-32; CM-32
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Cellulose carboxymethyl is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
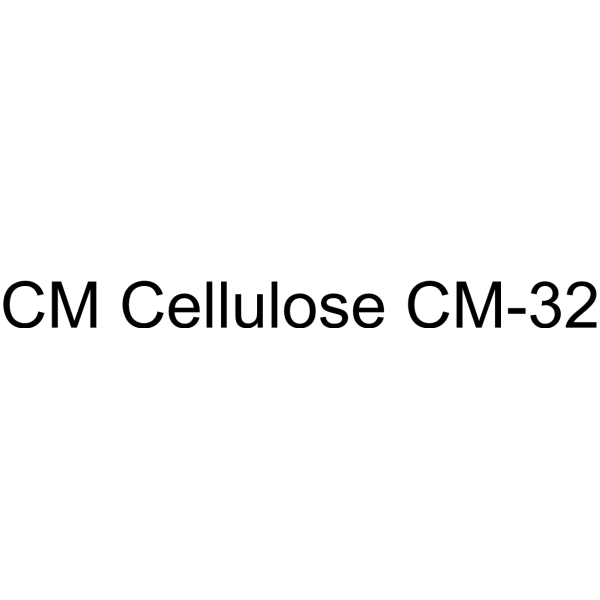
-
- HY-W145498
-
|
Cellotetraose
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
D-(+)-Cellotetraose (Cellotetraose) is a primary hydrolysis product of cellulose .
|
-
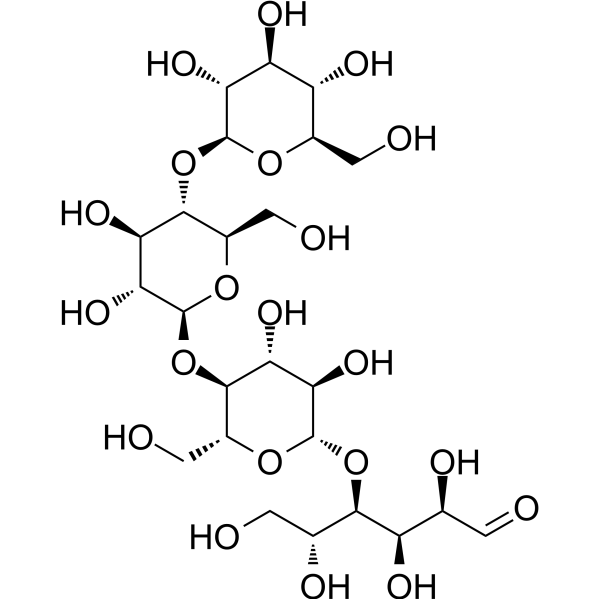
-
- HY-W145579
-
|
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
Cellopentaose is a penta oligosaccharide of cellulose .
|
-
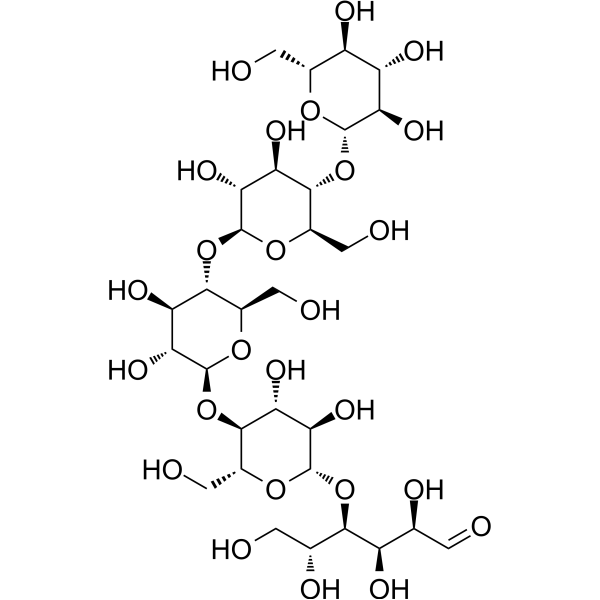
-
- HY-100557
-
|
|
|
|
|
Hydroxypropyl Cellulose is somewhat amphiphilic in character and is a surfactant. Hydroxypropyl Cellulose can be used as a pharmaceutical excipient, such as coating agent, emulsifier, suspension, tablet, thickener, viscosifier. Pharmaceutical excipients, or pharmaceutical auxiliaries, refer to other chemical substances used in the pharmaceutical process other than pharmaceutical ingredients. Pharmaceutical excipients generally refer to inactive ingredients in pharmaceutical preparations, which can improve the stability, solubility and processability of pharmaceutical preparations. Pharmaceutical excipients also affect the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination (ADME) processes of co-administered drugs .
|
-
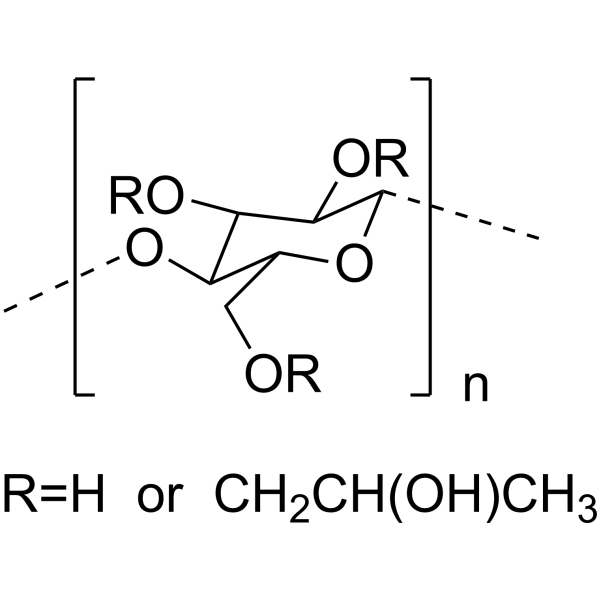
-
- HY-Y1889A
-
|
CMC-Na (MW 250000); CMC-Na (Viscosity:1500-3100 mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC-Na) (MW 250000) is a sodium salt of carboxymethyl cellulose. Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose has adsorption and corrosion inhibition on low-carbon steel in an acidic medium. Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose can be used as a thickener, paste and barrier agent .
|
-

-
- HY-W14549
-
|
Cellotriose
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
D-(+)-Cellotriose (Cellotriose) is an oligosaccharide, it is an intermediate in the enzyme hydrolysis of cellulose .
|
-
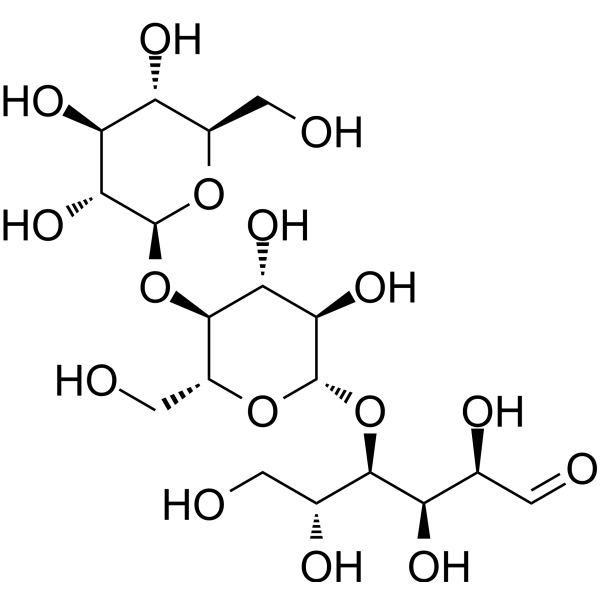
-
- HY-125861D
-
|
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
Methyl cellulose(Viscosity:40000mPa.s) is a natural polymer which gels on heating .
|
-

-
- HY-Y1889
-
|
CMC-Na (Viscosity:5000-15000 mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (Viscosity:5000-15000 mPa.s) is the sodium salt of cellulose arboxymethyl and frequently used as viscous agent, paste and barrier agent.
|
-
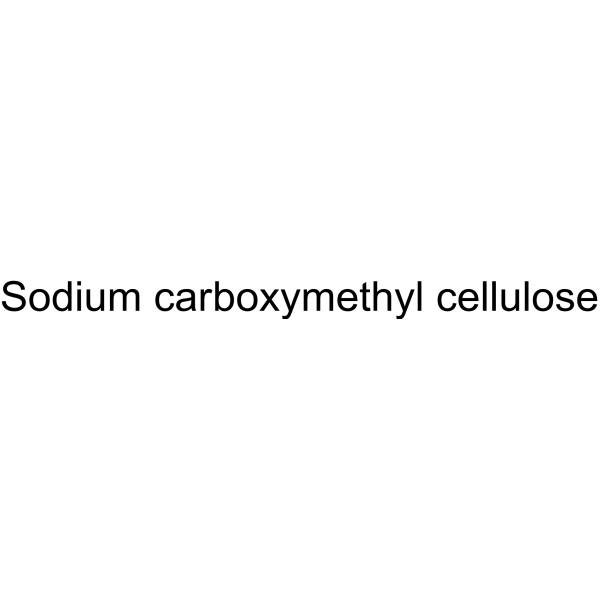
-
- HY-Y0703
-
|
CMC-Na (Viscosity:800-1200 mPa.s)
|
|
|
|
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (Viscosity:800-1200 mPa.s) is the sodium salt of cellulose arboxymethyl and frequently used as viscous agent, paste and barrier agent.
|
-
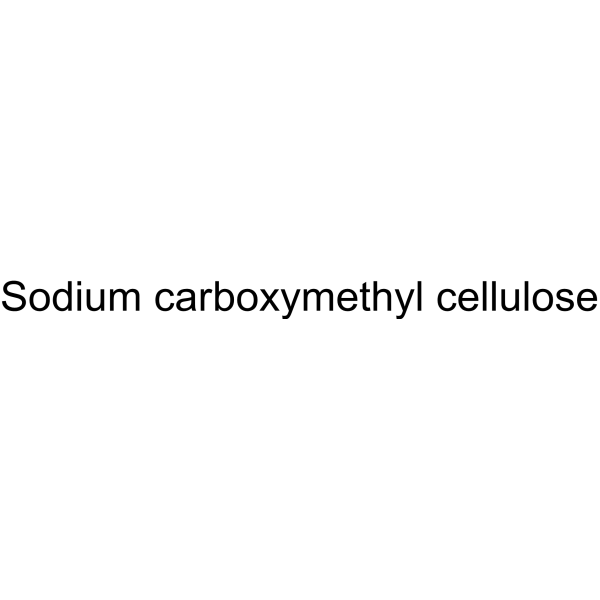
-
- HY-Y0703A
-
|
CMC-Na (Viscosity:1200-1400 mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (Viscosity:1200-1400 mPa.s) is the sodium salt of cellulose arboxymethyl and frequently used as viscous agent, paste and barrier agent.
|
-
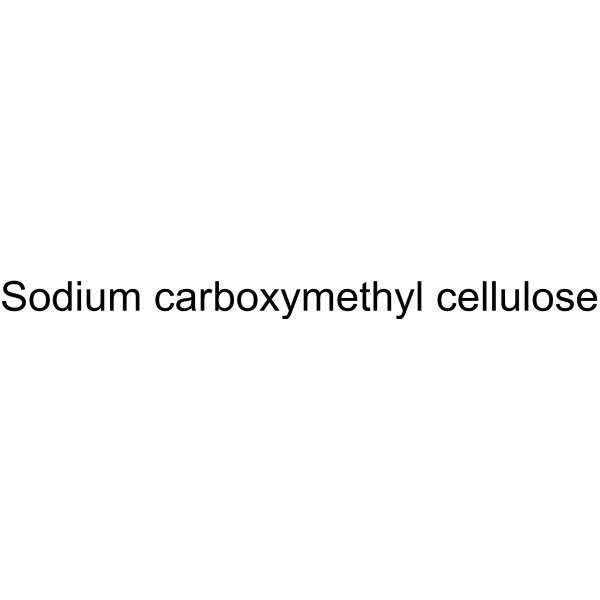
-
- HY-Y0703C
-
|
CMC-Na (Viscosity:300-800mpa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (Viscosity:300-800mpa.s) is the sodium salt of cellulose arboxymethyl and frequently used as viscous agent, paste and barrier agent.
|
-
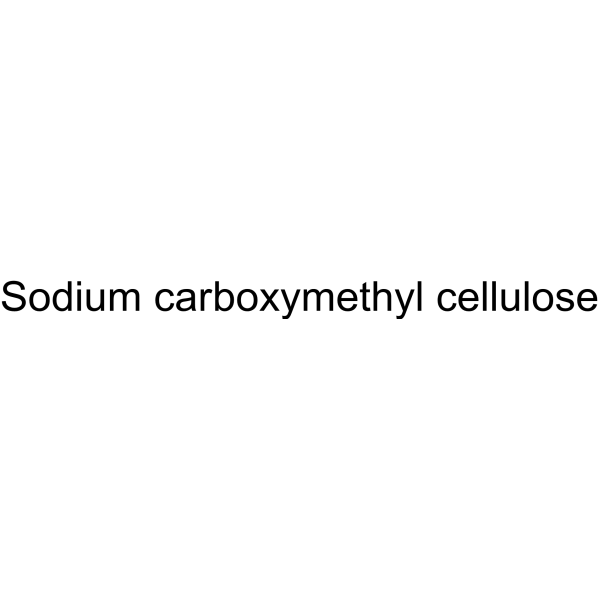
-
- HY-152927
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose acetate succinate (Mw: 20-100k Da) is a cosolvent for preparing SDDs of low-solubility agents. Hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose acetate succinate (Mw: 20-100k Da) exhibits no acute/subchronic/chronic toxicity in rats, with oral activity and LD50 >2.5 g/kg .
|
-

-
- HY-125861A
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Methyl cellulose(Viscosity:15mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-

-
- HY-125861B
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Methyl cellulose(Viscosity:400mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-

-
- HY-125861C
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Methyl cellulose(Viscosity:1500mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-

-
- HY-W011602
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Triethyl citrate is an ester of citric acid. Triethyl citrate can be used as a plasticizer for cellulosic plastic-based nanocomposites .
|
-
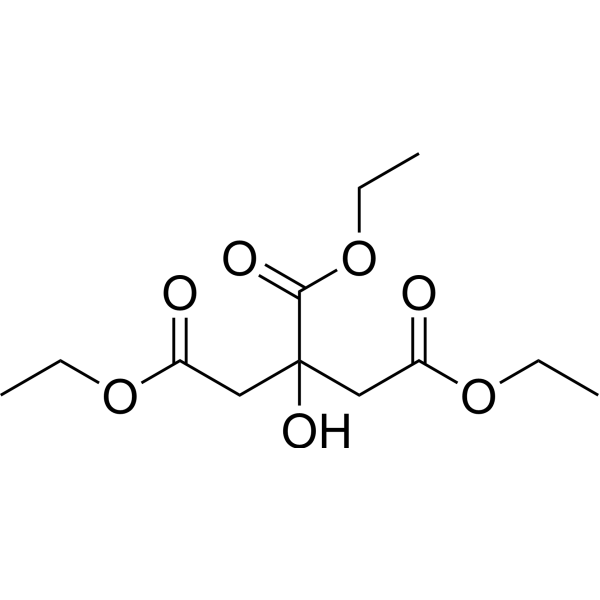
-
- HY-A0104
-
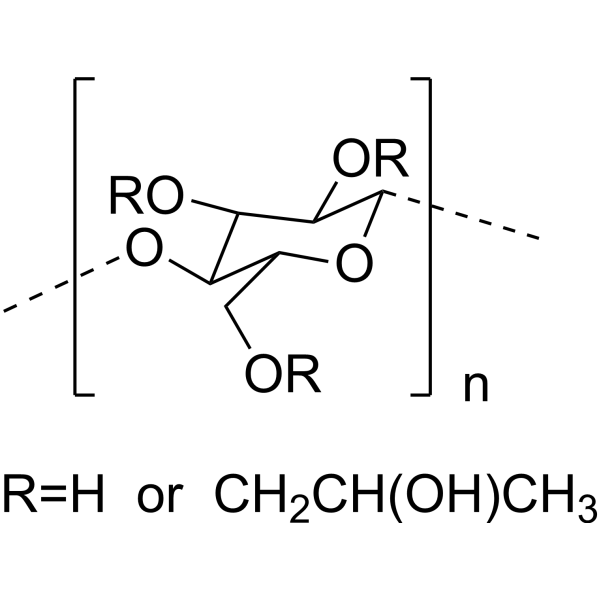
HPMC
3 Publications Verification
Hypromellose; (Hydroxypropyl)methyl cellulose; Celacol HPM 5000
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
HPMC (Hypromellose) is a hydrophilic, non-ionic cellulose ether used to form swellable-soluble matrices.
|
-
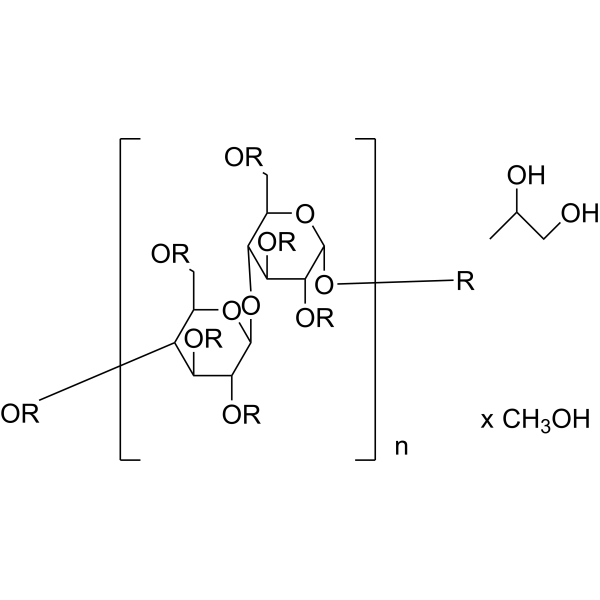
-
- HY-154704
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Calcium carboxymethyl cellulose can be used as an excipient. Pharmaceutical excipients, or pharmaceutical auxiliaries, refer to other chemical substances used in the pharmaceutical process other than pharmaceutical ingredients. Pharmaceutical excipients generally refer to inactive ingredients in pharmaceutical preparations, which can improve the stability, solubility and processability of pharmaceutical preparations. Pharmaceutical excipients also affect the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination (ADME) processes of co-administered drugs .
|
-
-
- HY-W345102
-
-
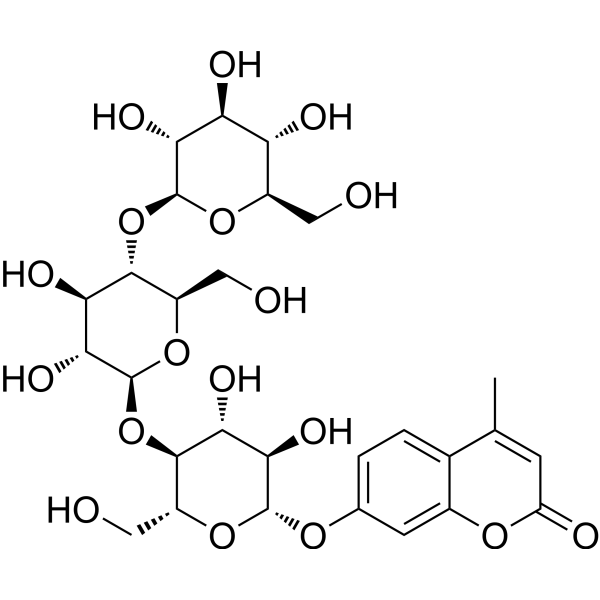
-
- HY-Y0703D
-
|
CMC-Na (average Mw 90000, DS=0.7, Viscosity:50-200 mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (average Mw 90000, DS=0.7, Viscosity:50-200 mPa.s) is the sodium salt of cellulose arboxymethyl and frequently used as viscous agent, paste and barrier agent .
|
-
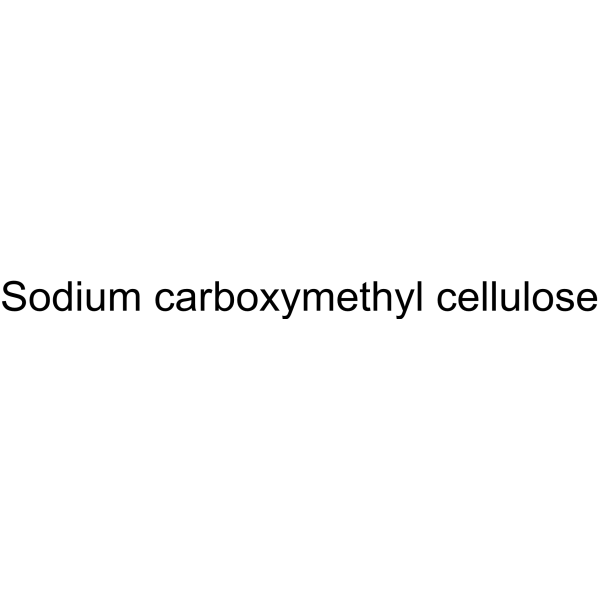
-
- HY-100557A
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Low-Substituted Hydroxypropyl Cellulose can be used as an excipient, such as Coating agents, emulsifiers, suspensions, tablets, thickeners, thickeners, etc. Pharmaceutical excipients, or pharmaceutical auxiliaries, refer to other chemical substances used in the pharmaceutical process other than pharmaceutical ingredients. Pharmaceutical excipients generally refer to inactive ingredients in pharmaceutical preparations, which can improve the stability, solubility and processability of pharmaceutical preparations. Pharmaceutical excipients also affect the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination (ADME) processes of co-administered drugs .
|
-
-
- HY-107846
-
Xylan
1 Publications Verification
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
Xylan represents the main hemicellulose component in the secondary plant cell walls of flowering plants. Xylan is a polysaccharide made from units of xylose and contains predominantly β-D-xylose units linked as in cellulose .
|
-

-
- HY-P1032S
-
|
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
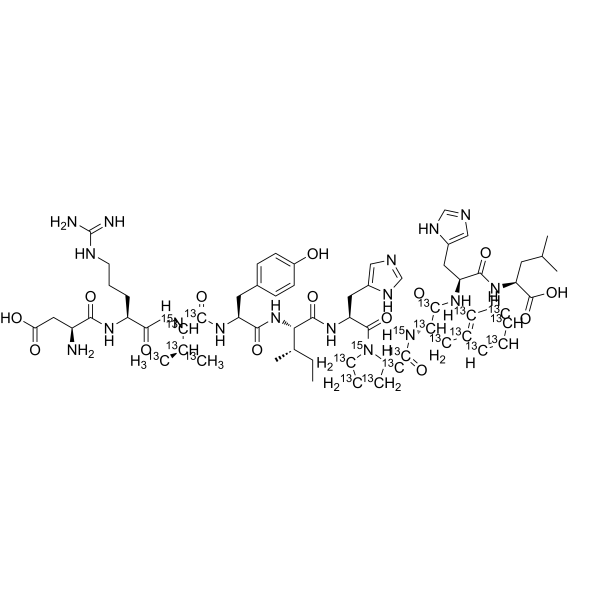
Angiotensin I- 13C19, 15N3 (human, mouse, rat) is the 13C and 15N labeled Angiotensin I (human, mouse, rat) (HY-P1032). Cellulose (Pectin glycosidase) is a natural high molecular weight polysaccharide found in many plants and organisms. It is widely used in manufacturing industries, such as in paper making, textiles, food and medicine, etc. As a renewable resource, Cellulose is biodegradable and sustainable, and can also be used to manufacture chemicals such as Cellulose Esters, Cellulose Acetate and Cellulose Nitrate. In addition, Cellulose is often used as a food additive to increase the stability and quality of food .
|
-
-
- HY-125861
-
|
Methyl cellulose(Viscosity:100000mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Cancer
|
|
Methylcellulose is a natural polymer which gels on heating. Methylcellulose is not toxic.
|
-

-
- HY-A0104J
-
|
Hypromellose (Type II,Viscosity:5mPa.s); (Hydroxypropyl)methyl cellulose (Type II,Viscosity:5mPa.s); Celacol HPM 5000 (Type II,Viscosity:5mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
HPMC (Hypromellose) (Type II,Viscosity:5mPa.s) is a hydrophilic, non-ionic cellulose ether used to form swellable-soluble matrices. HPMC (Type II,Viscosity:5mPa.s) is widely used in agent formulations due to its biocompatibility, uncharged nature, solubility in water and thermoplastic behavior .
|
-
-
- HY-163279
-
|
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
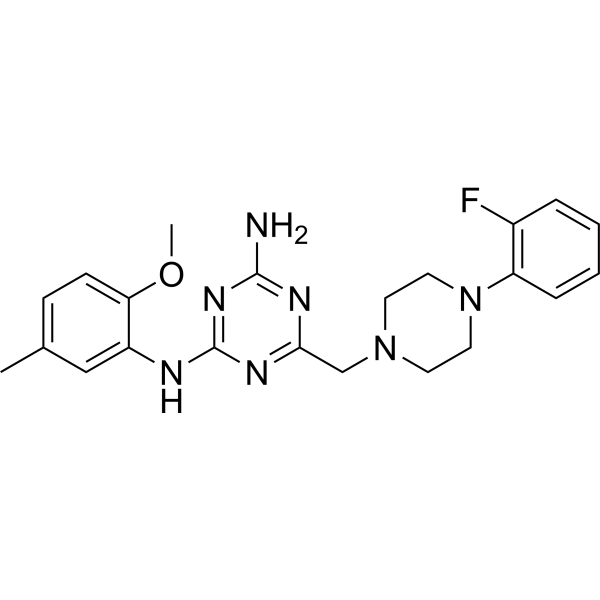
Fluopipamine is an antagonist for Cellulose Synthase 1 (CESA1) with an IC50 of 0.78 μM. Fluopipamine leads a decrease in glucose uptake into cellulose and hyperaccumulation of CESAs at the PM in etiolated Arabidopsis seedlings .
|
-
-
- HY-P2775
-
|
|
Glucosidase
|
Others
|
|
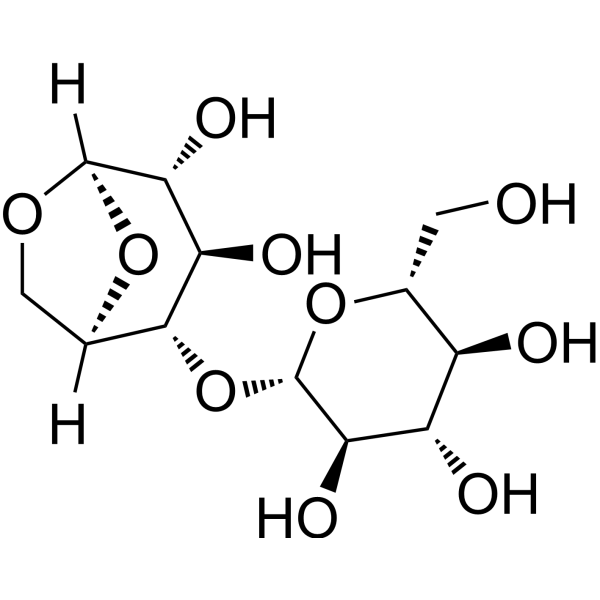
β-Glucosidase, almond is the rate-limiting enzyme of degradation of cellulose. β-Glucosidase is a major group among glycoside hydrolases. β-Glucosidase is involved in the degradation of cellulose in soils and has potential for monitoring biological soil quality .
|
-

-
- HY-W040094
-
-
-
- HY-E70107
-
|
Cbh1
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
Cellobiohydrolase I (Cbh1) belongs to glycoside hydrolase family 7 (GH7) that catalyzes the processive hydrolysis of cellulose into cellobiose .
|
-

-
- HY-N1915
-
|
|
|
|
|
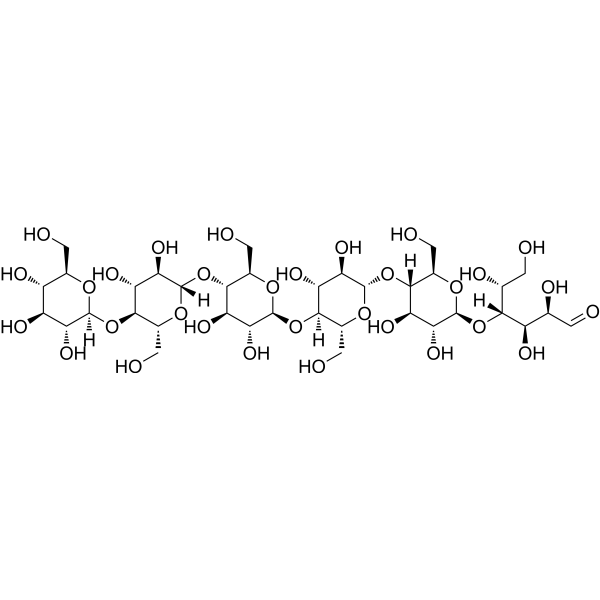
Cellohexaose is a glucose polymer with two or more glucose monomers produced from the breakdown of cellulose, consisting of a condensation of beta (1-4) linked D-glucose monomers .
|
-
-
- HY-N6840
-
|
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
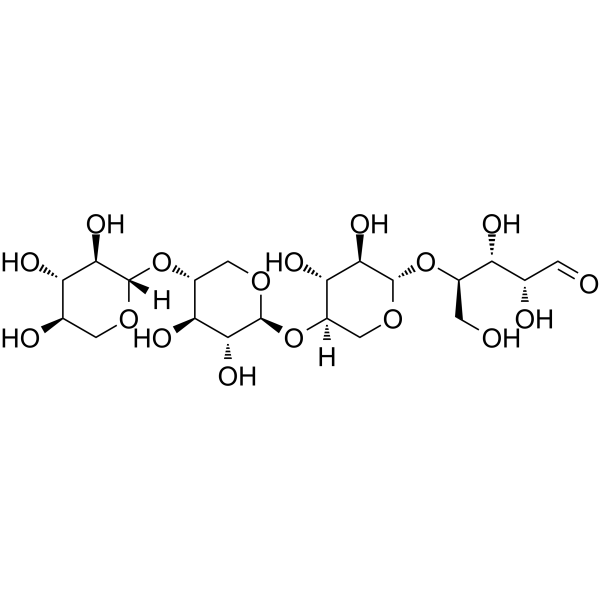
Xylotetraose is a hydrolysis product of Xylan . Xylan is a polysaccharide made from units of xylose and contains predominantly β-D-xylose units linked as in cellulose . Xylotetraose can be used for enzyme biochemical analysis .
|
-
-
- HY-W017782
-
|
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
2,5-Furandimethanol is obtained from 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural. 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, as a building block, is considered an important intermediate due to its rich chemistry and potential availability from carbohydrates such as fructose, glucose, sucrose, cellulose and inulin .
|
-
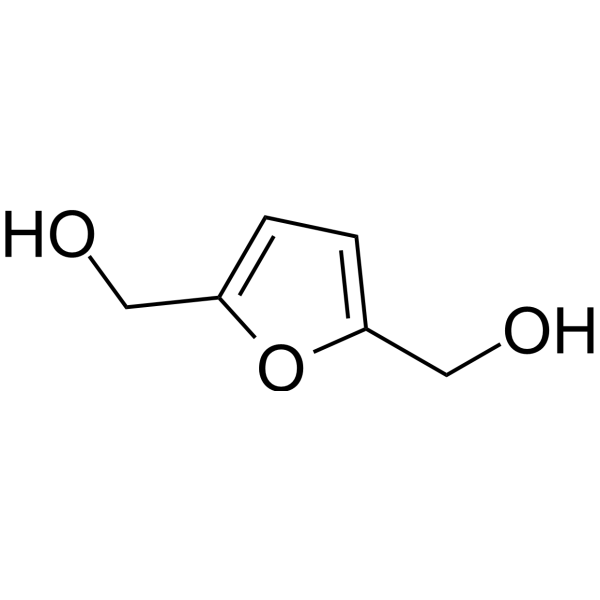
-
- HY-W004293
-
|
Tridecyl Alcohol
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
1-Tridecanol is an organic compound commonly used as a surfactant, lubricant, and stabilizer, among others. It can be used in some cleaning products, preservatives and plastic additives, and can help enhance their performance and stability. In addition, the compound is used in some industrial fields, for example in the manufacture of products such as cellulose and paints. Although the compound has no direct medical application, it plays an important role in consumer products and industrial production.
|
-
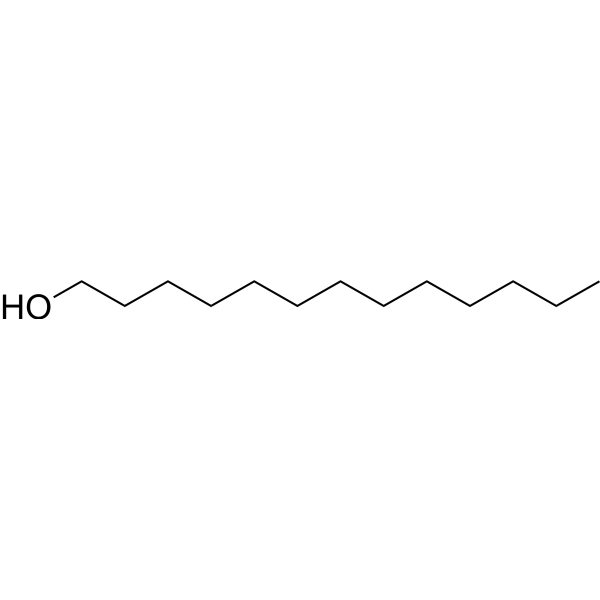
-
- HY-133673S
-
|
MCPP-d4
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
|
Others
|
|
Mono(3-carboxypropyl) phthalate-d4 (MCPP-d4) is a deuterium labeled Mono(3-carboxypropyl) phthalate (HY-133673). Mono(3-carboxypropyl) phthalate (MCPP) is a metabolite of Di-n-octyl phthalate. Di-n-octyl phthalate (DnOP) is a plasticizer used in polyvinyl chloride plastics, cellulose esters, and polystyrene resins .
|
-
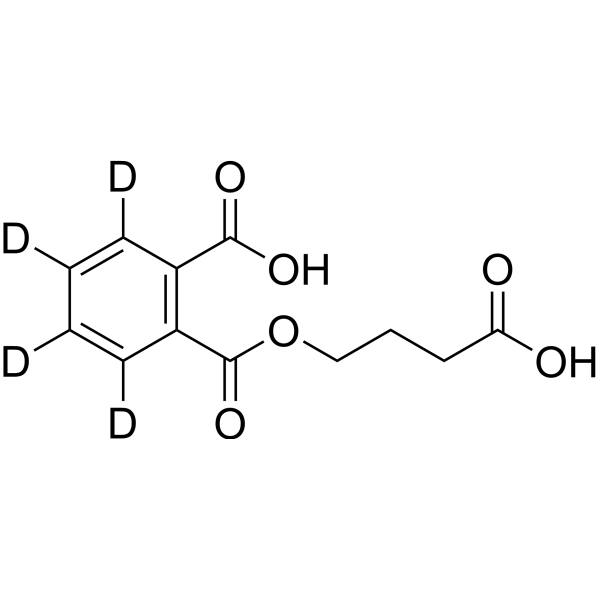
-
- HY-A0103
-
|
|
|
|
|
Xanthan gum is a microbial polysaccharide produced by Xanthomonas campestris. The structure of xanthan gum is based on a cellulose backbone of β-(1-4)-linked glucose units with a trisaccharide side of mannose-glucuronic acid-mannose attached to every other glucose unit in the backbone chain. Some terminal mannose units are pyruvated and some internal mannose units are acetylated. Due to its unique rheology and gelling properties, it is widely used as a food additive, thickener and stabilizer in the food and petroleum industries.
|
-
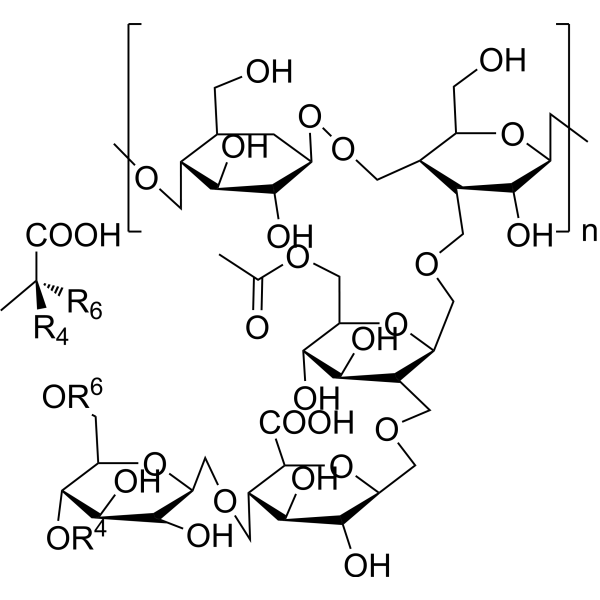
-
- HY-N10518
-
|
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
Celloheptaose is an oligosaccharide, consisting of seven glucose residues. Celloheptaose is the substrate of Polysaccharide monooxygenases (PMOs), to generate oxidized cellulo-oligosaccharides .
|
-
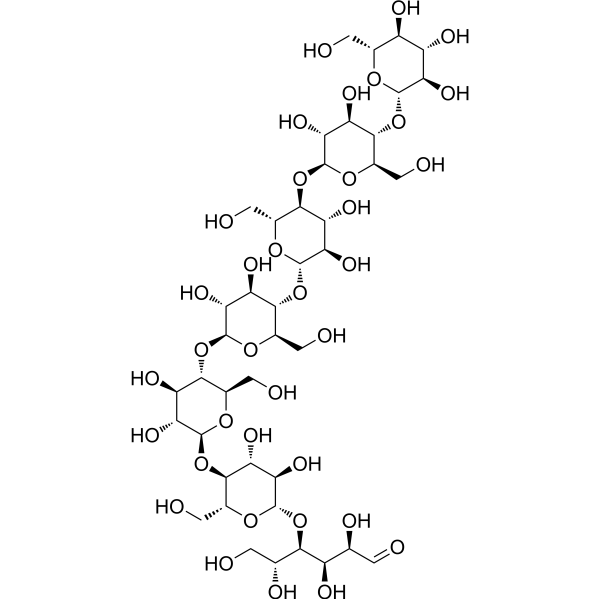
-
- HY-A0104B
-
|
Hypromellose (Type I,Viscosity:100mPa.s); (Hydroxypropyl)methyl cellulose (Type I,Viscosity:100mPa.s); Celacol HPM 5000 (Type I,Viscosity:100mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Hypromellose (Type I,Viscosity:100mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
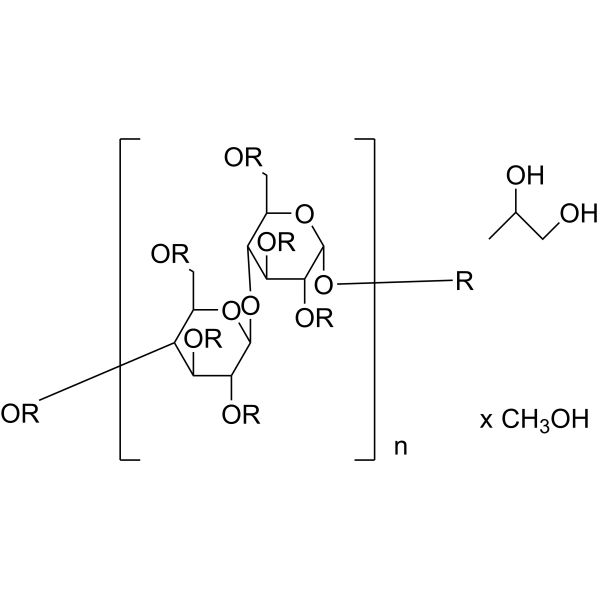
-
- HY-A0104A
-
|
Hypromellose (Type I,Viscosity:30mPa.s); (Hydroxypropyl)methyl cellulose (Type I,Viscosity:30mPa.s); Celacol HPM 5000 (Type I,Viscosity:30mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (Type I,Viscosity:30mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
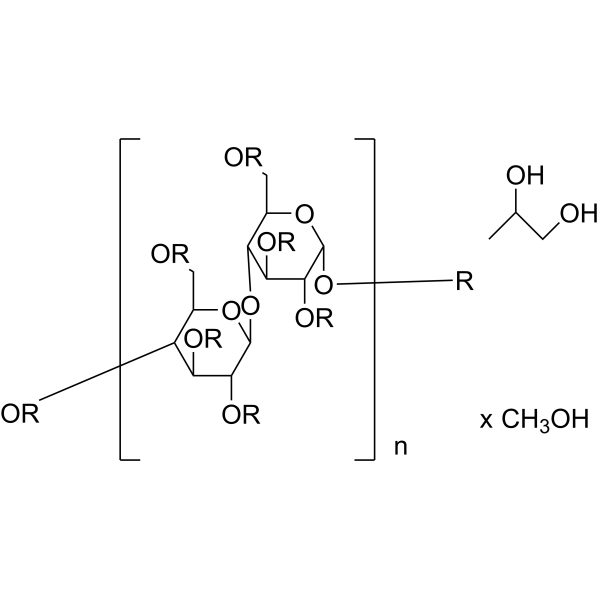
-
- HY-A0104D
-
|
Hypromellose (Type I,Viscosity:4000mPa.s); (Hydroxypropyl)methyl cellulose (Type I,Viscosity:4000mPa.s); Celacol HPM 5000 (Type I,Viscosity:4000mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (Type I,Viscosity:4000mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
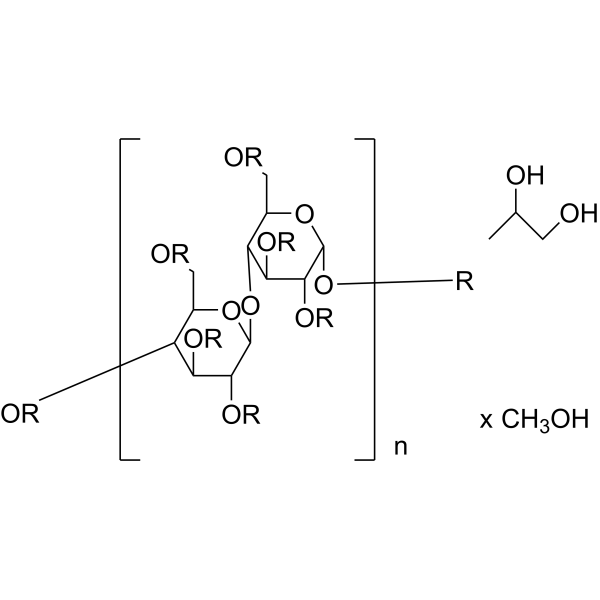
- HY-A0104C
-
|
Hypromellose (Type I,Viscosity:400mPa.s); (Hydroxypropyl)methyl cellulose (Type I,Viscosity:400mPa.s); Celacol HPM 5000 (Type I,Viscosity:400mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (Type I,Viscosity:400mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
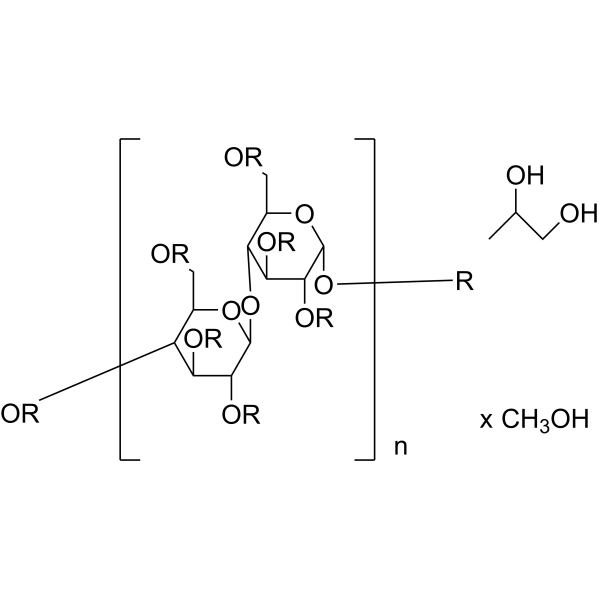
- HY-A0104I
-
|
Hypromellose (Type II,Viscosity:100000mPa.s); (Hydroxypropyl)methyl cellulose (Type II,Viscosity:100000mPa.s); Celacol HPM 5000 (Type II,Viscosity:100000mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (Type II,Viscosity:100000mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
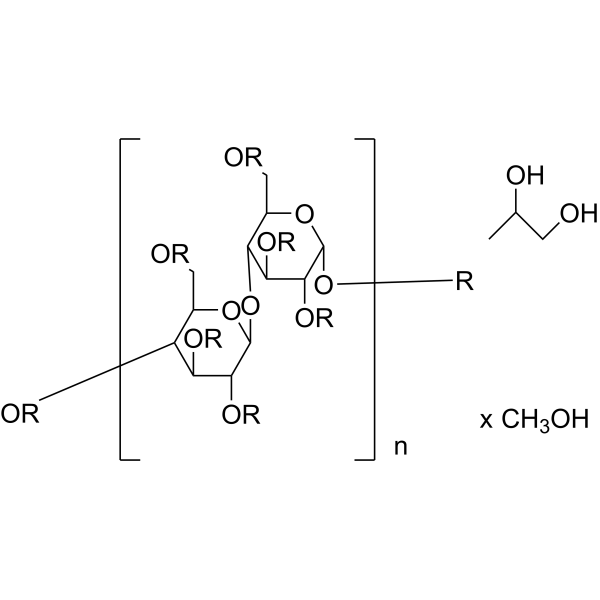
- HY-A0104E
-
|
Hypromellose (Type II,Viscosity:100mPa.s); (Hydroxypropyl)methyl cellulose (Type II,Viscosity:100mPa.s); Celacol HPM 5000 (Type II,Viscosity:100mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Hypromellose (Type II,Viscosity:100mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
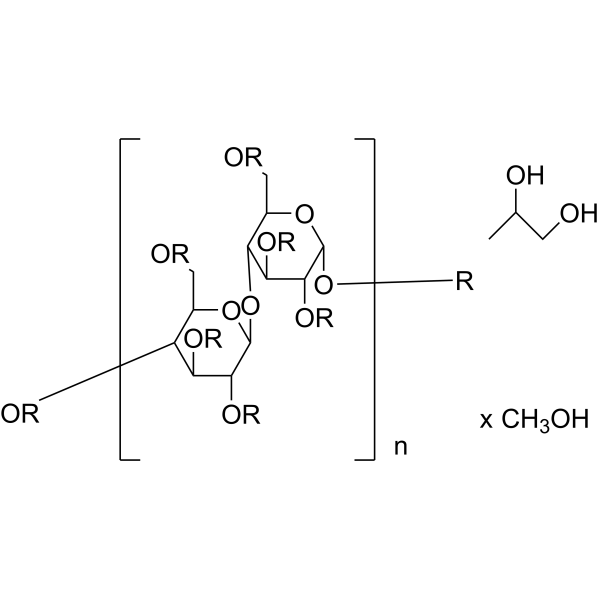
- HY-A0104H
-
|
Hypromellose (Type II,Viscosity:15000mPa.s); (Hydroxypropyl)methyl cellulose (Type II,Viscosity:15000mPa.s); Celacol HPM 5000 (Type II,Viscosity:15000mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Hypromellose (Type II,Viscosity:15000mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
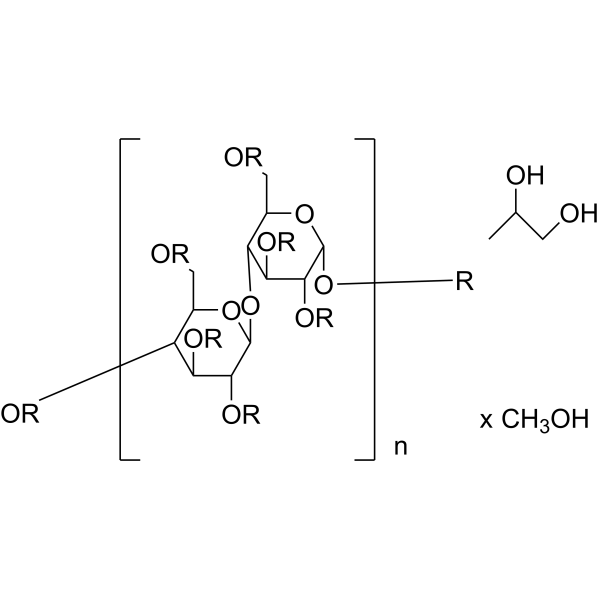
- HY-A0104F
-
|
Hypromellose (Type II,Viscosity:400mPa.s); (Hydroxypropyl)methyl cellulose (Type II,Viscosity:400mPa.s); Celacol HPM 5000 (Type II,Viscosity:400mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Hypromellose (Type II,Viscosity:400mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
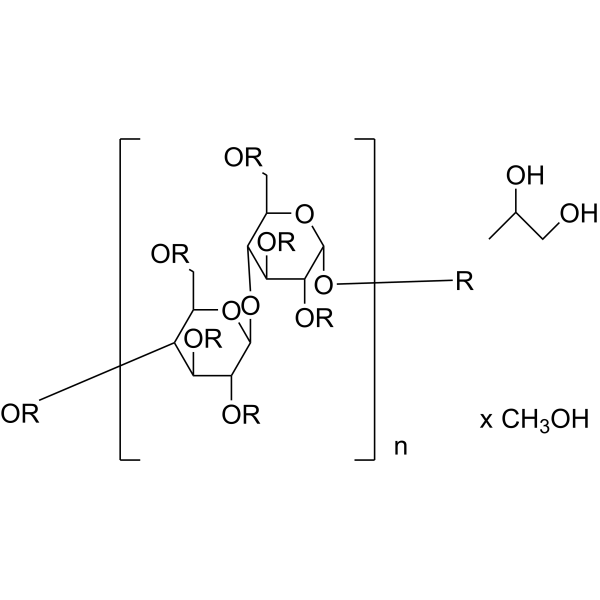
- HY-A0104G
-
|
Hypromellose (Type II,Viscosity:4000mPa.s); (Hydroxypropyl)methyl cellulose (Type II,Viscosity:4000mPa.s); Celacol HPM 5000 (Type II,Viscosity:4000mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Hypromellose (Type II,Viscosity:4000mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
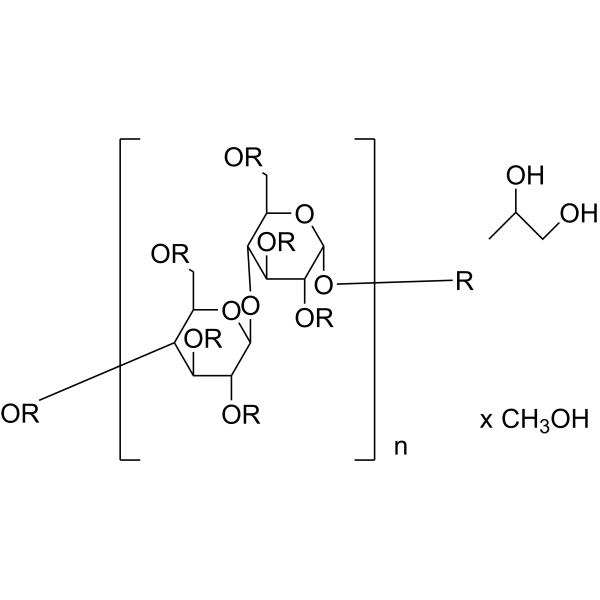
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Type |
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Type |
-
- HY-B2221C
-
|
Carboxymethyl cellulose CM-32; CM-32
|
Filter Medium
|
|
Cellulose carboxymethyl is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
- HY-Y1889A
-
|
CMC-Na (MW 250000); CMC-Na (Viscosity:1500-3100 mPa.s)
|
Co-solvents
|
|
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC-Na) (MW 250000) is a sodium salt of carboxymethyl cellulose. Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose has adsorption and corrosion inhibition on low-carbon steel in an acidic medium. Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose can be used as a thickener, paste and barrier agent .
|
-
- HY-Y1889
-
|
CMC-Na (Viscosity:5000-15000 mPa.s)
|
Co-solvents
|
|
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (Viscosity:5000-15000 mPa.s) is the sodium salt of cellulose arboxymethyl and frequently used as viscous agent, paste and barrier agent.
|
-
- HY-Y0703A
-
|
CMC-Na (Viscosity:1200-1400 mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (Viscosity:1200-1400 mPa.s) is the sodium salt of cellulose arboxymethyl and frequently used as viscous agent, paste and barrier agent.
|
-
- HY-W133892
-
|
cellulose monoacetate
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Acetylcellulose is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
- HY-Y0703C
-
|
CMC-Na (Viscosity:300-800mpa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (Viscosity:300-800mpa.s) is the sodium salt of cellulose arboxymethyl and frequently used as viscous agent, paste and barrier agent.
|
-
- HY-125861A
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Methyl cellulose(Viscosity:15mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
- HY-125861B
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Methyl cellulose(Viscosity:400mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
- HY-125861C
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Methyl cellulose(Viscosity:1500mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
- HY-Y0703D
-
|
CMC-Na (average Mw 90000, DS=0.7, Viscosity:50-200 mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (average Mw 90000, DS=0.7, Viscosity:50-200 mPa.s) is the sodium salt of cellulose arboxymethyl and frequently used as viscous agent, paste and barrier agent .
|
-
- HY-125861
-
|
Methyl cellulose(Viscosity:100000mPa.s)
|
Co-solvents
|
|
Methylcellulose is a natural polymer which gels on heating. Methylcellulose is not toxic.
|
-
- HY-B2220
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Cellulase is an enzyme catalyzing the hydrolysis of certain linkages in cellulose and other carbohydrates.
|
-
- HY-W004293
-
|
Tridecyl Alcohol
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
1-Tridecanol is an organic compound commonly used as a surfactant, lubricant, and stabilizer, among others. It can be used in some cleaning products, preservatives and plastic additives, and can help enhance their performance and stability. In addition, the compound is used in some industrial fields, for example in the manufacture of products such as cellulose and paints. Although the compound has no direct medical application, it plays an important role in consumer products and industrial production.
|
-
- HY-A0104B
-
|
Hypromellose (Type I,Viscosity:100mPa.s); (Hydroxypropyl)methyl cellulose (Type I,Viscosity:100mPa.s); Celacol HPM 5000 (Type I,Viscosity:100mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Hypromellose (Type I,Viscosity:100mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
- HY-A0104A
-
|
Hypromellose (Type I,Viscosity:30mPa.s); (Hydroxypropyl)methyl cellulose (Type I,Viscosity:30mPa.s); Celacol HPM 5000 (Type I,Viscosity:30mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (Type I,Viscosity:30mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
- HY-A0104D
-
|
Hypromellose (Type I,Viscosity:4000mPa.s); (Hydroxypropyl)methyl cellulose (Type I,Viscosity:4000mPa.s); Celacol HPM 5000 (Type I,Viscosity:4000mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (Type I,Viscosity:4000mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
- HY-A0104C
-
|
Hypromellose (Type I,Viscosity:400mPa.s); (Hydroxypropyl)methyl cellulose (Type I,Viscosity:400mPa.s); Celacol HPM 5000 (Type I,Viscosity:400mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (Type I,Viscosity:400mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
- HY-A0104I
-
|
Hypromellose (Type II,Viscosity:100000mPa.s); (Hydroxypropyl)methyl cellulose (Type II,Viscosity:100000mPa.s); Celacol HPM 5000 (Type II,Viscosity:100000mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (Type II,Viscosity:100000mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
- HY-A0104E
-
|
Hypromellose (Type II,Viscosity:100mPa.s); (Hydroxypropyl)methyl cellulose (Type II,Viscosity:100mPa.s); Celacol HPM 5000 (Type II,Viscosity:100mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Hypromellose (Type II,Viscosity:100mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
- HY-A0104H
-
|
Hypromellose (Type II,Viscosity:15000mPa.s); (Hydroxypropyl)methyl cellulose (Type II,Viscosity:15000mPa.s); Celacol HPM 5000 (Type II,Viscosity:15000mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Hypromellose (Type II,Viscosity:15000mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
- HY-A0104F
-
|
Hypromellose (Type II,Viscosity:400mPa.s); (Hydroxypropyl)methyl cellulose (Type II,Viscosity:400mPa.s); Celacol HPM 5000 (Type II,Viscosity:400mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Hypromellose (Type II,Viscosity:400mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
-
- HY-A0104G
-
|
Hypromellose (Type II,Viscosity:4000mPa.s); (Hydroxypropyl)methyl cellulose (Type II,Viscosity:4000mPa.s); Celacol HPM 5000 (Type II,Viscosity:4000mPa.s)
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Hypromellose (Type II,Viscosity:4000mPa.s) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Area |
-
- HY-P1032S
-
|
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
Angiotensin I- 13C19, 15N3 (human, mouse, rat) is the 13C and 15N labeled Angiotensin I (human, mouse, rat) (HY-P1032). Cellulose (Pectin glycosidase) is a natural high molecular weight polysaccharide found in many plants and organisms. It is widely used in manufacturing industries, such as in paper making, textiles, food and medicine, etc. As a renewable resource, Cellulose is biodegradable and sustainable, and can also be used to manufacture chemicals such as Cellulose Esters, Cellulose Acetate and Cellulose Nitrate. In addition, Cellulose is often used as a food additive to increase the stability and quality of food .
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Category |
Target |
Chemical Structure |
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Chemical Structure |
-
- HY-B2221S5
-
|
|
|
U- 13C Cellulose from broccoli is the 13C labeled Cellulose (HY-B2221). Cellulose is a natural high molecular weight polysaccharide found in many plants and organisms. It is widely used in manufacturing industries, such as in paper making, textiles, food and medicine, etc. As a renewable resource, Cellulose is biodegradable and sustainable, and can also be used to manufacture chemicals such as Cellulose Esters, Cellulose Acetate and Cellulose Nitrate. In addition, Cellulose is often used as a food additive to increase the stability and quality of food .
|
-

-
- HY-B2221S4
-
|
|
|
U-13C Cellulose high DP from maize (high purity) is the 13C labeled Cellulose .
|
-

-
- HY-B2221S2
-
|
|
|
U-13C Cellulose high DP from wheat is the cellulose (HY-B2221) isolated from wheat, that is consist of abundant glucose and all the carbon atoms are labeled with isotope 13C .
|
-
-
- HY-B2221S1
-
|
|
|
U- 13C Cellulose from chicory is the 13C labeled Cellulose (HY-B2221). Cellulose (Pectin glycosidase) is a natural high molecular weight polysaccharide found in many plants and organisms. It is widely used in manufacturing industries, such as in paper making, textiles, food and medicine, etc. As a renewable resource, Cellulose is biodegradable and sustainable, and can also be used to manufacture chemicals such as Cellulose Esters, Cellulose Acetate and Cellulose Nitrate. In addition, Cellulose is often used as a food additive to increase the stability and quality of food .
|
-
-
- HY-B2221S
-
|
|
|
U- 13C Cellulose high DP from potato is the 13C labeled Cellulose (HY-B2221). Cellulose (Pectin glycosidase) is a natural high molecular weight polysaccharide found in many plants and organisms. It is widely used in manufacturing industries, such as in paper making, textiles, food and medicine, etc. As a renewable resource, Cellulose is biodegradable and sustainable, and can also be used to manufacture chemicals such as Cellulose Esters, Cellulose Acetate and Cellulose Nitrate. In addition, Cellulose is often used as a food additive to increase the stability and quality of food .
|
-

-
- HY-B2221S3
-
|
|
|
U- 13C Cellulose high DP from maize is the 13C labeled Cellulose (HY-B2221). Cellulose (Pectin glycosidase) is a natural high molecular weight polysaccharide found in many plants and organisms. It is widely used in manufacturing industries, such as in paper making, textiles, food and medicine, etc. As a renewable resource, Cellulose is biodegradable and sustainable, and can also be used to manufacture chemicals such as Cellulose Esters, Cellulose Acetate and Cellulose Nitrate. In addition, Cellulose is often used as a food additive to increase the stability and quality of food .
|
-

-
- HY-P1032S
-
|
|
|
Angiotensin I- 13C19, 15N3 (human, mouse, rat) is the 13C and 15N labeled Angiotensin I (human, mouse, rat) (HY-P1032). Cellulose (Pectin glycosidase) is a natural high molecular weight polysaccharide found in many plants and organisms. It is widely used in manufacturing industries, such as in paper making, textiles, food and medicine, etc. As a renewable resource, Cellulose is biodegradable and sustainable, and can also be used to manufacture chemicals such as Cellulose Esters, Cellulose Acetate and Cellulose Nitrate. In addition, Cellulose is often used as a food additive to increase the stability and quality of food .
|
-

-
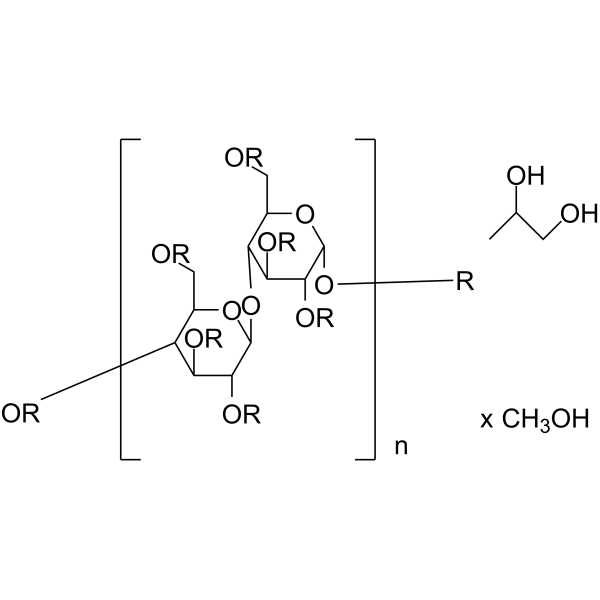
- HY-133673S
-
|
|
|
Mono(3-carboxypropyl) phthalate-d4 (MCPP-d4) is a deuterium labeled Mono(3-carboxypropyl) phthalate (HY-133673). Mono(3-carboxypropyl) phthalate (MCPP) is a metabolite of Di-n-octyl phthalate. Di-n-octyl phthalate (DnOP) is a plasticizer used in polyvinyl chloride plastics, cellulose esters, and polystyrene resins .
|
-

Your information is safe with us. * Required Fields.
Inquiry Information
- Product Name:
- Cat. No.:
- Quantity:
- MCE Japan Authorized Agent: