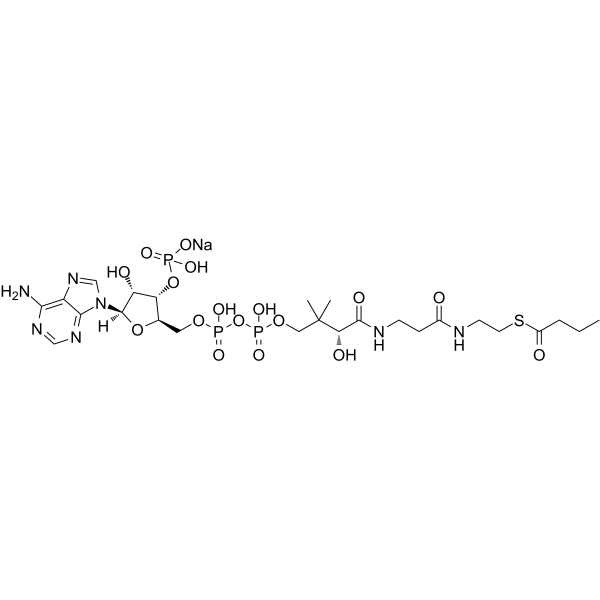Search Result
Results for "
STEP
" in MedChemExpress (MCE) Product Catalog:
7
Biochemical Assay Reagents
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Areas |
Chemical Structure |
-
- HY-W040209
-
|
α-NPO
|
Fluorescent Dye
|
Others
|
|
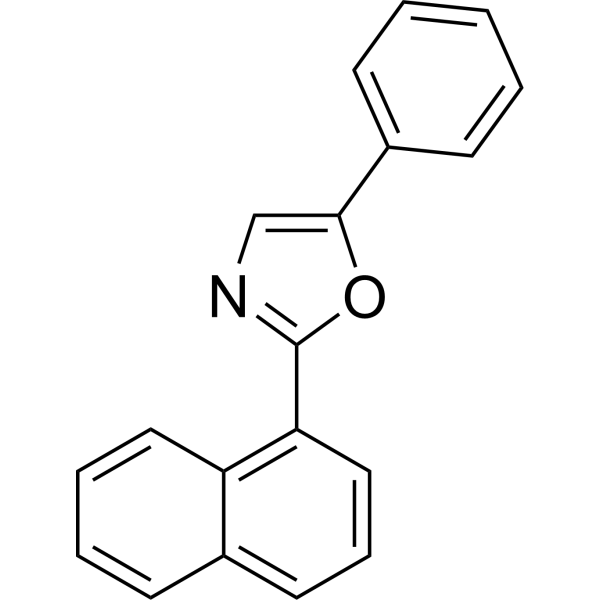
2-(Naphthalen-1-yl)-5-phenyloxazole (α-NPO) is an organic fluorescent dye. 2-(Naphthalen-1-yl)-5-phenyloxazole has a nitrogen atom in its structure that can interfere with the nitrogen content from the amination step .
|
-
-
- HY-10250A
-
|
TCN-P sodium
|
ATP Synthase
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
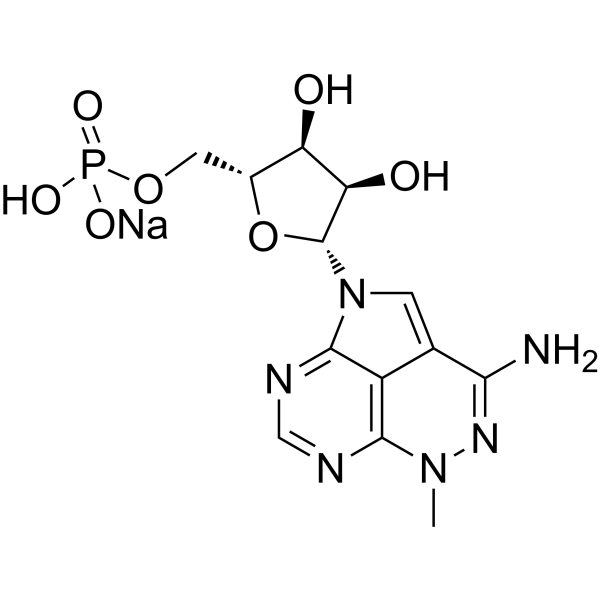
Triciribine phosphate sodium inhibits amidophosphoribosyltransferase by an allosteric mechanism which affects the first committed step of de novo purine biosynthesis. Triciribine phosphate sodium also inhibits IMP dehydrogenase which is the first committed step of guanosine nucleotide synthesis. Tricilibine phosphate does not affect ligase activity .
|
-
-
- HY-P3355
-
|
|
iGluR
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
p-fin4 is a peptide inhibitor of STEP Phosphatase-GluA2 AMPA receptor interaction with a Ki of 0.4 μM. p-fin4 restores the memory deficits and displays anxiolytic and antidepressant effects in a scopolamine-treated rat model. p-fin4 is a promising lead compound for novel cognitive enhancers and/or behavioral modulators .
|
-

-
- HY-P3354
-
|
|
iGluR
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
p3Ysh-3 is a peptide inhibitor of STEP Phosphatase-GluA2 AMPA receptor interaction with a Ki of 1.09 μM. p3Ysh-3 restores the memory deficits and displays anxiolytic and antidepressant effects in a scopolamine-treated rat model. p3Ysh-3 is a promising lead compound for novel cognitive enhancers and/or behavioral modulators .
|
-
-
- HY-10250
-
|
TCN-P
|
ATP Synthase
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
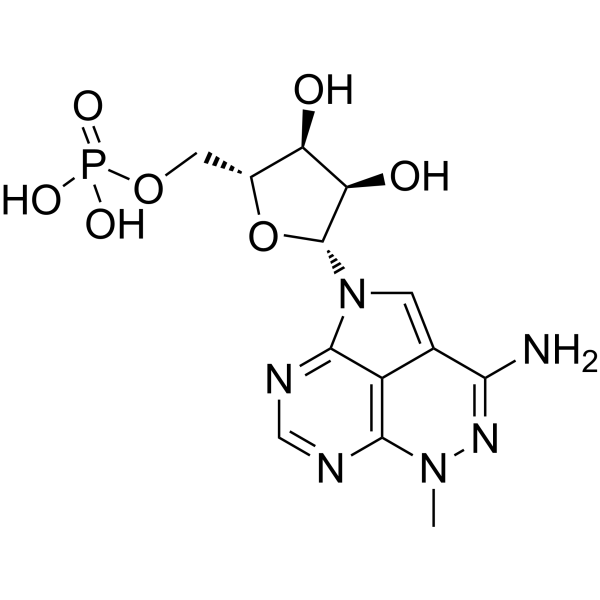
Triciribine phosphate (TCN-P) inhibits amidophosphoribosyltransferase by an allosteric mechanism which affects the first committed step of de novo purine biosynthesis. Triciribine phosphate also inhibits IMP dehydrogenase which is the first committed step of guanosine nucleotide synthesis. Tricilibine phosphate does not affect ligase activity .
|
-
-
- HY-N0537
-
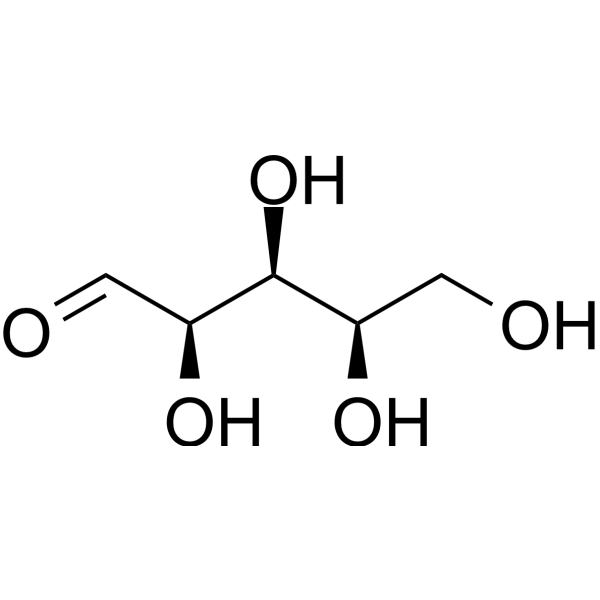
Xylose
2 Publications Verification
D-(+)-Xylose; (+)-Xylose; Wood sugar
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
D-(+)-xylose (Xylose) is a natural compound that is catalyzed by xylose isomerase to form xylulose, which is a key step in the anaerobic ethanol fermentation of xylose.
|
-
-
- HY-138177
-
|
Butyryl CoA sodium
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
Butyryl-Coenzyme A (Butyryl CoA) sodium is a coenzyme A-containing derivative of Butyric acid. Butyryl-Coenzyme A sodium is responsible for the final step of Butyrate production in bacteria .
|
-
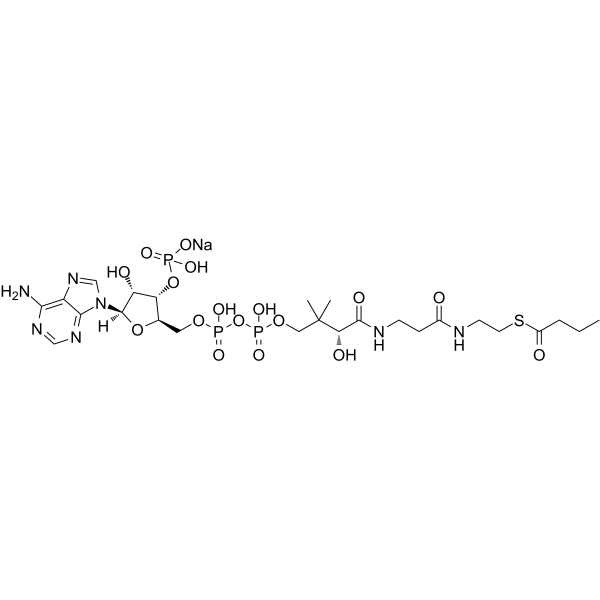
-
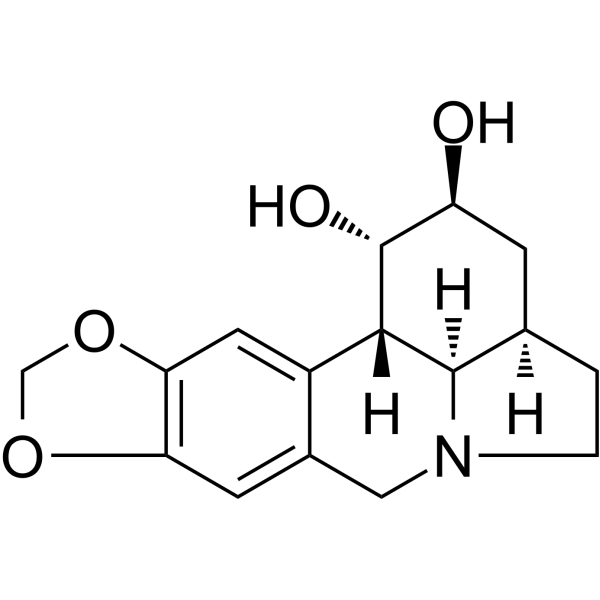
- HY-N2403
-
|
|
Others
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
Dihydrolycorine, isolated from Lycoris radiate Herb, is an inhibitor of protein synthesis in eukarytic cells by inhibiting the peptide bone formation step .
|
-
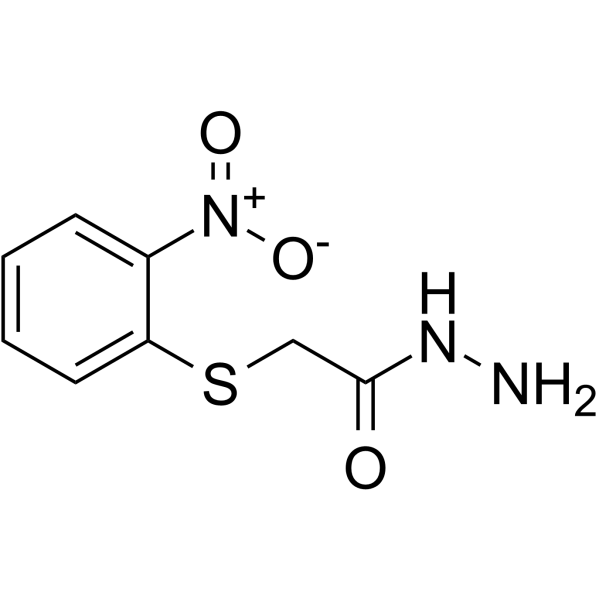
-
- HY-116872
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
MAC13772 is a potent inhibitor of the enzyme BioA (IC50=250 nM), the antepenultimate step in biotin biosynthesis. MAC13772 is a novel antibacterial compound .
|
-
-
- HY-E70121
-
|
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
Succinyl-CoA synthetase catalyzes the only substrate-level phosphoryl-ation step in the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Succinyl-CoA synthetase is a phosphate target for the activation of mitochondrial metabolism .
|
-
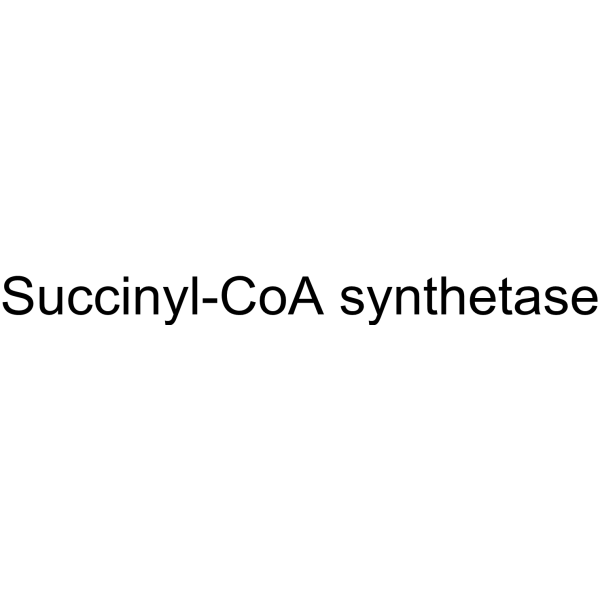
-
- HY-137899
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
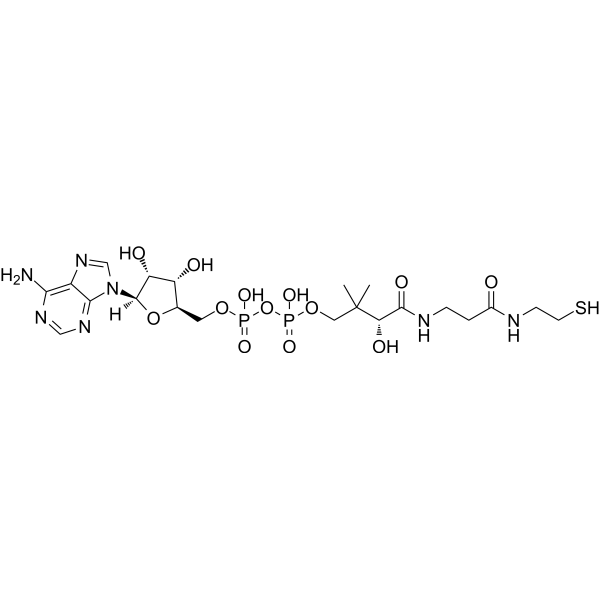
Dephospho-CoA is A direct precursor of Coenzyme A (CoA). Dephospho-CoA kinase (DPCK) catalyzes the ATP-dependent phosphorylation of Dephospho-CoA, the final step in coenzyme A (CoA) biosynthesis .
|
-
-
- HY-E70079
-
|
CBL
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Infection
|
|
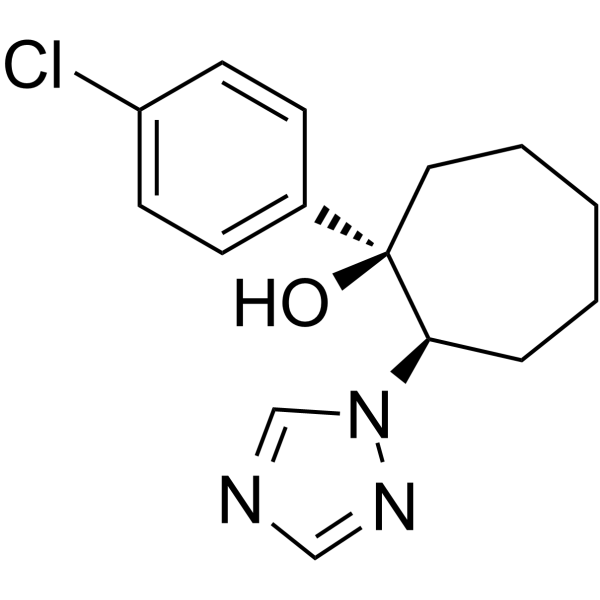
Cystathionine β-lyase, Recombinant Microorganisms (CBL) is an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of cystathionine to homocysteine, the penultimate step in methionine biosynthesis. Cystathionine β-lyase is important for bacterial virulence .
|
-

-
- HY-135307
-
|
Huanjunzuo
|
Fungal
|
Infection
|
|
SSF-109 is a broad-spectrum fungicide which has protective activity against plant disease. SSF-109 inhibits the biosynthesis of ergosterol at the 14α-demethylation step in Botrytis cinerea .
|
-
-
- HY-141690A
-
|
|
PI3K
|
Cancer
|
|
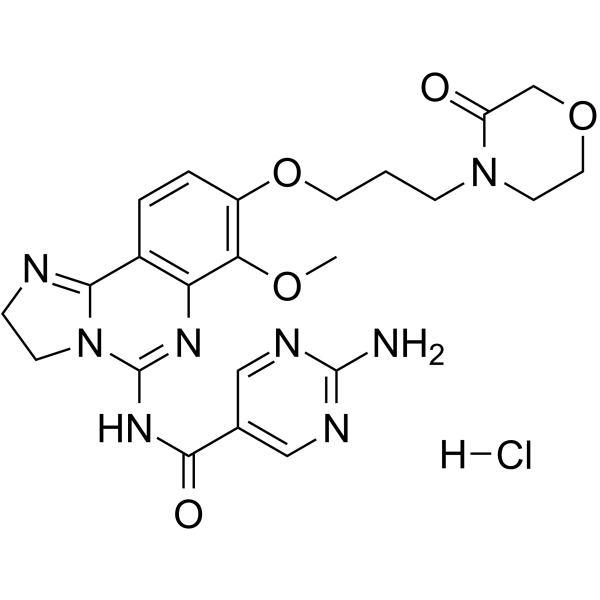
PI3K-IN-19 hydrochloride is a phosphotidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor extracted from patent WO2017153220, step 5 .
|
-
-
- HY-151855
-
|
|
ADC Linker
|
Others
|
|
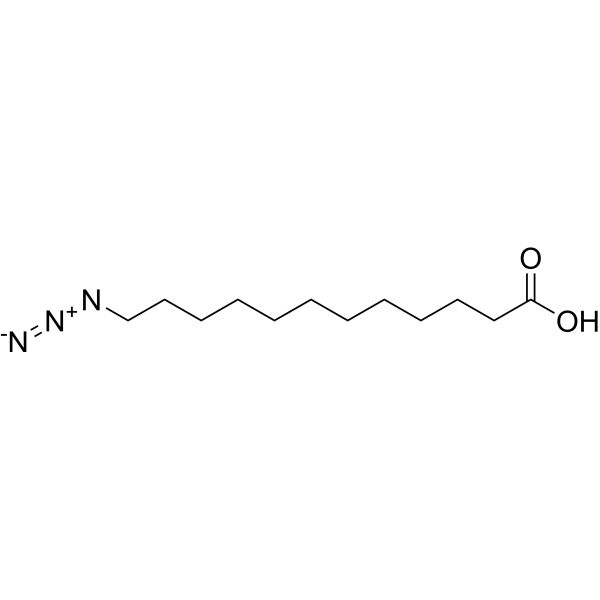
Azido Myristic Acid is a click chemistry reagent containing an azide group. Azido Myristic Acid can be used to identify and characterize post-translationally myristylated proteins with using a simple and robust two-step labeling and detection technique .
|
-
-
- HY-W422359A
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
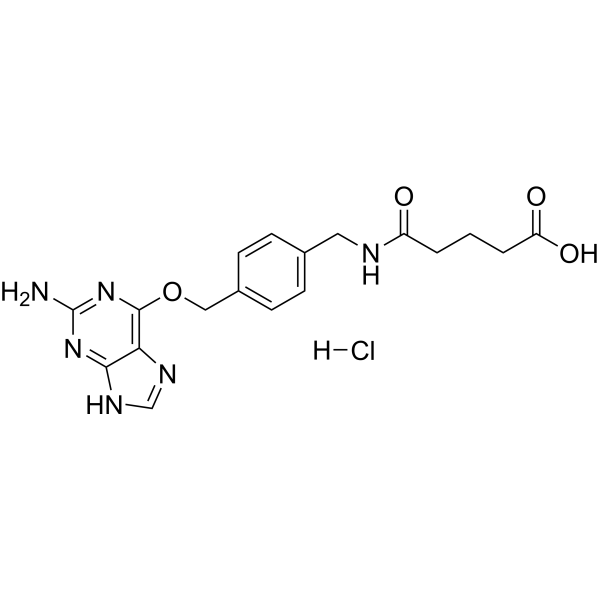
2-Aminopurine-O-Ph-NHCO-C3-COOH hydrochloride is the acid form in the previous step of the final product 2-Aminopurine-O-Ph-NHCO-C3-NHS ester (HY-143336) .
|
-
-
- HY-143450
-
|
|
Tyrosinase
|
Others
|
|
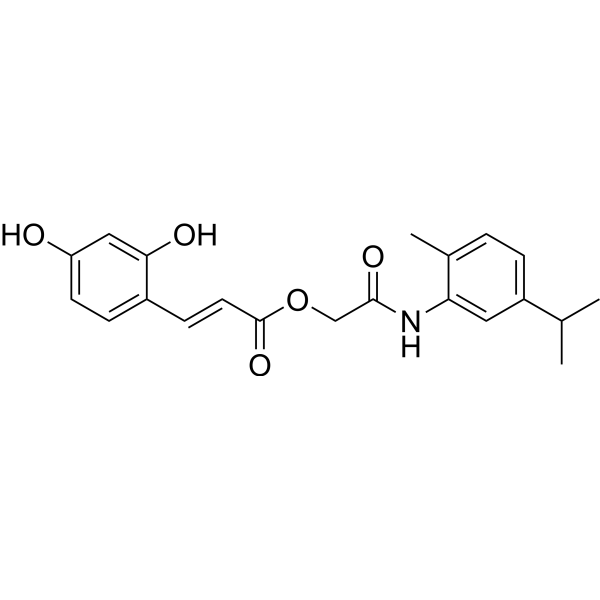
Tyrosinase-IN-3 (compound 54) is a potent inhibitor of tyrosinase. Tyrosinase is a copper-containing metalloenzyme that is responsible for the rate-limiting catalytic step in the melanin biosynthesis and enzymatic browning. Tyrosinase-IN-3 has the potential for the research of skin whitening agents and food preservatives .
|
-
-
- HY-143451
-
|
|
Tyrosinase
|
Others
|
|
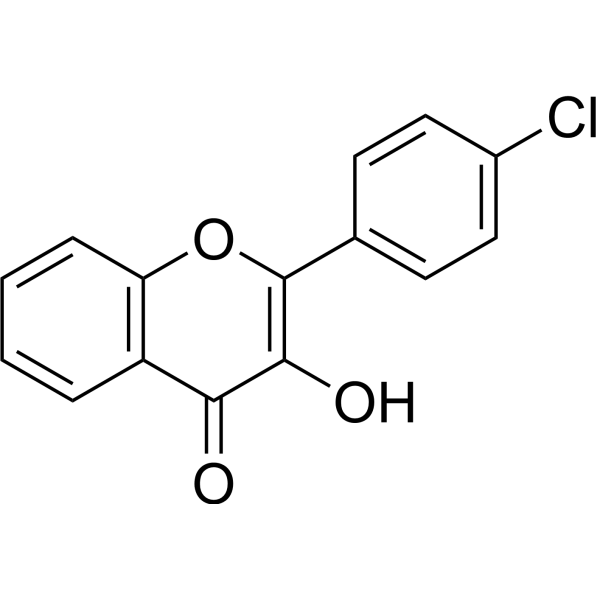
Tyrosinase-IN-4 (compound 34) is a potent inhibitor of tyrosinase. Tyrosinase is a copper-containing metalloenzyme that is responsible for the rate-limiting catalytic step in the melanin biosynthesis and enzymatic browning. Tyrosinase-IN-4 has the potential for the research of skin whitening agents and food preservatives .
|
-
-
- HY-143448
-
|
|
Tyrosinase
|
Others
|
|
Tyrosinase-IN-1 (compound 90) is a potent inhibitor of tyrosinase. Tyrosinase is a copper-containing metalloenzyme that is responsible for the rate-limiting catalytic step in the melanin biosynthesis and enzymatic browning. Tyrosinase-IN-1 has the potential for the research of skin whitening agents and food preservatives .
|
-
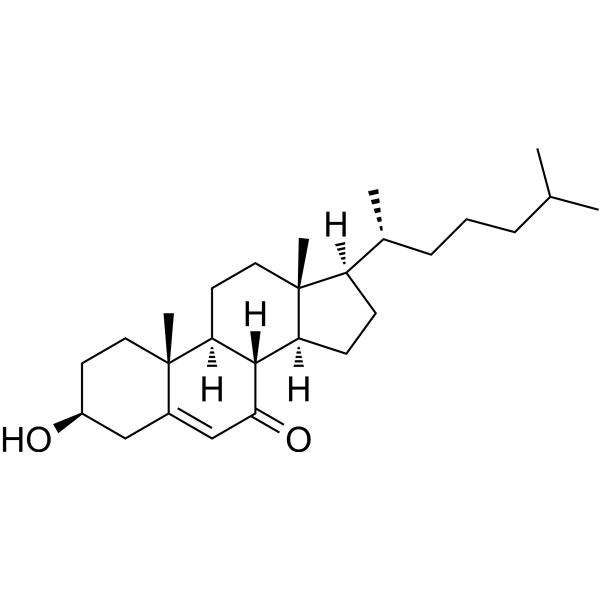
-
- HY-143449
-
|
|
Tyrosinase
|
Others
|
|
Tyrosinase-IN-2 (compound 67) is a potent inhibitor of tyrosinase. Tyrosinase is a copper-containing metalloenzyme that is responsible for the rate-limiting catalytic step in the melanin biosynthesis and enzymatic browning. Tyrosinase-IN-2 has the potential for the research of skin whitening agents and food preservatives .
|
-
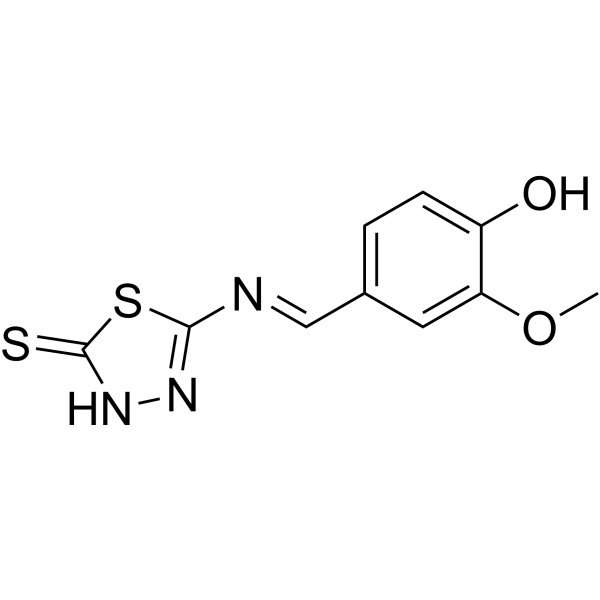
-
- HY-113342
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
7-Ketocholesterol, toxic oxysterol, inhibits the rate-limiting step in bile acid biosynthesis cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase, as well as strongly inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase (the rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis). 7-Ketocholesterol induces cell apoptosis .
|
-
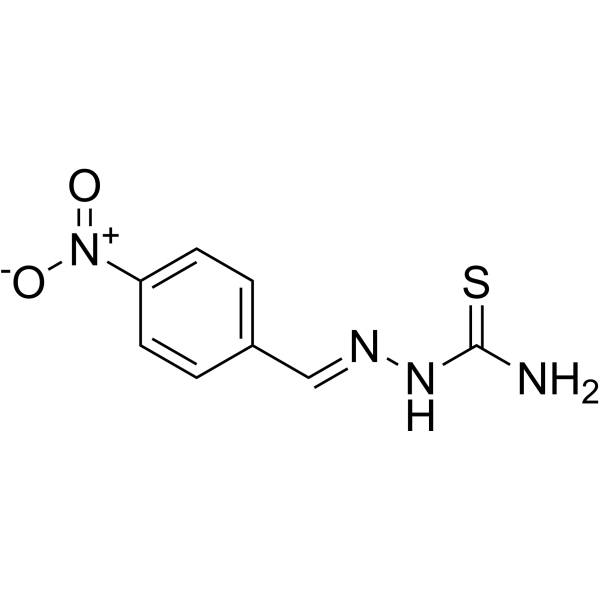
-
- HY-163209
-
|
(S,R,S)-AHPC-PEG6-NH2 hydrochloride
|
Ligands for E3 Ligase
|
Cancer
|
|
VH 032 amide-PEG6-amine hydrochloride (Step 4) is a functionalized von-Hippel-Lindau protein-ligand (VHL) for PROTAC development, consisting of an E3 ligand and a PEG6 ligand. Terminal amines can be coupled to target protein ligands .
|
-
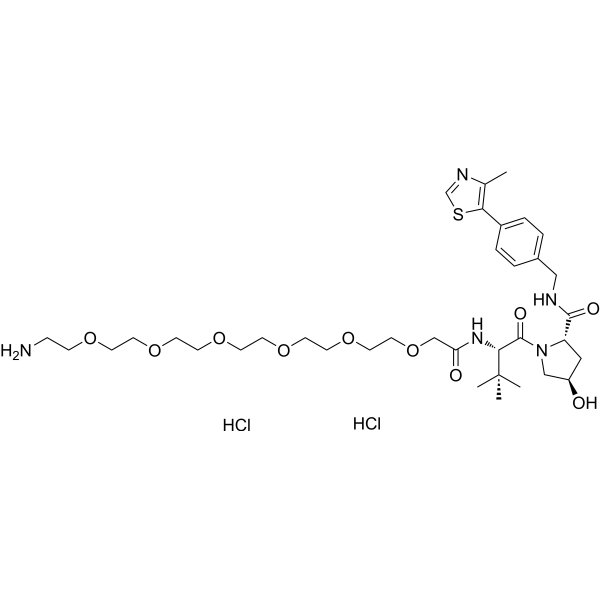
-
- HY-P2752
-
|
LPL
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
Lipoprotein lipase, Pseudomonas sp (LPL) is a multifunctional enzyme from adipose tissue, heart and skeletal muscle, islets and macrophages. Lipoprotein lipase promotes normal lipoprotein metabolism, delivery and utilization of tissue-specific substrates. Lipoprotein lipase catalyzes the rate-limiting step of lipids in blood circulation .
|
-

-
- HY-109045
-
|
BTA074; AP 611074
|
E1/E2/E3 Enzyme
HPV
|
Infection
|
|
Teslexivir (BTA074) is a potent antiviral agent. Teslexivir is a potent and selective inhibitor of the interaction between two essential viral proteins, E1 and E2, an association that is a necessary step in the DNA replication and thus viral production for Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) 6 and 11. Teslexivir can be used for condyloma research .
|
-
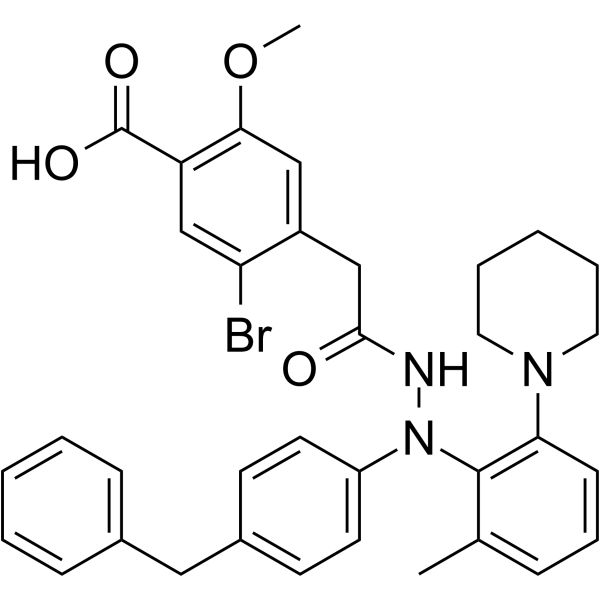
-
- HY-B1599
-
|
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Infection
|
|
Chloramphenicol palmitate is an orally active broad spectrum antibiotic and has a broad spectrum of activity against gram positive and gram negative bacteria. Chloramphenicol palmitate inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by blocking the peptidyl transferase step. Chloramphenicol palmitate can be used as bacterial selection agent in transformed cells containing chloramphenicol resistance genes .
|
-
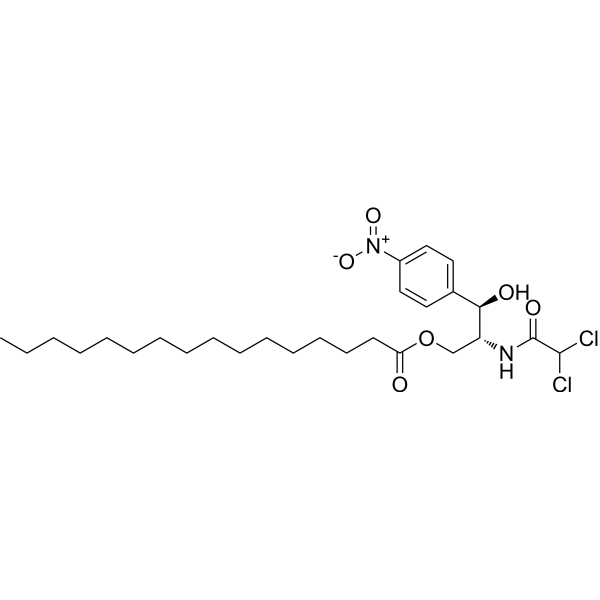
-
- HY-112732
-
|
|
Apoptosis
|
Metabolic Disease
Cancer
|
|
Sparfosic acid, a DNA antimetabolite agent, is a potent inhibitor of aspartate transcarbamoyl transferase, the enzyme catalyzing the second step of de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis. Sparfosic acid synergistically enhances the cytotoxicity of a combination of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and interferon-alpha (IFN) against human colon cancer cell lines .
|
-
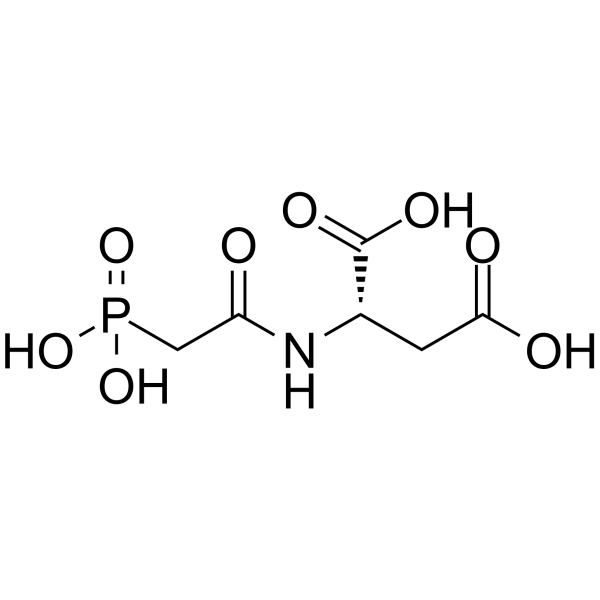
-
- HY-109045A
-
|
BTA074 hydrochloride; AP 611074 hydrochloride
|
E1/E2/E3 Enzyme
HPV
|
Infection
|
|
Teslexivir (BTA074) hydrochloride is a potent antiviral agent. Teslexivir hydrochloride is a potent and selective inhibitor of the interaction between two essential viral proteins, E1 and E2, an association that is a necessary step in the DNA replication and thus viral production for Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) 6 and 11. Teslexivir hydrochloride can be used for condyloma research .
|
-
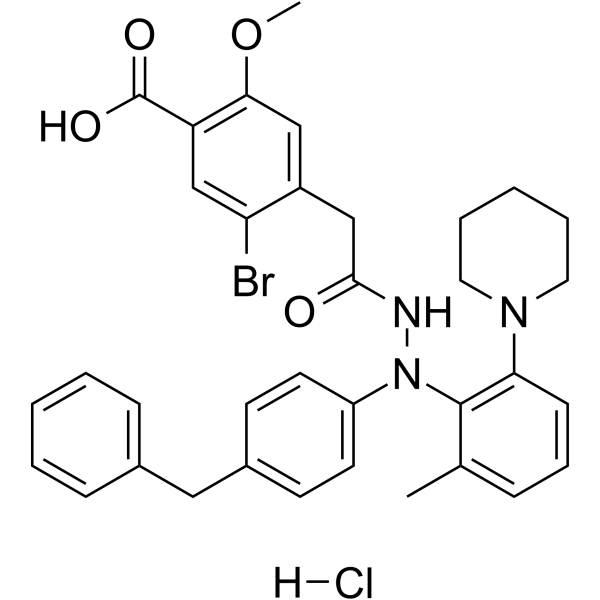
-
- HY-113149
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
Reactive Oxygen Species
|
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
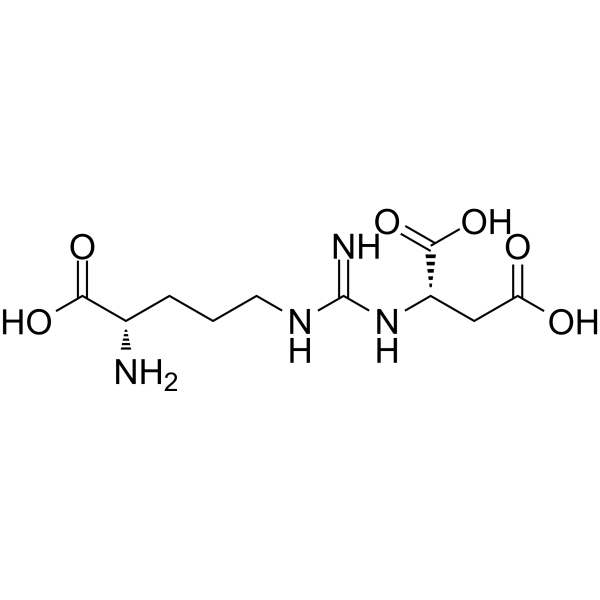
Argininosuccinic acid participates in the fourth step of the urea cycle, with being cleaved to arginine and fumaric acid by argininosuccinic acid lyase (ASL). Argininosuccinic acid reduces reduced glutathione (GSH) level, and increases the production of reactive oxygen species in cerebral cortex and striatum. Argininosuccinic acid causes lipid peroxidation and protein oxidation, and induces oxidative stress in the developing rat brain .
|
-
-
- HY-W016628
-
|
L-Gulonolactone
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
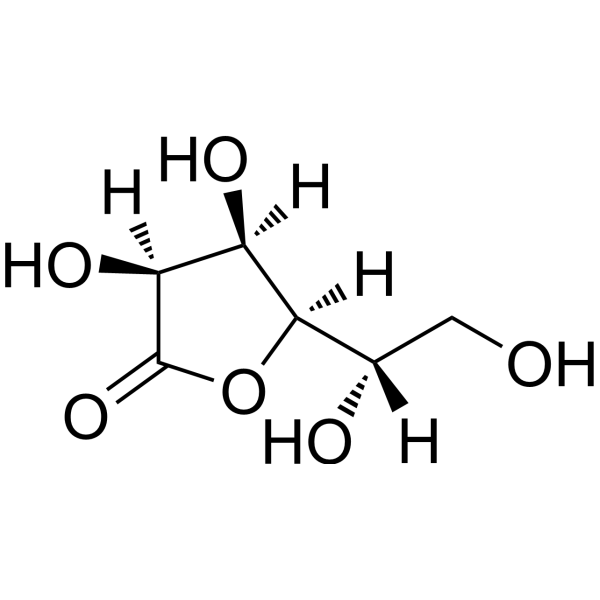
L-Gulono-1,4-lactone is a substrate of L-gulono-1,4-lactone oxidoreductase, which catalyzes the last step of the biosynthesis of L-ascorbic (Vatamin) C. In other words, L-Gulono-1,4-lactone is a direct precursor of vitamin C in animals, in plants and in some protists.
|
-
-
- HY-N0240
-
|
|
Others
|
Cancer
|
|
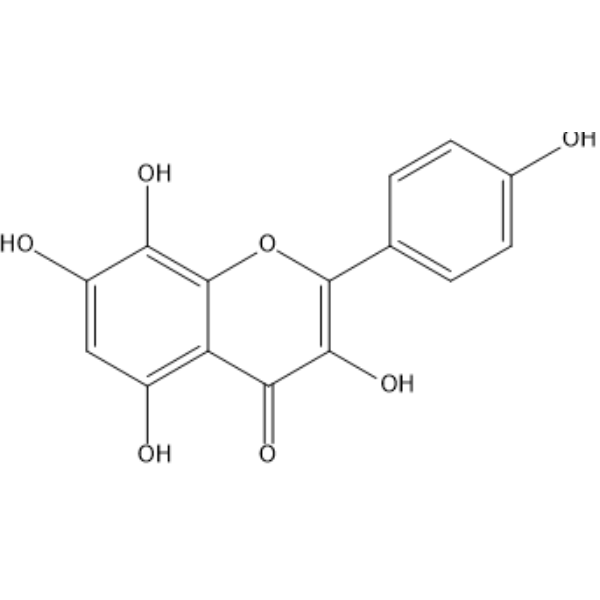
Herbacetin is a natural flavonoid from flaxseed, exerts various pharmacological activities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anticancer effects . Herbacetin is an Ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) allosteric inhibitor, directly binds to Asp44, Asp243, and Glu384 on ODC. Ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) is a rate-limiting enzyme in the first step of polyamine biosynthesis .
|
-
-
- HY-P2832
-
|
ACS
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
Acyl coenzyme A synthetase (ACS), namely acetyl coenzyme A synthetase, is often used in biochemical research. Acyl coenzyme A synthetase can catalyze the activation of fatty acids by coenzyme A through a two-step thioesterification reaction to produce acyl coenzyme A, and then participate in a variety of anabolic and catabolic lipid metabolism pathways, and participate in the TCA cycle in aerobic respiration .
|
-

-
- HY-P2917
-
|
GyK
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
Glycerol kinase (EC 2.7.1.30) (GyK) is a bacterial sugar kinase, is often used in biochemical studies. Glycerol kinase catalyzes the first step of glycerol metabolism by transforming the triol into glycerol-3-P (G3P). Glycerol kinase is crucial for regulating channel/facilitator-independent uptake of glycerol into the cell .
|
-
-
- HY-113149A
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
Reactive Oxygen Species
|
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
Argininosuccinic acid disodium participates in the fourth step of the urea cycle and is cleaved into arginine and fumarate by argininosuccinate lyase (ASL). Argininosuccinic acid disodium reduces reduced glutathione (GSH) concentrations and increases reactive oxygen species production in the cerebral cortex and striatum. Argininosuccinic acid disodium causes lipid peroxidation and protein oxidation and also induces oxidative stress in the developing rat brain .
|
-
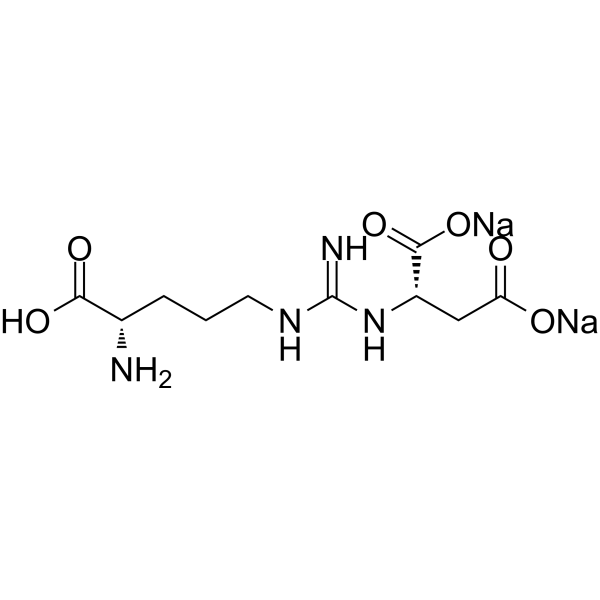
-
- HY-112732B
-
|
|
Apoptosis
|
Metabolic Disease
Cancer
|
|
Sparfosic acid trisodium is a DNA antimetabolite agent and a potent inhibitor of aspartate transcarbamoyl transferase. Aspartate transcarbamoyl transferase catalyzes the second step of de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis. Sparfosic acid trisodium synergistically enhances the cytotoxicity of a combination of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and interferon-alpha (IFN) against human colon cancer cell lines .
|
-
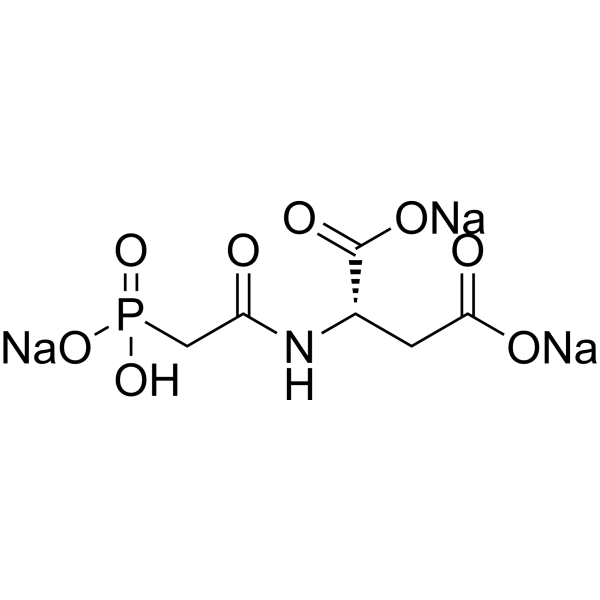
-
- HY-148161
-
|
|
DNA/RNA Synthesis
|
Cancer
|
|
L82-G17 is an uncompetitive DNA ligase I (Lig I)-selective inhibitor. L82-G17 inhibits the third step of the ligation reaction, phosphodiester bond formation. L82-G17can be used as a probe of the catalytic activity .
|
-
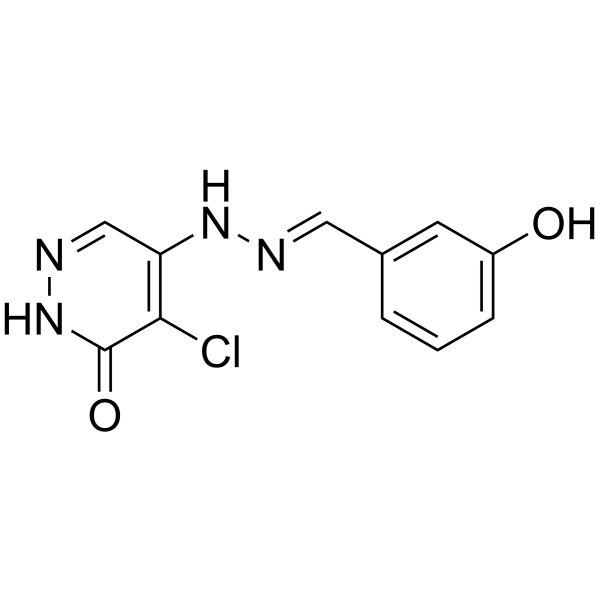
-
- HY-161304
-
|
|
HDAC
|
Cancer
|
|
HDAC6-IN-33 (compound 6) is a selective and irreversible HDAC6 inhibitor with an IC50 of 193 nM. HDAC6-IN-33 shows no activity against HDAC1-4. HDAC6-IN-33 is a tight-binding HDAC6 inhibitor capable of inhibiting HDAC6 via a two-step slow-binding mechanism .
|
-
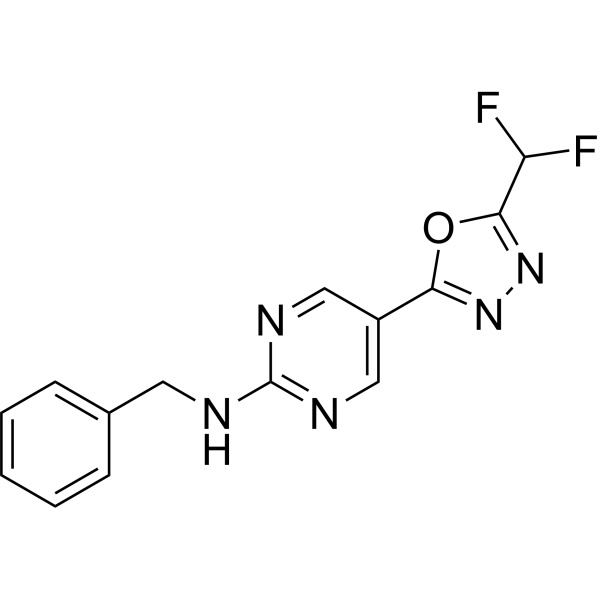
-
- HY-10016
-
E 2012
Maximum Cited Publications
6 Publications Verification
|
γ-secretase
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
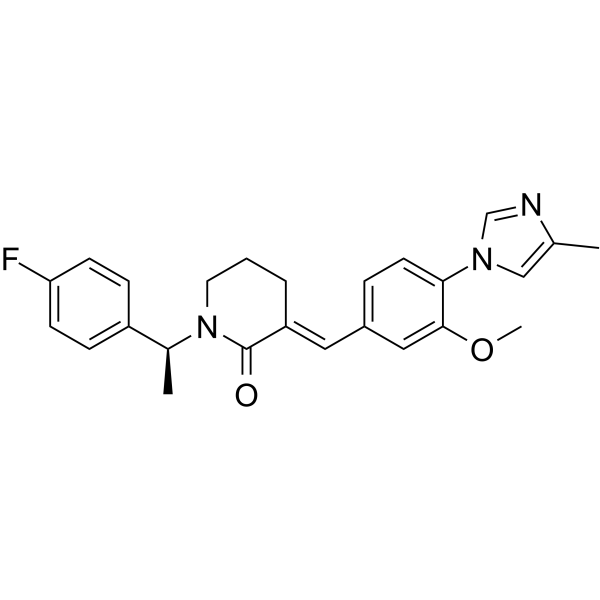
E 2012 is a potent gamma (γ) secretase modulator without affecting Notch processing. E 2012 inhibits 3β-hydroxysterol Δ24-reductase (DHCR24) at the final step in the cholesterol biosynthesis. E 2012 aims at Alzheimer's disease by reduction of amyloid β-42, and induces cataract following repeated doses in the rat .
|
-
-
- HY-113149R
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
Reactive Oxygen Species
|
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
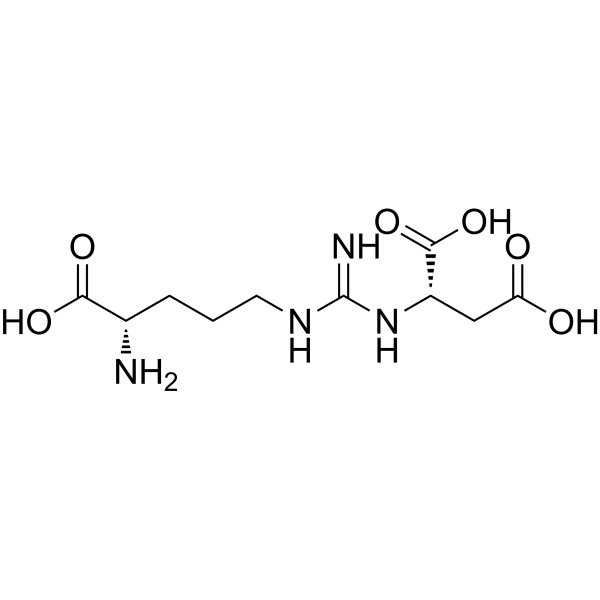
Argininosuccinic acid (Standard) is the analytical standard of Argininosuccinic acid. This product is intended for research and analytical applications. Argininosuccinic acid participates in the fourth step of the urea cycle, with being cleaved to arginine and fumaric acid by argininosuccinic acid lyase (ASL). Argininosuccinic acid reduces reduced glutathione (GSH) level, and increases the production of reactive oxygen species in cerebral cortex and striatum. Argininosuccinic acid causes lipid peroxidation and protein oxidation, and induces oxidative stress in the developing rat brain .
|
-
-
- HY-B1599R
-
|
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Infection
|
|
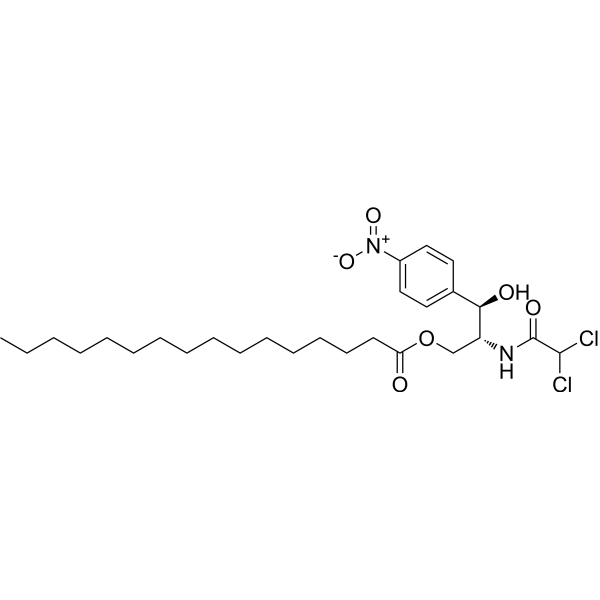
Chloramphenicol palmitate (Standard) is the analytical standard of Chloramphenicol palmitate. This product is intended for research and analytical applications. Chloramphenicol palmitate is an orally active broad spectrum antibiotic and has a broad spectrum of activity against gram positive and gram negative bacteria. Chloramphenicol palmitate inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by blocking the peptidyl transferase step. Chloramphenicol palmitate can be used as bacterial selection agent in transformed cells containing chloramphenicol resistance genes .
|
-
-
- HY-124591
-
|
|
5-HT Receptor
Monoamine Oxidase
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
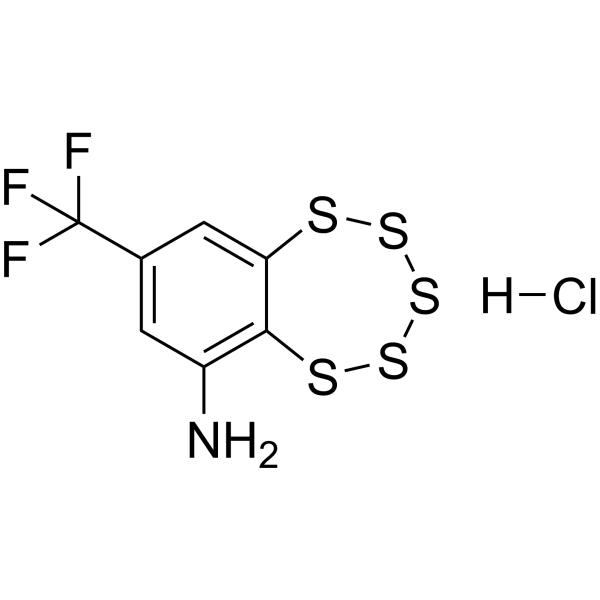
TC-2153 is a selective inhibitor of striatal-enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase (STEP), with psychotropic activity and low acute toxicity. TC-2153 increases the expression of brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF) in the brain. And it decreases MAOA and 5-HT1A receptors mRNA level in midbrain. TC-2153 also inhibits 5-HT2A receptor-mediated signaling .
|
-
-
- HY-131030
-
|
JF669, SE; JF669, NHS
|
Fluorescent Dye
|
Others
|
|
Janelia Fluor 669, SE (JF669, SE), a red fluorescent dye, can be directly reacted with the available thiol-containing HaloTag ligand under mild conditions (DIEA, DMF) to afford a JF669HaloTag ligand in a single step (Ex = 669 nm; Em = 682 nm) . Janelia Fluor products are licensed under U.S. Pat. Nos. 9,933,417, 10,018,624 and 10,161,932 and other patents from Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
|
-
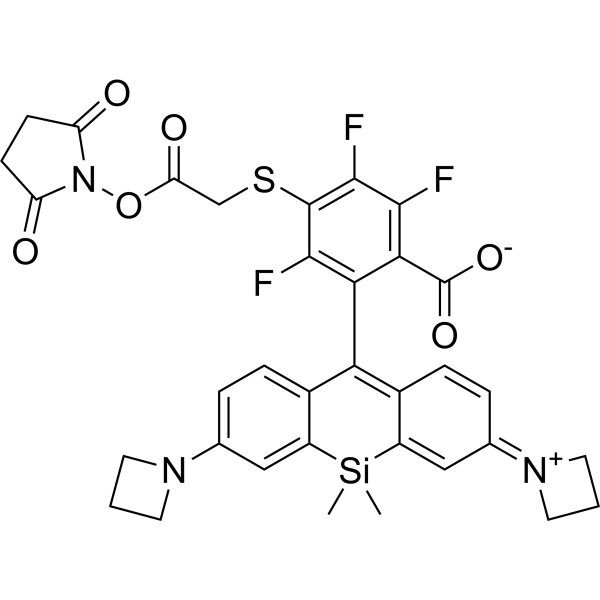
-
- HY-110078
-
|
|
p97
Apoptosis
|
Cancer
|
|
Eeyarestatin I, a potent endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein degradation (ERAD) inhibitor, is a potent protein translocation inhibitor. Eeyarestatin I inhibits Sec61 translocon. Eeyarestatin I targets the p97-associated deubiquitinating process (PAD) and inhibits atx3-dependent deubiquitination. Eeyarestatin I interferes at a step prior to proteasomal degradation. Eeyarestatin I induces cell death via the proapoptotic protein NOXA and has anticancer effects .
|
-
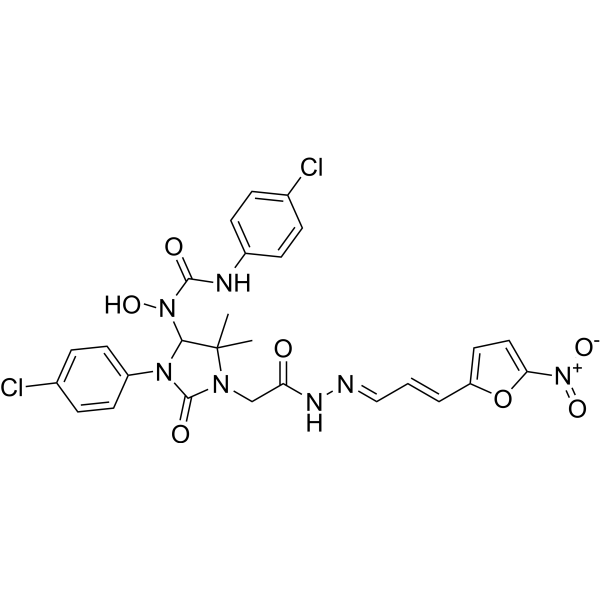
-
- HY-B1119
-
|
|
Bacterial
Fungal
Antibiotic
Apoptosis
|
Infection
Cancer
|
|
Triclosan is a broad-spectrum antibacterial agent that inhibits bacterial fatty acid synthesis at the enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase (FabI) step. Triclosan inhibits E. coli enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase (FabI) and FabI containing a glycine-to-valine substitution at position 93 (FabIG93V) with IC50s of 2 µM and 10 µM, respectively. Triclosan causes apoptotic effect in cultured rat neural stem cells (NSC). Triclosan exacerbates colitis and colitis-associated colorectal tumorigenesis in animal models .
|
-
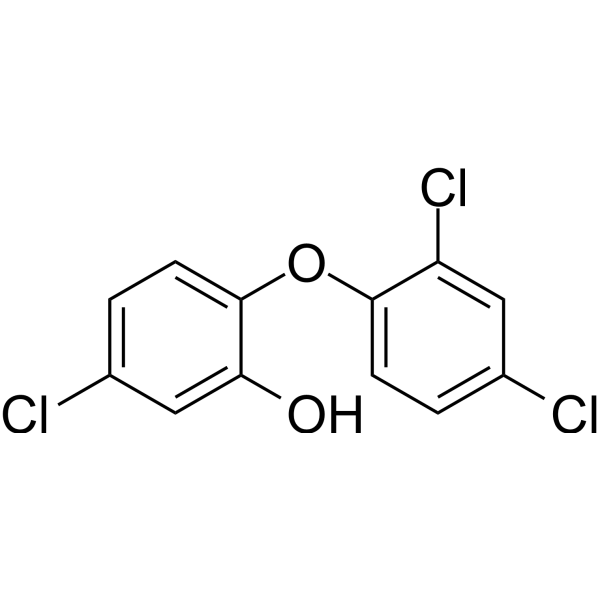
-
- HY-151656
-
|
Azido Palmitic Acid
|
ADC Linker
|
Others
|
|
15-Azido-pentadecanoic acid is a click chemistry reagent containing an azide group. Azido Palmitic Acid can be used to identify and characterize post-translationally palmitylated proteins with using a simple and robust two-step labeling and detection technique . 15-Azido-pentadecanoic acid is a click chemistry reagent, it contains an Azide group and can undergo copper-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition reaction (CuAAc) with molecules containing Alkyne groups. Strain-promoted alkyne-azide cycloaddition (SPAAC) can also occur with molecules containing DBCO or BCN groups.
|
-
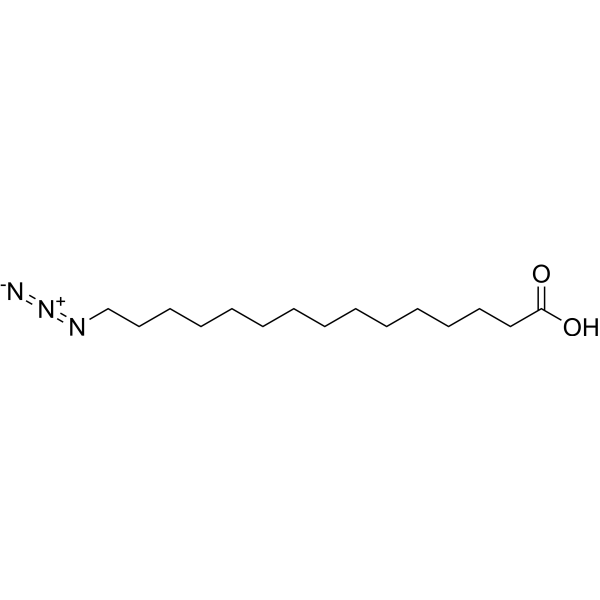
-
- HY-155156
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
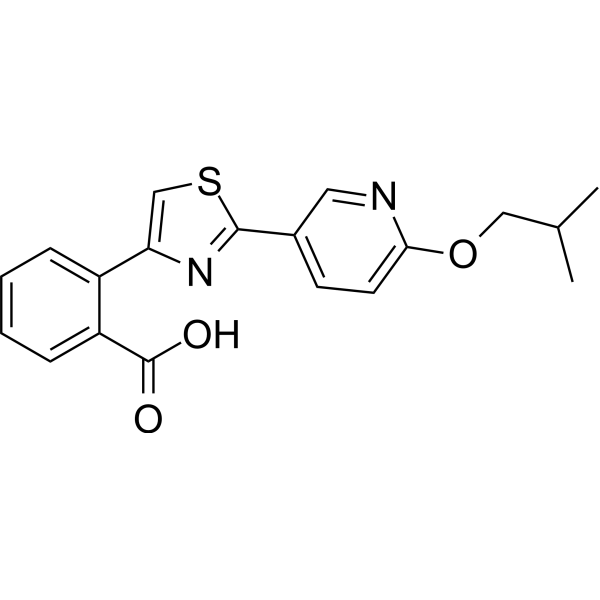
PF-07238025 is a BCKDC kinase (BDK) inhibitor (EC50=19 nM). PF-07238025 stabilizes the interaction between BDK and BCKDH core subunit E2 and prevents phosphorylation of E1. While BDK mediates branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase (BCKDH) phosphorylation, and inhibition of BCKDH is involved in controlling the rate-limiting step of branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) degradation. Impaired BCAA catabolism has been associated with several diseases, particularly cardiometabolic diseases, including heart failure (HF), type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and obesity. PF-07238025 improved cardiometabolic endpoints and improves glucose tolerance in mice .
|
-
-
- HY-155157
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
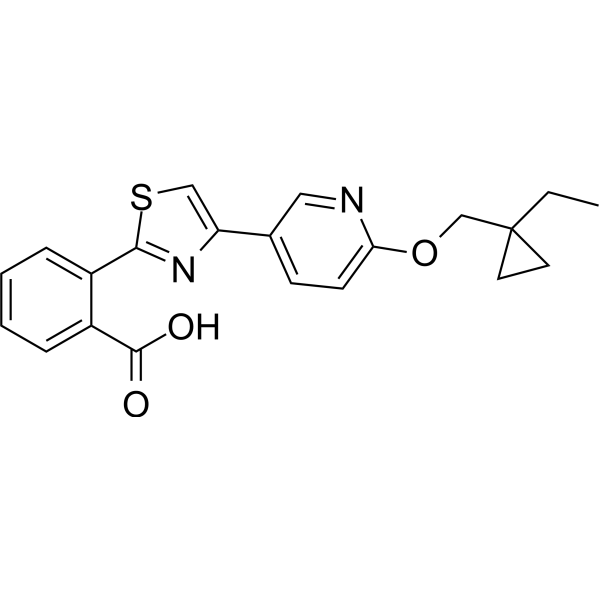
PF-07247685 is a BCKDC kinase (BDK) inhibitor (EC50=2.2 nM). PF-07247685 stabilizes the interaction between BDK and BCKDH core subunit E2 and prevents phosphorylation of E1. While BDK mediates branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase (BCKDH) phosphorylation, and inhibition of BCKDH is involved in controlling the rate-limiting step of branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) degradation. Impaired BCAA catabolism has been associated with several diseases, particularly cardiometabolic diseases, including heart failure (HF), type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and obesity. PF-07247685 improved cardiometabolic endpoints and improves glucose tolerance in mice .
|
-
-
- HY-42771
-
|
|
E3 Ligase Ligand-Linker Conjugates
Autophagy
Apoptosis
|
Cancer
|
|
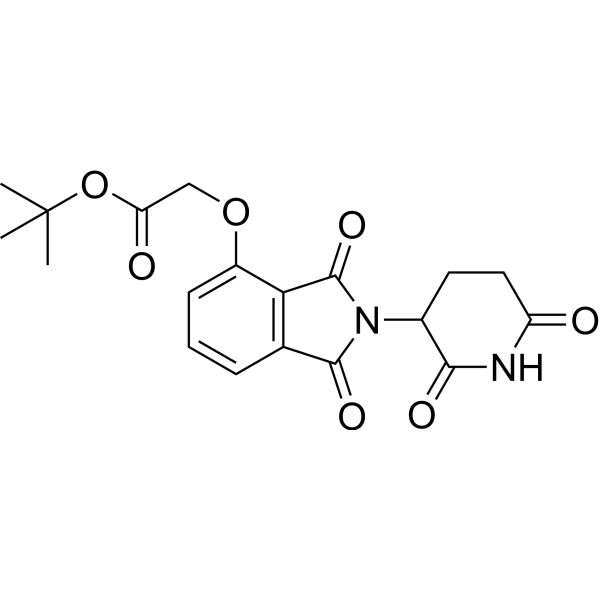
Thalidomide-4-O-CH2-COO(t-Bu) is t-Bu modified Thalidomide (HY-14658), which is the final step intermediate in the synthesis of Thalidomide-4-OH (HY-123096). Thalidomide-4-O-CH2-COO(t-Bu) acts as a Cereblon ligand to recruit CRBN proteins. The t-Bu protecting group at the end of Thalidomide-4-O-CH2-COO(t-Bu) can be removed under acidic conditions to participate in the synthesis of PROTAC molecules. Thalidomide-4-O-CH2-COO(t-Bu) is a key intermediate in the synthesis of CRBN-based designed PROTAC molecules.
|
-
-
-
HY-L090
-
|
|
1288 compounds
|
|
Transcription is the essential first step in the conversion of the genetic information in the DNA into protein and the major point at which gene expression is controlled. Transcription of protein-coding genes is accomplished by the multi-subunit enzyme RNA polymerase II and an ensemble of ancillary proteins, called transcription factors (TFs). Transcription factors play an important role in the long-term regulation of cell growth, differentiation and responses to environmental cues. Deregulated transcription factors contribute to the pathogenesis of a plethora of human diseases, ranging from diabetes, inflammatory disorders and cardiovascular disease to many cancers, and thus these proteins hold great therapeutic potential.
MCE offers a unique collection of 1288 compounds with validated transcription factor targets modulating properties. MCE transcription factor-targeted compound library is an effective tool for researching transcription factors as drug targets as well as modulation of TFs for different therapeutic applications.
|
-
-
HY-L100
-
|
|
129 compounds
|
|
Cancer is a multi-step process which involves initiation, promotion and progression. Chemical carcinogens can alter any of these processes to induce their carcinogenic effects. People are continuously exposed exogenously to varying amounts of chemicals that have been shown to have carcinogenic or mutagenic properties in experimental systems. Exposure can occur exogenously when these agents are present in food, air or water, and also endogenously when they are products of metabolism or pathophysiologic states such as inflammation. The administration of chemical carcinogens is one of the most commonly used methods to induce tumors in several organs in laboratory animals in order to study oncologic diseases of humans.
MCE offers a unique collection of 129 chemical carcinogens which have been identified with carcinogenic activity either in humans or in animal models. MCE Tumorigenesis-Related Compound Library is a powerful tool for studying oncologic diseases of humans. Standard opration based on safety data sheet will not cause harm to the body.
|
-
-
HY-L912V
-
|
|
10,000,000 compounds
|
|
With MCE's 40,662 BBs, covering around 273 reaction types, more than 40 million molecules were generated. Compounds which comply with Ro5 criteria were selected. Inappropriate chemical structures, such as PAINS motifs and synthetically difficult accessible, were removed. Based on Morgan Fingerprint, molecular clustering analysis was carried out, and molecules close to each clustering center were extracted to form this drug-like and synthesizable diversity library. These selected molecules have 805,822 unique Bemis-Murcko Scaffolds (BMS) with diversified chemical space. This library is highly recommended for AI-based lead discovery, ultra-large virtual screening and novel lead discovery.
|
-
-
HY-L910V
-
|
|
50,000 compounds
|
|
MegaUni 50K Virtual Diversity Library consists of 50,000 novel, synthetically accessible, lead-like compounds. With MCE's 40,662 Building Blocks, covering around 273 reaction types, more than 40 million molecules were generated. Based on Morgan Fingerprint and Tanimoto Coefficient, molecular clustering analysis was carried out, and molecules closest to each clustering center were extracted to form a drug-like and synthesizable diversity library. The selected 50,000 drug-like molecules have 46,744 unique Bemis-Murcko Scaffolds (BMS), each containing only 1-3 compounds. This diverse library is highly recommended for virtual screening and novel lead discovery.
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Type |
-
- HY-W040209
-
|
α-NPO
|
Fluorescent Dyes/Probes
|
|
2-(Naphthalen-1-yl)-5-phenyloxazole (α-NPO) is an organic fluorescent dye. 2-(Naphthalen-1-yl)-5-phenyloxazole has a nitrogen atom in its structure that can interfere with the nitrogen content from the amination step .
|
-
- HY-131030
-
|
JF669, SE; JF669, NHS
|
Fluorescent Dyes/Probes
|
|
Janelia Fluor 669, SE (JF669, SE), a red fluorescent dye, can be directly reacted with the available thiol-containing HaloTag ligand under mild conditions (DIEA, DMF) to afford a JF669HaloTag ligand in a single step (Ex = 669 nm; Em = 682 nm) . Janelia Fluor products are licensed under U.S. Pat. Nos. 9,933,417, 10,018,624 and 10,161,932 and other patents from Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Type |
-
- HY-111487
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
α-methylacyl-CoA racemase 1 is an enzyme that catalyzes a key chiral inversion step in the metabolism of branched-chain fatty acids, and used as a maker in prostate and other cancer.
|
-
- HY-E70155
-
|
EC:2.4.1.65; Fucosyltransferase 5; Fucosyltransferase V
|
Enzyme Substrates
|
|
Fucosyltransferase 5 (EC:2.4.1.65, Fucosyltransferase 5, Fucosyltransferase V) is responsible for the terminal step in the synthesis of Lex, sialy-Lex, and Lea antigens .
|
-
- HY-E70009
-
|
ACO
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Acyl-CoA oxidase (ACO) catalyses the first and rate-determining step of the peroxisomal beta-oxidation of fatty acids and a major producer of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) .
|
-
- HY-E70158
-
|
EC:2.4.1.152; FUT9
|
Enzyme Substrates
|
|
Fucosyltransferase 9 (EC:2.4.1.152, FUT9) catalyzes the last step in the biosynthesis of Lewis antigen, the addition of a fucose to precursor polysaccharides. Fucosyltransferase 9 synthesizes the LeX oligosaccharide (CD15) .
|
-
- HY-P2991
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase (GALT) catalyzes the second step of the Leloir pathway of galactose metabolism, namely the conversion of galactose to glucose. Galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase absence results in classic galactosemia in humans and can be used for metabolic disease research .
|
-
- HY-P2832
-
|
ACS
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Acyl coenzyme A synthetase (ACS), namely acetyl coenzyme A synthetase, is often used in biochemical research. Acyl coenzyme A synthetase can catalyze the activation of fatty acids by coenzyme A through a two-step thioesterification reaction to produce acyl coenzyme A, and then participate in a variety of anabolic and catabolic lipid metabolism pathways, and participate in the TCA cycle in aerobic respiration .
|
-
- HY-E70156
-
|
EC:2.4.1.-; FUT7
|
Enzyme Substrates
|
|
Fucosyltransferase 7 (FUT7) is a golgi stack membrane protein. Fucosyltransferase 7catalyzes the final fucosylation step in the synthesis of Lewis antigens and generates a unique glycosylated product sialyl Lewis X (sLeX). Fucosyltransferase 7 catalyzes alpha-1,3 glycosidic linkages involved in the expression of sialyl Lewis X antigens .
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Area |
-
- HY-P5423A
-
|
|
Peptides
|
Others
|
|
GALA (TFA) is a biological active peptide (GALA, a pH-sensitive fusogenic peptide, is a promising method to accelerate this step in order to enhance the expression of the desired proteins.) .
|
-
- HY-P3355
-
|
|
iGluR
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
p-fin4 is a peptide inhibitor of STEP Phosphatase-GluA2 AMPA receptor interaction with a Ki of 0.4 μM. p-fin4 restores the memory deficits and displays anxiolytic and antidepressant effects in a scopolamine-treated rat model. p-fin4 is a promising lead compound for novel cognitive enhancers and/or behavioral modulators .
|
-
- HY-P3354
-
|
|
iGluR
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
p3Ysh-3 is a peptide inhibitor of STEP Phosphatase-GluA2 AMPA receptor interaction with a Ki of 1.09 μM. p3Ysh-3 restores the memory deficits and displays anxiolytic and antidepressant effects in a scopolamine-treated rat model. p3Ysh-3 is a promising lead compound for novel cognitive enhancers and/or behavioral modulators .
|
-
- HY-P5423
-
|
|
Peptides
|
Others
|
|
GALA is a biological active peptide. (GALA, a pH-sensitive fusogenic peptide, is a promising method to accelerate this step in order to enhance the expression of the desired proteins.)
|
-
- HY-P2991
-
|
|
Peptides
|
Others
|
|
Galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase (GALT) catalyzes the second step of the Leloir pathway of galactose metabolism, namely the conversion of galactose to glucose. Galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase absence results in classic galactosemia in humans and can be used for metabolic disease research .
|
-
- HY-K1027
-
|
|
|
MCE Rapid Blocking Buffer (TBS-T) Powder (100 mL of 1×) mainly consists of fish gelatin protein, and is widely used for the antibody blocking step in Western Blot or ELISA within 15 minutes.
|
-
- HY-K1078
-
|
|
|
MCE One Step TUNEL Apoptosis Detection Kit (FITC) provides a rapid and convenient method to detect cell apoptosis. After staining cells with this kit, live cells have no fluorescence, apoptosis cells show green fluorescence.
|
-
- HY-K1079
-
1 Publications Verification
|
|
MCE One Step TUNEL Apoptosis Detection Kit (Cyanine 3) provides a rapid and convenient method to detect cell apoptosis. After staining cells with this kit, live cells have no fluorescence, apoptosis cells show red fluorescence.
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Category |
Target |
Chemical Structure |
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
|
Classification |
-
- HY-151855
-
|
|
|
Azide
Labeling and Fluorescence Imaging
|
|
Azido Myristic Acid is a click chemistry reagent containing an azide group. Azido Myristic Acid can be used to identify and characterize post-translationally myristylated proteins with using a simple and robust two-step labeling and detection technique .
|
-
- HY-151656
-
|
Azido Palmitic Acid
|
|
Azide
Labeling and Fluorescence Imaging
|
|
15-Azido-pentadecanoic acid is a click chemistry reagent containing an azide group. Azido Palmitic Acid can be used to identify and characterize post-translationally palmitylated proteins with using a simple and robust two-step labeling and detection technique . 15-Azido-pentadecanoic acid is a click chemistry reagent, it contains an Azide group and can undergo copper-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition reaction (CuAAc) with molecules containing Alkyne groups. Strain-promoted alkyne-azide cycloaddition (SPAAC) can also occur with molecules containing DBCO or BCN groups.
|
Your information is safe with us. * Required Fields.
Inquiry Information
- Product Name:
- Cat. No.:
- Quantity:
- MCE Japan Authorized Agent: